A screening method for phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 activity - PubMed (original) (raw)
A screening method for phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 activity
Ulla Beckman-Sundh et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
Abstract Introduction. Research in the field of protein-bound phosphohistidine phosphorylation has been hampered by the difficulties in analysis and detection of phosphohistidine. Therefore a screening method was developed primarily for the analysis of phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) activity. Methods. A highly positively charged substrate, Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA, containing the peptide surrounding the phosphorylated histidine in ion channel KCa3.1 was chemically phosphorylated using phosphoramidate. Excess phosphoramidate was removed by anion exchange chromatography using a micro spin column. After incubation of the eluate with PHPT1, the removed phosphate was bound on a consecutive anion exchange spin column. The eluate was assayed in a micro plate format for remaining phosphate in the substrate Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His(P)-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA. Histone H4, also highly positive in charge, was subjected to the same procedure to explore the possibility to use other substrates to PHPT1 in this assay format. Results. It was found that Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His(P)-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA and phosphohistone H4 were dephosphorylated by PHPT1. The apparent K(m) for Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His(P)-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA was in the order of 10 μM.Using this method, phosphohistidine phosphatase activity was detected in mouse liver cell sap with Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His(P)-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA as substrate. Discussion. The described method for determination of PHPT1 activity is comparably much easier and faster than presently used methods for detection of phosphohistidine phosphatase activity. It is also sensitive, since the lower activity limit was 5 pmol phosphate released per min. It has the potential to be used both for more rapid screening for inhibitors and activators to phosphohistidine phosphatases and for screening of histidine kinases.
Figures
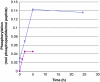
Figure 1.
Phosphorylation of peptides by phosphoramidate as a function of time. The concentration of Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA and Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-Ala-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA was 0.5 mM and that of phosphoramidate 3.9 mM. The incubation was performed at room temperature and interrupted by centrifugation of 50 μL of the reaction mixture through two consecutive spin columns containing 210 μL DEAE-Sephacel equilibrated in 25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0. The phosphate and peptide concentration in the final eluate was determined by malachite reagent and by measuring the absorbance at 320 nm, respectively. The values are given as means of duplicate analysis. (◊) Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA and (▪) Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-Ala-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA. Details are given in Material and methods.
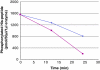
Figure 2.
The PHPT1 activity as a function of enzyme concentration. The concentration of Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His(P)-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA was 24 μM in this experiment, and the enzyme was diluted 1/10 (▪) and 1/20 (◊), the former corresponding to 2.5 pmol per 50 μL incubation. The dephosphorylation was performed at 30°C and was interrupted by centrifugation of 50 μL of the reaction mixture through a spin column containing 210 μL DEAE-Sephacel equilibrated in 25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0. The phosphate in the final eluate was determined by malachite reagent and peptide by absorbance at 320 nm. Details are given in Material and methods.
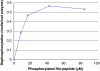
Figure 3.
Activity of PHPT1 as a function of phosphopeptide concentration. After phosphorylation of 2 mM Ac-Val-Arg-Leu-Lys-His-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-pNA, phosphoramidate was removed by centrifugation through DEAE-Sephacel as described in Material and methods and diluted. The concentration of phosphopeptide was determined in each sample. Purified PHPT1 (1 pmol) was added to each concentration, and dephosphorylation was performed at 30°C in duplicate for 4, 8, and 12 min for each concentration. The reaction was interrupted by centrifugation of 50 μL through a spin column containing 210 μL DEAE-Sephacel equilibrated in 25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0. The phosphate in the final eluate was determined by malachite reagent and peptide by absorbance at 320 nm. Details are given in Material and methods. The initial rate for each phosphopeptide concentration was plotted as a function of phosphopeptide concentration. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
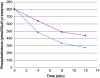
Figure 4.
Dephosphorylation of purified and recombinant histone H4. Histone H4 was, after phosphorylation with phosphoramidate to 1.29 mol/mol, dephosphorylated with 2 pmoles PHPT1 for indicated times. The reaction was performed at 30°C and was interrupted by centrifugation of 50 μL of the reaction mixture through a spin column containing 210 μL DEAE-Sephacel equilibrated in 25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.5 at indicated times. Each time point was analysed in duplicate. The phosphate in the final eluate was determined by malachite reagent and histone by absorbance at 280 nm. Details are given in Material and methods.(◊) 40 μM purified phosphohistone H4, and (▪) 20 μM recombinant phosphohistone H4.
Similar articles
- Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) also dephosphorylates phospholysine of chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine.
Ek P, Ek B, Zetterqvist Ö. Ek P, et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2015 Mar;120(1):20-7. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2014.996720. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Ups J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25574816 Free PMC article. - Histidine Phosphorylation: Protein Kinases and Phosphatases.
Ning J, Sala M, Reina J, Kalagiri R, Hunter T, McCullough BS. Ning J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063217 Free PMC article. Review. - Immunohistochemical localization of phosphohistidine phosphatase PHPT1 in mouse and human tissues.
Zhang XQ, Sundh UB, Jansson L, Zetterqvist O, Ek P. Zhang XQ, et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2009;114(2):65-72. doi: 10.1080/03009730802642337. Ups J Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19396692 Free PMC article. - Two phosphatases for 6-phospholysine and 3-phosphohistidine from rat brain.
Ohmori H, Kuba M, Kumon A. Ohmori H, et al. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7625-7. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8385112 - A journey from phosphotyrosine to phosphohistidine and beyond.
Hunter T. Hunter T. Mol Cell. 2022 Jun 16;82(12):2190-2200. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.007. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35654043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) also dephosphorylates phospholysine of chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine.
Ek P, Ek B, Zetterqvist Ö. Ek P, et al. Ups J Med Sci. 2015 Mar;120(1):20-7. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2014.996720. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Ups J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25574816 Free PMC article. - Histidine Phosphorylation: Protein Kinases and Phosphatases.
Ning J, Sala M, Reina J, Kalagiri R, Hunter T, McCullough BS. Ning J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Klumpp S, Krieglstein J. Reversible phosphorylation of histidine residues in proteins from vertebrates. Sci Signal. 2009;2:pe13. - PubMed
- Ek P, Pettersson G, Ek B, Gong F, Li J-P, Zetterqvist Ö. Identification and characterization of a mammalian 14-kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 2002;269:5016–23. - PubMed
- Klumpp S, Hermesmeier J, Selke D, Bechmann G, van den Brulle J, Weidner G, et al. Protein histidine phosphatase: A novel enzyme with potency for neuronal signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:1420–4. - PubMed
- Boyer PD, DeLuca M, Erner KE, Hultquist DE, Peter JB. Identification of phosphohistidine in digests from a probable intermediate of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:PC3306–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous