Modulation of ischemia-induced NMDAR1 activation by environmental enrichment decreases oxidative damage - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2011 Dec;28(12):2485-92.
doi: 10.1089/neu.2011.1842. Epub 2011 Aug 29.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21612313
- PMCID: PMC3235341
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2011.1842
Comparative Study
Modulation of ischemia-induced NMDAR1 activation by environmental enrichment decreases oxidative damage
Teresita L Briones et al. J Neurotrauma. 2011 Dec.
Retraction in
- Retractions of DOI: 10.1089/neu.2008.0707 and 10.1089/neu.2011.1842.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] J Neurotrauma. 2015 Jun 1;32(11):863. doi: 10.1089/neu.2015.28999.retractions. J Neurotrauma. 2015. PMID: 26018334 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
In this study, we examined whether enriched environment (EE) housing has direct neuroprotective effects on oxidative damage following transient global cerebral ischemia. Fifty-two adult male Wistar rats were included in the study and received either ischemia or sham surgery. Once fully awake, rats in each group were randomly assigned to either: EE housing or socially paired housing (CON). Animals remained in their assigned environment for 7 days, and then were killed. Our data showed that glutamate receptor expression was significantly higher in the hippocampus of the ischemia CON group than in the ischemia EE group. Furthermore, the oxidative DNA damage, protein oxidation, and neurodegeneration in the hippocampus of the ischemia CON group were significantly increased compared to the ischemia EE group. These results suggest that EE housing possibly modulated the ischemia-induced glutamate excitotoxicity, which then attenuated the oxidative damage and neurodegeneration in the ischemia EE rats.
Figures
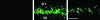
FIG. 1.
Representative photomicrographs of Fluoro-Jade staining in the sham (left panel), ischemia CON (middle panel), and ischemia EE (right panel) animals. SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. Scale bar=100 μm.
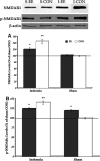
FIG. 2.
Representative Western blot of sham (S) and ischemia (I) groups (upper panel). NMDAR1 levels significantly increased in the ischemic rats compared to the sham groups but housing rats in EE after injury attenuated that upregulation (A). Significant elevation in NMDAR1 activity was also seen after ischemic injury but modulated by EE housing (post-hoc comparison between ischemia EE and ischemia CON). Significant increase in NMDAR1 activity was also seen in the sham EE rats compared to the sham control animals (B). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. EE,enriched environment; CON, controls.
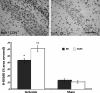
FIG. 3.
Representative photomicrographs of 8-OHdG immunostaining in the ischemic animals taken from the CA3 area where most of the immunoreactivities were observed (upper panel). Significantly increased oxidative DNA damage was seen in the ischemic rats compared to the sham groups (bar graph). However, post-hoc comparisons between the ischemia EE and ischemia CON groups showed that housing rats in the enriched environment after injury significantly attenuated oxidative damage to DNA. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. EE, enriched environment; CON, controls; Isch, ischemia. Scale bar=50 μm.
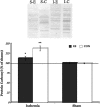
FIG. 4.
Representative oxyblot staining in the sham (S) and ischemia (I) groups (upper panel). Significantly increased protein carbonyl levels were seen in the ischemia group compared to shams. However, post-hoc comparisons between the ischemia EE and ischemia CON groups showed that housing rats in the enriched environment after ischemic injury resulted in a significant reduction in protein carbonylation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. EE or E, enriched environment; CON or C, controls.
Comment in
- Findings of research misconduct.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2015 Apr 17:NOT-OD-15-093. NIH Guide Grants Contracts (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 25898421 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Findings of Research Misconduct.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Fed Regist. 2015 Apr 7;80(66):18638. Fed Regist. 2015. PMID: 27737269 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Environmental enrichment influences BDNF and NR1 levels in the hippocampus and restores cognitive impairment in chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats.
Sun H, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu H, Zhu H, Yang Y. Sun H, et al. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010 Nov;7(4):268-80. doi: 10.2174/156720210793180819. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20854252 - The alterations of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor expressions and oxidative DNA damage in the CA1 area at the early time after ischemia-reperfusion insult.
Won MH, Kang T, Park S, Jeon G, Kim Y, Seo JH, Choi E, Chung M, Cho SS. Won MH, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2001 Mar 30;301(2):139-42. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(01)01625-1. Neurosci Lett. 2001. PMID: 11248442 - [Effects of sodium tanshinone B on the protein expression of NMDAR1 in rat hippocampal subfields following focal ischemia/reperfusion injury].
Cai Q, Huang SY, Tan JZ. Cai Q, et al. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;32(8):1073-6. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23173256 Chinese. - Long-term effects of enriched environment following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia on behavior, BDNF and synaptophysin levels in rat hippocampus: Effect of combined treatment with G-CSF.
Griva M, Lagoudaki R, Touloumi O, Nousiopoulou E, Karalis F, Georgiou T, Kokaraki G, Simeonidou C, Tata DA, Spandou E. Griva M, et al. Brain Res. 2017 Jul 15;1667:55-67. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 8. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28495306 - The impact of enriched environments on cerebral oxidative balance in rodents: a systematic review of environmental variability effects.
Ramos TL, de Sousa Fernandes MS, da Silva Fidélis DE, Jurema Santos GC, Albuquerque RB, Ferreira DJS, de Souza RF, Badicu G, Yagin FH, Yagin B, Alwhaibi RM, Souto FO, Lagranha CJ. Ramos TL, et al. Front Neurosci. 2024 Apr 11;18:1366747. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1366747. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38665291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Altered Levels of Zinc and N-methyl-D-aspartic Acid Receptor Underlying Multiple Organ Dysfunctions After Severe Trauma.
Wang G, Yu X, Wang D, Xu X, Chen G, Jiang X. Wang G, et al. Med Sci Monit. 2015 Sep 3;21:2613-20. doi: 10.12659/MSM.895075. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26335029 Free PMC article. - The impact of microglial activation on blood-brain barrier in brain diseases.
da Fonseca AC, Matias D, Garcia C, Amaral R, Geraldo LH, Freitas C, Lima FR. da Fonseca AC, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Nov 3;8:362. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00362. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25404894 Free PMC article. Review. - Combining the Antipsychotic Drug Haloperidol and Environmental Enrichment after Traumatic Brain Injury Is a Double-Edged Sword.
Folweiler KA, Bondi CO, Ogunsanya EA, LaPorte MJ, Leary JB, Radabaugh HL, Monaco CM, Kline AE. Folweiler KA, et al. J Neurotrauma. 2017 Jan 15;34(2):451-458. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4417. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Neurotrauma. 2017. PMID: 26975872 Free PMC article. - Exercising New Neurons to Vanquish Alzheimer Disease.
Llorens-Martín M. Llorens-Martín M. Brain Plast. 2018 Dec 12;4(1):111-126. doi: 10.3233/BPL-180065. Brain Plast. 2018. PMID: 30564550 Free PMC article. Review. - Noninvasive strategies to promote functional recovery after stroke.
Faralli A, Bigoni M, Mauro A, Rossi F, Carulli D. Faralli A, et al. Neural Plast. 2013;2013:854597. doi: 10.1155/2013/854597. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 23864962 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Abe K. Aoki M. Kawagoe J. Yoshida T. Hattori A. Kogure K. Itoyama Y. Ischemic delayed neuronal death. Stroke. 1994;26:1478–1489. - PubMed
- Andin J. Hallbeck M. Mohammed A.H. Marcusson J. Influence of environmental enrichment on steady-state mRNA levels for EAAC1, AMPA1 and NMDA2A receptors subunits in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2007;1174:18–27. - PubMed
- Ankarcrona M. Dypbukt J.H. Bonfoco E. Zhivotovsky B. Porrenius S. Lipton S.A. Nicotera P. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitchondrial function. Neuron. 1995;15:961–973. - PubMed
- Artola A. von Frijtag J.C. Fermont P.C.J. Gispen W.H. Schrama L.H. Kamal A. Spruijt B.M. Long-lasting modulation of the inducion of LTD and LTP in rat hippocampal CA1 by behavioural stress and environmental enrichment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006;23:261–272. - PubMed
- Beckman J. S. Koppenol W. H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;271:C1424–C1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources