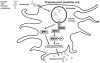Interferon regulatory factors in human lupus pathogenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Interferon regulatory factors in human lupus pathogenesis
Rafah Salloum et al. Transl Res. 2011 Jun.
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a severe multisystem autoimmune disease that results from both genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Many lines of investigation support interferon alpha (IFN-α) as a causal agent in human lupus, and high levels of serum IFN-α are a heritable risk factor for SLE. Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) are a family of transcription factors involved in host defense, which can induce transcription of IFN-α and other immune response genes after activation. In SLE, circulating immune complexes that contain nucleic acid are prevalent. These complexes are recognized by endosomal Toll-like receptors, resulting in activation of downstream IRF proteins. Genetic variants in the IRF5 and IRF7 genes have been associated with SLE susceptibility, and these same variants are associated with increased serum IFN-α in SLE patients. The increase in serum IFN-α related to IRF5 and 7 genotypes is observed only in patients with particular antibody specificities. This suggests that chronic stimulation of the endosomal Toll-like receptors by autoantibody immune complexes is required for IRF SLE-risk variants to cause elevation of circulating IFN-α and subsequent risk of SLE. Recently, genetic variation in the IRF8 gene has been associated with SLE and multiple sclerosis, and studies support an impact of IRF8 genotype on the IFN-α pathway. In summary, the SLE-associated polymorphisms in the IRF family of proteins seem to be gain-of-function variants, and understanding the impact of these variants on the IFN-α pathway in vivo may guide therapeutic strategies directed at the Toll-like receptor/IRF/IFN-α pathway in SLE.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Figure 1
Proposed relationship between SLE immune complexes, endosomal TLRs, and downstream IRF proteins with respect to IFN-α production in SLE patients. A plasmacytoid dendritic cell is shown, as these cells are thought to be the major IFN-α producing cells.
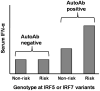
Figure 2
Representation of the interaction between autoantibodies and IRF5 and IRF7 genotype upon serum IFN-α levels in SLE patients. Bars on the graph represent median serum IFN-α levels in a group of SLE patients defined by the labels on the graph. “Risk” refers to subjects who carry IRF5 or IRF7 polymorphisms associated with SLE susceptibility in case-control studies, and “non-risk” refers to subjects who lack these variants.
Comment in
- Linking interferon regulatory factors to the pathogenesis of human lupus.
Patel DR. Patel DR. Transl Res. 2011 Jun;157(6):323-5. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.02.011. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21575915 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- IRF5 haplotypes demonstrate diverse serological associations which predict serum interferon alpha activity and explain the majority of the genetic association with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Niewold TB, Kelly JA, Kariuki SN, Franek BS, Kumar AA, Kaufman KM, Thomas K, Walker D, Kamp S, Frost JM, Wong AK, Merrill JT, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Tikly M, Ramsey-Goldman R, Reveille JD, Petri MA, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP, Alarcón GS, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS, Vyse TJ, James JA, Gaffney PM, Moser KL, Crow MK, Harley JB. Niewold TB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Mar;71(3):463-8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200463. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22088620 Free PMC article. - Interferon regulatory factors: critical mediators of human lupus.
Jensen MA, Niewold TB. Jensen MA, et al. Transl Res. 2015 Feb;165(2):283-95. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 25445206 Free PMC article. Review. - Interferon regulatory factor 5 in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Cham CM, Ko K, Niewold TB. Cham CM, et al. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:780436. doi: 10.1155/2012/780436. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23251221 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic variation near IRF8 is associated with serologic and cytokine profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis.
Chrabot BS, Kariuki SN, Zervou MI, Feng X, Arrington J, Jolly M, Boumpas DT, Reder AT, Goulielmos GN, Niewold TB. Chrabot BS, et al. Genes Immun. 2013 Dec;14(8):471-8. doi: 10.1038/gene.2013.42. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Genes Immun. 2013. PMID: 23965942 Free PMC article. - Linking interferon regulatory factors to the pathogenesis of human lupus.
Patel DR. Patel DR. Transl Res. 2011 Jun;157(6):323-5. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.02.011. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21575915 No abstract available.
Cited by
- The genetics of lupus: a functional perspective.
Guerra SG, Vyse TJ, Cunninghame Graham DS. Guerra SG, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 29;14(3):211. doi: 10.1186/ar3844. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22640752 Free PMC article. Review. - Protein-protein interactions in cGAS-STING pathway: a medicinal chemistry perspective.
Zhang SD, Li H, Zhou YL, Liu XC, Li DC, Hao CF, You QD, Xu XL. Zhang SD, et al. Future Med Chem. 2024;16(17):1801-1820. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2383164. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39263789 Review. - Activation and regulation of interferon-β in immune responses.
Sin WX, Li P, Yeong JP, Chin KC. Sin WX, et al. Immunol Res. 2012 Sep;53(1-3):25-40. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8293-7. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22411096 Review. - IRF5 haplotypes demonstrate diverse serological associations which predict serum interferon alpha activity and explain the majority of the genetic association with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Niewold TB, Kelly JA, Kariuki SN, Franek BS, Kumar AA, Kaufman KM, Thomas K, Walker D, Kamp S, Frost JM, Wong AK, Merrill JT, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Tikly M, Ramsey-Goldman R, Reveille JD, Petri MA, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP, Alarcón GS, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS, Vyse TJ, James JA, Gaffney PM, Moser KL, Crow MK, Harley JB. Niewold TB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Mar;71(3):463-8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200463. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22088620 Free PMC article. - Regulating STING in health and disease.
Li Y, Wilson HL, Kiss-Toth E. Li Y, et al. J Inflamm (Lond). 2017 Jun 7;14:11. doi: 10.1186/s12950-017-0159-2. eCollection 2017. J Inflamm (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28596706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979;301(1):5–8. - PubMed
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32. - PubMed
- Crow MK, Kirou KA, Wohlgemuth J. Microarray analysis of interferon-regulated genes in SLE. Autoimmunity. 2003;36(8):481–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- L30 AI071651-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK42086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK042086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical