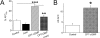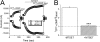8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate-Na stimulates human alveolar fluid clearance by releasing external Na+ self-inhibition of epithelial Na+ channels - PubMed (original) (raw)
8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate-Na stimulates human alveolar fluid clearance by releasing external Na+ self-inhibition of epithelial Na+ channels
Dong-Yun Han et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Nov.
Abstract
Salt absorption via alveolar epithelial Na(+) channels (ENaC) is a critical step for maintaining an airspace free of flooding. Previously, we found that 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate-Na (CPT-cGMP) activated native and heterologous ENaC. To investigate the potential pharmacological relevance, we applied this compound intratracheally to human lungs and found that ex vivo alveolar fluid clearance was increased significantly. Furthermore, this compound eliminated self-inhibition in human lung H441 cells and in oocytes expressing human αβγ but not δβγ channels. To further elucidate this novel mechanism, we constructed mutants abolishing (β(ΔV348) and γ(H233R)) or augmenting (α(Y458A) and γ(M432G)) self-inhibition. The mutants eliminating self-inhibition lost their responses to CPT-cGMP, whereas those enhancing self-inhibition facilitated the stimulatory effects of this compound. CPT-cGMP was unable to activate a high P(o) mutant (β(S520C)) and plasmin proteolytically cleaved channels. Our data suggest that elimination of self-inhibition of αβγ ENaC may be a novel mechanism for CPT-cGMP to stimulate salt reabsorption in human lungs.
Figures
Figure 1.
Stimulation of human alveolar fluid clearance (AFC) by 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate-Na (CPT-cGMP). AFC was measured by delivering 0.9% NaCl with 5% BSA into human lung lobes ex vivo. The instillate was collected after 60 minutes, and AFC was measured as described in M
aterials and
M
ethods
. (A) AFC in the presence and absence of amiloride (Amil) and CPT-cGMP. n = 15 for controls; n = 5 for other groups. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (B) Amiloride-inhibitable AFC fraction associated with ENaC. *P < 0.05.
Figure 2.
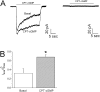
CPT-cGMP alters self-inhibition in human lung epithelial cells. (A) Self-inhibition traces recorded at −60 mV in H441 cells in the absence (Basal) and presence of CPT-cGMP and amiloride (right). (B) Sustained (Isus)/maximal (I0max) current ratio. *P < 0.05; n = 5.
Figure 3.
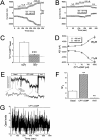
Activation of whole-cell and single-channel epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) activities by CPT-cGMP. (A and B) Current traces of αβγ (A) and δβγ (B) ENaC channels digitized at the holding potentials of −100 mV and +80 mV. (C) Activation by CPT-cGMP as revealed by increased fold in current levels at −100 mV. ***P < 0.001. (D) Dose–response curves of αβγ ENaC. The median effective concentration values at −100 mV and +80 mV are shown. (E) Single-channel tracings in an outside-out patch. Membrane potential, −60 mV. (F) Single-channel activity before (Basal) and after perfusion of CPT-cGMP and amiloride (Amil). n = 6. **P < 0.01. (G) Single-channel tracings in a cell-attached patch.
Figure 4.
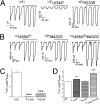
CPT-cGMP modifies self-inhibition of αβγ ENaC in oocytes. Self-inhibition was measured by fast switching the low Na+ bath solution (1 mM) to regular ND96 medium (96 mM). (A) Representative whole-cell current trace digitized at −60 mV. CPT-cGMP (0.2 mM) was added after the first three sweeps and washed out for the last three sweeps. (B) Current ratio. n = 9. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus the first sweep. (C) Comparison of CPT-cGMP on self-inhibition of αβγ and δβγ ENaC channels. Paired traces were recorded before and after application of CPT-cGMP.
Figure 5.
Responses of self-inhibition mutant to CPT-cGMP. (A) Representative current traces of mutants eliminating self-inhibition. Application of CPT-cGMP is indicated by horizontal lines. (B) Current tracings of mutants boosting self-inhibition. (C and D) Fold increased by CPT-cGMP for mutants abolishing (C) and facilitating self-inhibition (D). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus αβγ ENaC. n = 10 to 14.
Figure 6.
Effects of CPT-cGMP on fully opened channels. (A) Representative traces showing the responses of αβS520Cγ to CPT-cGMP (0.2 mM) before and after the addition of MTSET (1 mM). (B) Activation of ENaC by CPT-cGMP. The current ratios are 3.1 ± 0.1 before MTSET and 1.1 ± 0.03 after MTSET, respectively. ***P < 0.001. n = 11.
Figure 7.
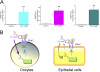
Analysis of cell cGMP contents by ELISA. (A) Average cell cGMP contents in instilled lungs (left), H441 cells (middle), and oocytes (right). n = 6 lungs, 10 H441 monolayers, and 100 oocytes. **P < 0.01. (B) Divergent regulation of ENaC by CPT-cGMP in oocytes (left) and epithelial cells (right). Heterologous ENaC channels are not regulated by cGMP/PKG and cAMP/PKA pathways. CPT-cGMP therefore does not regulate cloned human ENaC in oocytes via the cGMP/PKG signaling pathway and only serves as an external ligand. This compound stimulates native ENaC function by acting as an external ligand and activating internal PKG in sequence. cGMP is anticipated to accumulate around ENaC as an autocrine.
Similar articles
- CPT-cGMP Is A New Ligand of Epithelial Sodium Channels.
Ji HL, Nie HG, Chang Y, Lian Q, Liu SL. Ji HL, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 28;12(4):359-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13764. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27019621 Free PMC article. Review. - Cpt-cAMP activates human epithelial sodium channels via relieving self-inhibition.
Molina R, Han DY, Su XF, Zhao RZ, Zhao M, Sharp GM, Chang Y, Ji HL. Molina R, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jul;1808(7):1818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419751 Free PMC article. - 8-pCPT-cGMP stimulates alphabetagamma-ENaC activity in oocytes as an external ligand requiring specific nucleotide moieties.
Nie HG, Zhang W, Han DY, Li QN, Li J, Zhao RZ, Su XF, Peng JB, Ji HL. Nie HG, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):F323-34. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00307.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20007351 Free PMC article. - Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by cGMP/PKGII.
Nie HG, Chen L, Han DY, Li J, Song WF, Wei SP, Fang XH, Gu X, Matalon S, Ji HL. Nie HG, et al. J Physiol. 2009 Jun 1;587(Pt 11):2663-76. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.170324. Epub 2009 Apr 9. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19359370 Free PMC article. - Treatment of pulmonary edema by ENaC activators/stimulators.
Fronius M. Fronius M. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;6(1):13-27. doi: 10.2174/1874467211306010003. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23547931 Review.
Cited by
- δ ENaC: a novel divergent amiloride-inhibitable sodium channel.
Ji HL, Zhao RZ, Chen ZX, Shetty S, Idell S, Matalon S. Ji HL, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Dec 15;303(12):L1013-26. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00206.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22983350 Free PMC article. Review. - Epithelial Sodium Channels in Pulmonary Epithelial Progenitor and Stem Cells.
Liu Y, Jiang BJ, Zhao RZ, Ji HL. Liu Y, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Aug 15;12(9):1150-4. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.15747. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27570489 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanisms and Treatment of Halogen Inhalation-Induced Pulmonary and Systemic Injuries in Pregnant Mice.
Lambert JA, Carlisle MA, Lam A, Aggarwal S, Doran S, Ren C, Bradley WE, Dell'Italia L, Ambalavanan N, Ford DA, Patel RP, Jilling T, Matalon S. Lambert JA, et al. Hypertension. 2017 Aug;70(2):390-400. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09466. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28607126 Free PMC article. - CPT-cGMP Is A New Ligand of Epithelial Sodium Channels.
Ji HL, Nie HG, Chang Y, Lian Q, Liu SL. Ji HL, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 28;12(4):359-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13764. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27019621 Free PMC article. Review. - Proliferative regulation of alveolar epithelial type 2 progenitor cells by human Scnn1d gene.
Zhao R, Ali G, Chang J, Komatsu S, Tsukasaki Y, Nie HG, Chang Y, Zhang M, Liu Y, Jain K, Jung BG, Samten B, Jiang D, Liang J, Ikebe M, Matthay MA, Ji HL. Zhao R, et al. Theranostics. 2019 Oct 18;9(26):8155-8170. doi: 10.7150/thno.37023. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31754387 Free PMC article.
References
- Garty H, Benos DJ. Characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel. Physiol Rev 1988;68:309–373 - PubMed
- Garty H. Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by aldosterone: open questions and emerging answers. Kidney Int 2000;57:1270–1276 - PubMed
- Rossier BC, Pradervand S, Schild L, Hummler E. Epithelial sodium channel and the control of sodium balance: interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Annu Rev Physiol 2002;64:877–897 - PubMed
- Horisberger JD, Chraibi A. Epithelial sodium channel: a ligand-gated channel? Nephron, Physiol 2004;96:37–41 - PubMed
- Lingueglia E, Deval E, Lazdunski M. Fmrfamide-gated sodium channel and asic channels: a new class of ionotropic receptors for fmrfamide and related peptides. Peptides 2006;27:1138–1152 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources