Dietary omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and Alzheimer's disease: interaction with apolipoprotein E genotype - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Dietary omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and Alzheimer's disease: interaction with apolipoprotein E genotype
P Barberger-Gateau et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
Epidemiological studies suggest a protective role of omega-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) against Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, most intervention studies of supplementation with n-3 PUFA have yielded disappointing results. One reason for such discordant results may result from inadequate targeting of individuals who might benefit from the supplementation, in particular because of their genetic susceptibility to AD. The ε4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene (ApoE) is a genetic risk factor for late-onset AD. ApoE plays a key role in the transport of cholesterol and other lipids involved in brain composition and functioning. The action of n-3 PUFA on the aging brain might therefore differ according to ApoE polymorphism. The aim of this review is to examine the interaction between dietary fatty acids and ApoE genotype on the risk for AD. Carriers of the ε4 allele tend to be the most responsive to changes in dietary fat and cholesterol. Conversely, several epidemiological studies suggest a protective effect of long-chain n-3 PUFA on cognitive decline only in those who do not carry ε4 but with inconsistent results. An intervention study showed that only non-carriers had increased concentrations of long-chain n-3 PUFA in response to supplementation. The mechanisms underlying this gene-by-diet interaction on AD risk may involve impaired fatty acids and cholesterol transport, altered metabolism of n-3 PUFA, glucose or ketones, or modification of other risk factors of AD in ε4 carriers. Further research is needed to explain the differential effect of n-3 PUFA on AD according to ApoE genotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest (if any)
The authors report no conflict of interest
Figures
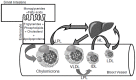
Figure 1
Metabolism of lipoproteins starting with absorption in the small intestine. LPL = lipoprotein lipase, HL = hepatic lipase, VLDL = very low density lipoproteins, IDL = intermediate density lipoproteins, LDL = low density lipoproteins
Similar articles
- Apolipoprotein E genotype moderates the association between dietary polyunsaturated fat and brain function: an exploration of cerebral glutamate and cognitive performance.
Oleson S, Eagan D, Kaur S, Hertzing WJ, Alkatan M, Davis JN, Tanaka H, Haley AP. Oleson S, et al. Nutr Neurosci. 2020 Sep;23(9):696-705. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2018.1547857. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Nutr Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 30465491 Free PMC article. - [Multifunctional Roles of APOE in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis].
Tokutake T, Kasuga K, Hara N, Ikeuchi T. Tokutake T, et al. Brain Nerve. 2016 Jul;68(7):703-12. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416200498. Brain Nerve. 2016. PMID: 27395454 Japanese. - ApoE genotype: from geographic distribution to function and responsiveness to dietary factors.
Egert S, Rimbach G, Huebbe P. Egert S, et al. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012 Aug;71(3):410-24. doi: 10.1017/S0029665112000249. Epub 2012 May 8. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012. PMID: 22564824 Review. - n-3 Fatty acid erythrocyte membrane content, APOE varepsilon4, and cognitive variation: an observational follow-up study in late adulthood.
Whalley LJ, Deary IJ, Starr JM, Wahle KW, Rance KA, Bourne VJ, Fox HC. Whalley LJ, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Feb;87(2):449-54. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.2.449. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18258638 - The effect of APOE genotype on Alzheimer's disease risk is influenced by sex and docosahexaenoic acid status.
Pontifex M, Vauzour D, Minihane AM. Pontifex M, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2018 Sep;69:209-220. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 21. Neurobiol Aging. 2018. PMID: 29909178 Review.
Cited by
- Relationship between diet and plasma long-chain n-3 PUFAs in older people: impact of apolipoprotein E genotype.
Samieri C, Lorrain S, Buaud B, Vaysse C, Berr C, Peuchant E, Cunnane SC, Barberger-Gateau P. Samieri C, et al. J Lipid Res. 2013 Sep;54(9):2559-67. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P036475. Epub 2013 Jun 25. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23801662 Free PMC article. - Characterization and Optimization of Culture Conditions for Aurantiochytrium sp. SC145 Isolated from Sand Cay (Son Ca) Island, Vietnam, and Antioxidative and Neuroprotective Activities of Its Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Mixture.
Hien HTM, Thom LT, Ha NC, Tam LT, Thu NTH, Nguyen TV, Loan VT, Dan NT, Hong DD. Hien HTM, et al. Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 14;20(12):780. doi: 10.3390/md20120780. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547927 Free PMC article. - Dietary fat composition and dementia risk.
Morris MC, Tangney CC. Morris MC, et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Sep;35 Suppl 2:S59-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.03.038. Epub 2014 May 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24970568 Free PMC article. Review. - Apolipoprotein E4 mediates insulin resistance-associated cerebrovascular dysfunction and the post-prandial response.
Johnson LA, Torres ER, Weber Boutros S, Patel E, Akinyeke T, Alkayed NJ, Raber J. Johnson LA, et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 May;39(5):770-781. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17746186. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 29215310 Free PMC article. - Cerebrospinal fluid lipidomics: effects of an intravenous triglyceride infusion and apoE status.
Hanson AJ, Banks WA, Bettcher LF, Pepin R, Raftery D, Craft S. Hanson AJ, et al. Metabolomics. 2019 Dec 12;16(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s11306-019-1627-x. Metabolomics. 2019. PMID: 31832778 Free PMC article.
References
- Fotuhi M, Hachinski V, Whitehouse PJ. Changing perspectives regarding late-life dementia. Nat Rev Neurol. 2009;5:649–58. - PubMed
- Schmitz G, Ecker J. The opposing effects of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids. Prog Lipid Res. 2008;47:147. - PubMed
- Plourde M, Cunnane S. Extremely limited conversion of long chain omega 3 polyunsaturates in adults: implications for their dietary essentiality and use as supplements. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007;32:619–634. - PubMed