Aβ oligomer-induced synapse degeneration in Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Aβ oligomer-induced synapse degeneration in Alzheimer's disease
Kyle C Wilcox et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
Aβ oligomers cause a collection of molecular events associated with memory loss in Alzheimer's disease, centering on disrupting the maintenance of synapse structure and function. In this brief review of the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ oligomers, we focus on the neuronal properties governing oligomer targeting and toxicity-especially with respect to binding sites and mechanisms of binding. We also discuss ways in which mechanistic insights from other diseases offer clues in the pursuit of the molecular basis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
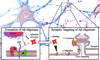
Fig. 1
Formation and synaptic targeting of Aβ oligomers. A neuron is represented with blue neurites and red dendritic spines (background image). Following APP cleavage at the neural membrane by β- and γ-secretase, the 42-residue Aβ peptide (red) can be deposited into senile plaques or can alternatively form a collection of oligomeric species (left inset). Some component of this collection of oligomers interacts with neurons to form synaptic clusters which are associated with a variety of synaptic pathologies including the internalization of receptors involved in synapse function and maintenance and the initiation of toxic signaling cascades (right inset)
Similar articles
- Alzheimer's therapeutics targeting amyloid beta 1-42 oligomers I: Abeta 42 oligomer binding to specific neuronal receptors is displaced by drug candidates that improve cognitive deficits.
Izzo NJ, Staniszewski A, To L, Fa M, Teich AF, Saeed F, Wostein H, Walko T 3rd, Vaswani A, Wardius M, Syed Z, Ravenscroft J, Mozzoni K, Silky C, Rehak C, Yurko R, Finn P, Look G, Rishton G, Safferstein H, Miller M, Johanson C, Stopa E, Windisch M, Hutter-Paier B, Shamloo M, Arancio O, LeVine H 3rd, Catalano SM. Izzo NJ, et al. PLoS One. 2014 Nov 12;9(11):e111898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111898. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25390368 Free PMC article. - N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are required for synaptic targeting of Alzheimer's toxic amyloid-β peptide oligomers.
Decker H, Jürgensen S, Adrover MF, Brito-Moreira J, Bomfim TR, Klein WL, Epstein AL, De Felice FG, Jerusalinsky D, Ferreira ST. Decker H, et al. J Neurochem. 2010 Dec;115(6):1520-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07058.x. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20950339 - Is covalently crosslinked Abeta responsible for synaptotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease?
Naylor R, Hill AF, Barnham KJ. Naylor R, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008 Dec;5(6):533-9. doi: 10.2174/156720508786898433. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008. PMID: 19075579 Review. - Liraglutide can reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease.
McClean PL, Hölscher C. McClean PL, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt A:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23973293 - Synaptic changes in Alzheimer's disease and its models.
Pozueta J, Lefort R, Shelanski ML. Pozueta J, et al. Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 22;251:51-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.050. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 22687952 Review.
Cited by
- Beta amyloid-induced depression of hippocampal long-term potentiation is mediated through the amylin receptor.
Kimura R, MacTavish D, Yang J, Westaway D, Jhamandas JH. Kimura R, et al. J Neurosci. 2012 Nov 28;32(48):17401-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3028-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23197731 Free PMC article. - Intraneuronal Aβ detection in 5xFAD mice by a new Aβ-specific antibody.
Youmans KL, Tai LM, Kanekiyo T, Stine WB Jr, Michon SC, Nwabuisi-Heath E, Manelli AM, Fu Y, Riordan S, Eimer WA, Binder L, Bu G, Yu C, Hartley DM, LaDu MJ. Youmans KL, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2012 Mar 16;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-7-8. Mol Neurodegener. 2012. PMID: 22423893 Free PMC article. - Neuronal Aβ42 is enriched in small vesicles at the presynaptic side of synapses.
Yu Y, Jans DC, Winblad B, Tjernberg LO, Schedin-Weiss S. Yu Y, et al. Life Sci Alliance. 2018 Jun 14;1(3):e201800028. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201800028. eCollection 2018 Jun. Life Sci Alliance. 2018. PMID: 30456353 Free PMC article. - Synaptic mitochondrial pathology in Alzheimer's disease.
Du H, Guo L, Yan SS. Du H, et al. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Jun 15;16(12):1467-75. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4277. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21942330 Free PMC article. Review. - nNOS-CAPON interaction mediates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity, especially in the early stages.
Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Liang HY, Zhang L, Zhou QG, Ni HY, Luo CX, Zhu DY. Zhang Y, et al. Aging Cell. 2018 Jun;17(3):e12754. doi: 10.1111/acel.12754. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Aging Cell. 2018. PMID: 29577585 Free PMC article.
References
- Alarcon JM, Brito JA, Hermosilla T, Atwater I, Mears D, Rojas E. Ion channel formation by Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-peptide (Aβ40) in unilamellar liposomes is determined by anionic phospholipids. Peptides. 2006;27:95–104. - PubMed
- Balducci C, Beeg M, Stravalaci M, Bastone A, Sclip A, Biasini E, Tapella L, Colombo L, Manzoni C, Borsello T, Chiesa R, Gobbi M, Salmona M, Forloni G. Synthetic amyloid-β oligomers impair long-term memory independently of cellular prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:2295–2300. - PMC - PubMed
- Barghorn S, Nimmrich V, Striebinger A, Krantz C, Keller P, Janson B, Bahr M, Schmidt M, Bitner RS, Harlan J, Barlow E, Ebert U, Hillen H. Globular amyloid beta-peptide oligomer—a homogenous and stable neuropathological protein in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2005;95:834–847. - PubMed
- Bear MF, Huber KM, Warren ST. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:370–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical