Volume depletion versus dehydration: how understanding the difference can guide therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Volume depletion versus dehydration: how understanding the difference can guide therapy
Gautam Bhave et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
Although often used interchangeably, dehydration and volume depletion are not synonyms. Dehydration refers to loss of total-body water, producing hypertonicity, which now is the preferred term in lieu of dehydration, whereas volume depletion refers to a deficit in extracellular fluid volume. In particular, hypertonicity implies intracellular volume contraction, whereas volume depletion implies blood volume contraction. Using a case of hyperglycemic hypertonic nonketosis as an example, we examine the changing composition of body fluid spaces to explore the distinction between dehydration and hypertonicity from volume depletion.
Copyright © 2011 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
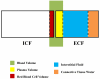
Figure 1. Schematic Representation of Body Water Compartments
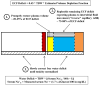
Figure 2. Body Fluid Derangements and Fluid Therapy Strategy in HHNK with Volume Depletion & Hypertonicity
Circulating volume depletion is the overriding initial therapeutic goal followed by interstitial fluid depletion which account for 1/4th and 3/4th of the ECFV deficit respectively. Correction of tonicity with free water or hypotonic solutions is conducted slowly ensuring serum Na+G falls at a rate < 10 mEq/day.
Similar articles
- Language guiding therapy: the case of dehydration versus volume depletion.
Mange K, Matsuura D, Cizman B, Soto H, Ziyadeh FN, Goldfarb S, Neilson EG. Mange K, et al. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Nov 1;127(9):848-53. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-9-199711010-00020. Ann Intern Med. 1997. PMID: 9382413 Review. - Managing the dehydrated child.
Driggers DA. Driggers DA. Am Fam Physician. 1982 Nov;26(5):189-94. Am Fam Physician. 1982. PMID: 7148628 - Evaluation and treatment of cancer-related fluid deficits: volume depletion and dehydration.
Sarhill N, Walsh D, Nelson K, Davis M. Sarhill N, et al. Support Care Cancer. 2001 Sep;9(6):408-19. doi: 10.1007/s005200100251. Support Care Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11585267 Review. - Dehydration versus volume depletion--and the importance of getting it right.
Spital A. Spital A. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007 May;49(5):721-2. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.03.012. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007. PMID: 17472857 No abstract available. - Efficacy of Glucose or Amino Acid-Based Commercial Beverages in Meeting Oral Rehydration Therapy Goals After Acute Hypertonic and Isotonic Dehydration.
Cheuvront SN, Kenefick RW, Charkoudian N, Mitchell KM, Luippold AJ, Bradbury KE, Vidyasagar S. Cheuvront SN, et al. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018 Sep;42(7):1185-1193. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1142. Epub 2018 Jan 28. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29377181 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- Serum sodium variation is a major determinant of peridialytic blood pressure trends in haemodialysis outpatients.
Jaques DA, Davenport A. Jaques DA, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 12;11(1):7882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86960-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33846430 Free PMC article. - Cerebral Ultrasound Time-Harmonic Elastography Reveals Softening of the Human Brain Due to Dehydration.
Kreft B, Bergs J, Shahryari M, Danyel LA, Hetzer S, Braun J, Sack I, Tzschätzsch H. Kreft B, et al. Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 11;11:616984. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.616984. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33505319 Free PMC article. - Fluid balance concepts in medicine: Principles and practice.
Roumelioti ME, Glew RH, Khitan ZJ, Rondon-Berrios H, Argyropoulos CP, Malhotra D, Raj DS, Agaba EI, Rohrscheib M, Murata GH, Shapiro JI, Tzamaloukas AH. Roumelioti ME, et al. World J Nephrol. 2018 Jan 6;7(1):1-28. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v7.i1.1. World J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29359117 Free PMC article. Review. - Evaluation and management of hypernatremia in adults: clinical perspectives.
Yun G, Baek SH, Kim S. Yun G, et al. Korean J Intern Med. 2023 May;38(3):290-302. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.346. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Korean J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36578134 Free PMC article. Review. - Accuracy of the caval index and the expiratory diameter of the inferior vena cava for the diagnosis of dehydration in elderly.
Orso D, Guglielmo N, Federici N, Cugini F, Ban A, Mearelli F, Copetti R. Orso D, et al. J Ultrasound. 2016 Apr 8;19(3):203-9. doi: 10.1007/s40477-016-0200-y. eCollection 2016 Sep. J Ultrasound. 2016. PMID: 27635166 Free PMC article.
References
- Chumlea WC, Guo SS, Zeller CM, et al. Total body water reference values and prediction equations for adults. Kidney Int. 2001;59:2250–2258. - PubMed
- Watson PE, Watson ID, Batt RD. Total body water volumes for adult males and females estimated from simple anthropometric measurements. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980;33:27–39. - PubMed
- Edelman IS, Leibman J. Anatomy of body water and electrolytes. Am J Med. 1959;27:256–277. - PubMed
- Gennari FJ. Current concepts. Serum osmolality. Uses and limitations. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:102–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical