Glutamatergic medications for the treatment of drug and behavioral addictions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Glutamatergic medications for the treatment of drug and behavioral addictions
M Foster Olive et al. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Feb.
Abstract
Historically, most pharmacological approaches to the treatment of addictive disorders have utilized either substitution-based methods (i.e., nicotine replacement or opioid maintenance) or have targeted monoaminergic or endogenous opioidergic neurotransmitter systems. However, substantial evidence has accumulated indicating that ligands acting on glutamatergic transmission are also of potential utility in the treatment of drug addiction, as well as various behavioral addictions such as pathological gambling. The purpose of this review is to summarize the pharmacological mechanisms of action and general clinical efficacy of glutamatergic medications that are currently approved or are being investigated for approval for the treatment of addictive disorders. Medications with effects on glutamatergic transmission that will be discussed include acamprosate, N-acetylcysteine, d-cycloserine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, memantine, modafinil, and topiramate. We conclude that manipulation of glutamatergic neurotransmission is a relatively young but promising avenue for the development of improved therapeutic agents for the treatment of drug and behavioral addictions.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
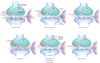
Figure 1
Putative glutamatergic mechanisms of action of 8 anti-addiction medications. Acamprosate - The molecular target(s) of acamprosate is still uncertain, but several studies have indicated it modulates the activity of NMDA receptors and restores balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission that is altered by chronic alcohol consumption. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a cystine prodrug that stimulants the cystine-glutamate exchanger (xc-) on glia to normalize extracellular levels of glutamate, which are reduced in the nucleus accumbens during cocaine withdrawal. This normalization of extracellular glutamate levels restores glutamatergic tone on release-inhibiting presynaptic mGluR2/3 receptors, which in turn inhibits the ability of exposure to cocaine (and perhaps cocaine-associated cues) to elevate extracellular glutamate and evoke cocaine craving or relapse. D-cycloserine (DCS) is a partial agonist at the glyine co-agonist binding site on NR1 subunits that are intrinsic to all NMDA receptors, and thus DCS potentiates cation influx through the NMDA receptor complex. Modafinil has numerous actions on neurons and its precise molecular targets have yet to be identified. However, several microdialysis studies have shown that modafinil increases extracellular levels of glutamate in various brain regions. Gabapentin, lamotrigine, topiramate are anticonvulsants that have numerous mechanisms of action, one of which is the reduction of the release of glutamate by blocking cation influx through presynaptic Na+ and Ca2+ channels. Topiramate has the unique ability to also antagonize GluR5-containing AMPA receptors. Memantine is a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist.
Similar articles
- Glutamatergic substrates of drug addiction and alcoholism.
Gass JT, Olive MF. Gass JT, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 1;75(1):218-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.06.039. Epub 2007 Jun 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17706608 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting the glutamatergic system to treat pathological gambling: current evidence and future perspectives.
Pettorruso M, De Risio L, Martinotti G, Di Nicola M, Ruggeri F, Conte G, Di Giannantonio M, Janiri L. Pettorruso M, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:109786. doi: 10.1155/2014/109786. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25013755 Free PMC article. Review. - Efficacy of Pharmacological Interventions in Targeting Decision-Making Impairments across Substance and Behavioral Addictions.
Chamberlain SR, Grant JE. Chamberlain SR, et al. Neuropsychol Rev. 2019 Mar;29(1):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s11065-019-09400-z. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Neuropsychol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30852805 Free PMC article. Review. - Metabotropic glutamatergic receptors and their ligands in drug addiction.
Pomierny-Chamioło L, Rup K, Pomierny B, Niedzielska E, Kalivas PW, Filip M. Pomierny-Chamioło L, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jun;142(3):281-305. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24362085 Review. - Systematic review of N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of addictions.
Asevedo E, Mendes AC, Berk M, Brietzke E. Asevedo E, et al. Braz J Psychiatry. 2014 Apr-Jun;36(2):168-75. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2013-1244. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Braz J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24676047 Review.
Cited by
- Serotonin at the nexus of impulsivity and cue reactivity in cocaine addiction.
Cunningham KA, Anastasio NC. Cunningham KA, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):460-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.030. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23850573 Free PMC article. Review. - Glutamatergic and GABAergic susceptibility loci for heroin and cocaine addiction in subjects of African and European ancestry.
Levran O, Peles E, Randesi M, Correa da Rosa J, Ott J, Rotrosen J, Adelson M, Kreek MJ. Levran O, et al. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Jan 4;64:118-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26277529 Free PMC article. - Safety and efficacy of acamprosate for the treatment of alcohol dependence.
Yahn SL, Watterson LR, Olive MF. Yahn SL, et al. Subst Abuse. 2013;6:1-12. doi: 10.4137/SART.S9345. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Subst Abuse. 2013. PMID: 23399877 Free PMC article. - Frequency of alcohol consumption in humans; the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors and downstream signaling pathways.
Meyers JL, Salling MC, Almli LM, Ratanatharathorn A, Uddin M, Galea S, Wildman DE, Aiello AE, Bradley B, Ressler K, Koenen KC. Meyers JL, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 23;5(6):e586. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.70. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26101849 Free PMC article. - N-acetylcysteine in the Treatment of Internet Gaming Disorder.
Singh A, Singh G, Singh S, Kazi SE, Gill M. Singh A, et al. Cureus. 2022 Sep 1;14(9):e28662. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28662. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36199646 Free PMC article.
References
- Ahmad S, Fowler LJ, Whitton PS. Effects of acute and chronic lamotrigine treatment on basal and stimulated extracellular amino acids in the hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 2004;1029:41–47. - PubMed
- Akhondzadeh S, Hampa AD. Topiramate prevents ecstasy consumption: a case report. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005;19:601–602. - PubMed
- al Qatari M, Bouchenafa O, Littleton J. Mechanism of action of acamprosate. Part II. Ethanol dependence modifies effects of acamprosate on NMDA receptor binding in membranes from rat cerebral cortex. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:810–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AA013852/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA024355/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024355/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013852-09/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA025606/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA025606-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA013852/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA024355-04/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA025606/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical