Impact of medicated feed on the development of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria at integrated pig-fish farms in Vietnam - PubMed (original) (raw)
Impact of medicated feed on the development of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria at integrated pig-fish farms in Vietnam
Son Thi Thanh Dang et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jul.
Abstract
Integrated livestock-fish aquaculture utilizes animal excreta, urine, and feed leftovers as pond fertilizers to enhance the growth of plankton and other microorganisms eaten by the fish. However, antimicrobial-resistant bacteria may be transferred and develop in the pond due to selective pressure from antimicrobials present in animal feed, urine, and feces. In an experimental pig-fish farm located in periurban Hanoi, Vietnam, nine piglets were provided feed containing 5 μg of tetracycline (TET)/kg pig weight/day and 0.45 μg of enrofloxacin (ENR)/kg pig weight/day during the second and fourth (last) months of the experiment. The aim of this study was to determine the association between the provision of pig feed with antimicrobials and the development of antimicrobial resistance, as measured in a total of 520 Escherichia coli and 634 Enterococcus strains isolated from pig manure and water-sediment pond samples. MIC values for nalidixic acid (NAL) and ENR showed that E. coli and Enterococcus spp. overall exhibited significant higher frequencies of resistance toward NAL and ENR during the 2 months when pigs were administered feed with antimicrobials, with frequencies reaching 60 to 80% in both water-sediment and manure samples. TET resistance for both indicators was high (>80%) throughout the study period, which indicates that TET-resistant E. coli and Enterococcus spp. were present in the piglets before the initiation of the experiment. PCR-based identification showed similar relative occurrences of Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus faecalis, and other Enterococcus spp. in the water-sediment and manure samples, suggesting that Enterococcus spp. isolated in the ponds originated mainly from the pig manure. The development of antimicrobial resistance in integrated animal husbandry-fish farms and possible transfers and the impact of such resistance on food safety and human health should be further assessed.
Figures
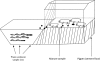
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of an experimental integrated pig-fish farm showing sample types and sites.
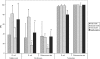
Fig. 2.
The frequency (percentage) of tetracycline- and quinolone-resistant E. coli and Enterococcus spp. isolated from pig manure during four monthly samplings. The asterisks placed above the bars indicate significant differences in average resistance compared to that from the previous month.
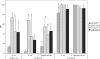
Fig. 3.
The frequency (percentage) of tetracycline- and quinolone-resistant E. coli and Enterococcus spp. isolated from water-sediment samples during four monthly samplings. The asterisks placed above the bars indicate significant differences in average resistance compared to that from the previous month.
Similar articles
- Escherichia coli contamination of fish raised in integrated pig-fish aquaculture systems in Vietnam.
Dang ST, Dalsgaard A. Dang ST, et al. J Food Prot. 2012 Jul;75(7):1317-9. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-501. J Food Prot. 2012. PMID: 22980016 - Species composition and antimicrobial resistance genes of Enterococcus spp, isolated from integrated and traditional fish farms in Thailand.
Petersen A, Dalsgaard A. Petersen A, et al. Environ Microbiol. 2003 May;5(5):395-402. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2003.00430.x. Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12713465 - Impact of integrated fish farming on antimicrobial resistance in a pond environment.
Petersen A, Andersen JS, Kaewmak T, Somsiri T, Dalsgaard A. Petersen A, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002 Dec;68(12):6036-42. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.6036-6042.2002. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12450826 Free PMC article. - Overcoming China's animal waste disposal challenge brought by elevated levels of veterinary antimicrobial residues and antimicrobial resistance.
Cheng GM, Cheng H. Cheng GM, et al. Environ Int. 2024 Sep;191:109009. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.109009. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39278046 Review. - Antibiotic Resistance among Gastrointestinal Bacteria in Broilers: A Review Focused on Enterococcus spp. and Escherichia coli.
Ribeiro J, Silva V, Monteiro A, Vieira-Pinto M, Igrejas G, Reis FS, Barros L, Poeta P. Ribeiro J, et al. Animals (Basel). 2023 Apr 15;13(8):1362. doi: 10.3390/ani13081362. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Antimicrobials use and resistance on integrated poultry-fish farming systems in the Ayeyarwady Delta of Myanmar.
Gibson JS, Wai H, Oo SSML, Hmwe EMM, Wai SS, Htun LL, Lim HP, Latt ZM, Henning J. Gibson JS, et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16149. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73076-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999333 Free PMC article. - Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales of Shrimp and Salmon Available for Purchase by Consumers in Canada-A Risk Profile Using the Codex Framework.
Uhland FC, Li XZ, Mulvey MR, Reid-Smith R, Sherk LM, Ziraldo H, Jin G, Young KM, Reist M, Carson CA. Uhland FC, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;12(9):1412. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12091412. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760708 Free PMC article. Review. - Distribution of quinolones, sulfonamides, tetracyclines in aquatic environment and antibiotic resistance in indochina.
Suzuki S, Hoa PT. Suzuki S, et al. Front Microbiol. 2012 Feb 22;3:67. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00067. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22363337 Free PMC article. - Antibiotic use and resistance in emerging economies: a situation analysis for Viet Nam.
Nguyen KV, Thi Do NT, Chandna A, Nguyen TV, Pham CV, Doan PM, Nguyen AQ, Thi Nguyen CK, Larsson M, Escalante S, Olowokure B, Laxminarayan R, Gelband H, Horby P, Thi Ngo HB, Hoang MT, Farrar J, Hien TT, Wertheim HF. Nguyen KV, et al. BMC Public Health. 2013 Dec 10;13:1158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-1158. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 24325208 Free PMC article. - Qualitative Risk Assessment for Antimicrobial Resistance among Humans from Salmon Fillet Consumption Due to the High Use of Antibiotics against Bacterial Infections in Farmed Salmon.
Salgado-Caxito M, Zimin-Veselkoff N, Adell AD, Olivares-Pacheco J, Mardones FO. Salgado-Caxito M, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 15;11(5):662. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050662. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625306 Free PMC article.
References
- Alderman D. J., Hastings T. S. 1998. Antibiotic use in aquaculture: development of antibiotic resistance potential for consumer health risks. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 33:139–155
- Reference deleted.
- Cavaco L. M., et al. 2008. Prevalence of quinolone resistance mechanisms and associations to minimum inhibitory concentrations in quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from humans and swine in Denmark. Microb. Drug Resist. 14:163–169 - PubMed
- CLSI/NCCLS 2001. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 11th informational supplement. CLSI/NCCLS, Wayne, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous