Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data of the Pyrococcus horikoshii RadA intein - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data of the Pyrococcus horikoshii RadA intein
Andrzej Lyskowski et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011.
Abstract
The RadA intein from the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus horikoshii was cloned, expressed and purified for subsequent structure determination. The protein crystallized rapidly in several conditions. The best crystals, which diffracted to 1.75 Å resolution, were harvested from drops consisting of 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.5, 3.0 M NaCl and were cryoprotected with Paratone-N before flash-cooling. The collected data were processed in the orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 58.1, b = 67.4, c = 82.9 Å. Molecular replacement with Rosetta using energy- and density-guided structure optimization provided the initial solution, which is currently under refinement.
Figures
Figure 1
The insertion site of the _Pho_RadA intein within the _Pho_RadA protein. The primary structure of the _Pho_RadA intein is also shown. The Walker A motif is highlighted in grey.
Figure 2
Diffraction image of a _Pho_RadA intein crystal. The image was prepared using the ADXV program (
http://www.scripps.edu/\~arvai/adxv.html
). The resolution at the edge of the image is 1.75 Å. The data were collected on the ESRF ID23-1 beamline using an ADSC Quantum Q315R detector.
Figure 3
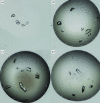
Crystals of the _Pho_RadA intein. (a, b) Crystals from the initial screen grown using (a) 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.5 and 3 M NaCl and (b) 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0, 15% Tacsimate pH 7.0 and 2% PEG 3350. (c, d) Crystals grown from the grid optimization conditions. (c) 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0, 15.2% Tacsimate pH 7.0. (d) 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0, 10.4% Tacsimate pH 7.0 and 3.0% PEG 3350.
Similar articles
- Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the KaiC-like protein PH0187 from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
Kang HJ, Kubota K, Miyazono K, Tanokura M. Kang HJ, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Jan 1;67(Pt 1):144-6. doi: 10.1107/S1744309110048426. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 21206047 Free PMC article. - Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of PH1010 from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3, a member of the archaeal DUF54 family of proteins.
Shirokane M, Sawano Y, Miyazono KI, Nagata K, Tanokura M. Shirokane M, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Jun 1;63(Pt 6):532-4. doi: 10.1107/S1744309107024487. Epub 2007 May 31. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007. PMID: 17554180 Free PMC article. - Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of PH1566, a putative ribosomal RNA-processing factor from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
Jia MZ, Ohtsuka J, Lee WC, Nagata K, Tanokura M. Jia MZ, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006 Jan 1;62(Pt 1):47-8. doi: 10.1107/S1744309105040613. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2006. PMID: 16511260 Free PMC article. - Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of archaeal 6-pyruvoyl tetrahydrobiopterin synthase homologue PH0634 from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
Bagautdinov B, Sugahara M, Kunishima N. Bagautdinov B, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 Jan 1;63(Pt 1):15-7. doi: 10.1107/S1744309106051578. Epub 2006 Dec 16. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007. PMID: 17183164 Free PMC article. - Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of hyperthermophilic L-threonine dehydrogenase from the archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii.
Higashi N, Matsuura T, Nakagawa A, Ishikawa K. Higashi N, et al. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005 Apr 1;61(Pt 4):432-4. doi: 10.1107/S174430910500881X. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005. PMID: 16511061 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- NMR and crystal structures of the Pyrococcus horikoshii RadA intein guide a strategy for engineering a highly efficient and promiscuous intein.
Oeemig JS, Zhou D, Kajander T, Wlodawer A, Iwaï H. Oeemig JS, et al. J Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 3;421(1):85-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.04.029. Epub 2012 May 2. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22560994 Free PMC article. - phenix.mr_rosetta: molecular replacement and model rebuilding with Phenix and Rosetta.
Terwilliger TC, Dimaio F, Read RJ, Baker D, Bunkóczi G, Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Afonine PV, Echols N. Terwilliger TC, et al. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012 Jun;13(2):81-90. doi: 10.1007/s10969-012-9129-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22418934 Free PMC article. - Improved crystallographic models through iterated local density-guided model deformation and reciprocal-space refinement.
Terwilliger TC, Read RJ, Adams PD, Brunger AT, Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW. Terwilliger TC, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012 Jul;68(Pt 7):861-70. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912015636. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012. PMID: 22751672 Free PMC article.
References
- Chong, S., Mersha, F. B., Comb, D. G., Scott, M. E., Landry, D., Vence, L. M., Perler, F. B., Benner, J., Kucera, R. B., Hirvonen, C. A., Pelletier, J. J., Paulus, H. & Xu, M.-Q. (1997). Gene, 192, 271–281. - PubMed
- Davis, E. O., Jenner, P. J., Brooks, P. C., Colston, M. J. & Sedgwick, S. G. (1992). Cell, 71, 201–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources