Autoimmune disease risk variant of IFIH1 is associated with increased sensitivity to IFN-α and serologic autoimmunity in lupus patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Aug 1;187(3):1298-303.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100857. Epub 2011 Jun 24.
Silvia N Kariuki, Beverly S Franek, Marissa Kumabe, Akaash A Kumar, Maria Badaracco, Rachel A Mikolaitis, Galen Guerrero, Tammy O Utset, Barbara E Drevlow, Laura S Zaacks, James S Grober, Lewis M Cohen, Kyriakos A Kirou, Mary K Crow, Meenakshi Jolly, Timothy B Niewold
Affiliations
- PMID: 21705624
- PMCID: PMC3304466
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100857
Autoimmune disease risk variant of IFIH1 is associated with increased sensitivity to IFN-α and serologic autoimmunity in lupus patients
Talin Robinson et al. J Immunol. 2011.
Abstract
Increased IFN-α signaling is a heritable risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). IFN induced with helicase C domain 1 (IFIH1) is a cytoplasmic dsRNA sensor that activates IFN-α pathway signaling. We studied the impact of the autoimmune-disease-associated IFIH1 rs1990760 (A946T) single nucleotide polymorphism upon IFN-α signaling in SLE patients in vivo. We studied 563 SLE patients (278 African-American, 179 European-American, and 106 Hispanic-American). Logistic regression models were used to detect genetic associations with autoantibody traits, and multiple linear regression was used to analyze IFN-α-induced gene expression in PBMCs in the context of serum IFN-α in the same blood sample. We found that the rs1990760 T allele was associated with anti-dsDNA Abs across all of the studied ancestral backgrounds (meta-analysis odds ratio = 1.34, p = 0.026). This allele also was associated with lower serum IFN-α levels in subjects who had anti-dsDNA Abs (p = 0.0026). When we studied simultaneous serum and PBMC samples from SLE patients, we found that the IFIH1 rs1990760 T allele was associated with increased IFN-induced gene expression in PBMCs in response to a given amount of serum IFN-α in anti-dsDNA-positive patients. This effect was independent of the STAT4 genotype, which modulates sensitivity to IFN-α in a similar way. Thus, the IFIH1 rs1990760 T allele was associated with dsDNA Abs, and in patients with anti-dsDNA Abs this risk allele increased sensitivity to IFN-α signaling. These studies suggest a role for the IFIH1 risk allele in SLE in vivo.
Figures
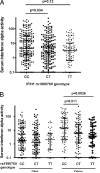
FIGURE 1
Serum IFN-α activity in SLE patients stratified by rs1990760 genotype and anti-dsDNA autoantibodies. A, All patients in aggregate. B, Patients stratified by presence or absence of anti-dsDNA Abs. The line indicating the central tendency represents the median, the error bars show the interquartile range, and the p value was calculated using the Mann–Whitney U test.
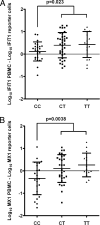
FIGURE 2
Difference in IFIT1 and MX1 expression in reporter cells versus PBMCs stratified by IFIH1 genotype. Relative expression values were log10-transformed, and the relative expression of each transcript in reporter cells exposed to patient sera was subtracted from the relative expression of the same transcript in PBMCs from the same blood sample. A, IFIT1. B, MX1. Lines indicate the mean, and error bars show the SDs. Data were distributed normally, and the p value was calculated using an unpaired t test for the difference between CC and CT or TT genotypes.
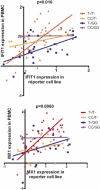
FIGURE 3
IFN-β–induced gene expression in PBMCs versus serum IFN-β activity in anti-dsDNA–positive SLE patients. Patients were stratified by IFIH1 rs1990760 and STAT4 rs7574865 genotypes. T indicates carriage of the risk allele in each case (includes both heterozygous and homozygous risk allele genotypes). Data were log-transformed, and the lines shown are the result of linear regression in each genotype category. The p values were calculated by the sum-of-squares F test for a difference in the slope of the regression line between genotype categories.
Similar articles
- Effects of type 1 diabetes-associated IFIH1 polymorphisms on MDA5 function and expression.
Looney BM, Xia CQ, Concannon P, Ostrov DA, Clare-Salzler MJ. Looney BM, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Nov;15(11):96. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0656-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26385483 Review. - Cutting edge: autoimmune disease risk variant of STAT4 confers increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha in lupus patients in vivo.
Kariuki SN, Kirou KA, MacDermott EJ, Barillas-Arias L, Crow MK, Niewold TB. Kariuki SN, et al. J Immunol. 2009 Jan 1;182(1):34-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.34. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19109131 Free PMC article. - Association study of IFIH1 rs1990760 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese population.
Cen H, Leng RX, Wang W, Zhou M, Feng CC, Zhu Y, Yang XK, Yang M, Zhai Y, Li BZ, Liu J, Pan HF, Ye DQ. Cen H, et al. Inflammation. 2013 Apr;36(2):444-8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9564-0. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 23108955 - Genetic polymorphisms of dsRNA ligating pattern recognition receptors TLR3, MDA5, and RIG-I. Association with systemic lupus erythematosus and clinical phenotypes.
Enevold C, Kjær L, Nielsen CH, Voss A, Jacobsen RS, Hermansen ML, Redder L, Oturai AB, Jensen PE, Bendtzen K, Jacobsen S. Enevold C, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2014 Oct;34(10):1401-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3012-4. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Rheumatol Int. 2014. PMID: 24719229 - Association of IFIH1 rs1990760 polymorphism with susceptibility to autoimmune diseases: a meta-analysis.
Cen H, Wang W, Leng RX, Wang TY, Pan HF, Fan YG, Wang B, Ye DQ. Cen H, et al. Autoimmunity. 2013 Nov;46(7):455-62. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2013.796937. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Autoimmunity. 2013. PMID: 23734776 Review.
Cited by
- Association of NCF2, IKZF1, IRF8, IFIH1, and TYK2 with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Cunninghame Graham DS, Morris DL, Bhangale TR, Criswell LA, Syvänen AC, Rönnblom L, Behrens TW, Graham RR, Vyse TJ. Cunninghame Graham DS, et al. PLoS Genet. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002341. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22046141 Free PMC article. - Effects of type 1 diabetes-associated IFIH1 polymorphisms on MDA5 function and expression.
Looney BM, Xia CQ, Concannon P, Ostrov DA, Clare-Salzler MJ. Looney BM, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Nov;15(11):96. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0656-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26385483 Review. - Mitochondria in innate immunity signaling and its therapeutic implications in autoimmune diseases.
Jiao Y, Yan Z, Yang A. Jiao Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1160035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160035. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122709 Free PMC article. Review. - Functionally impaired plasmacytoid dendritic cells and non-haematopoietic sources of type I interferon characterize human autoimmunity.
Psarras A, Alase A, Antanaviciute A, Carr IM, Md Yusof MY, Wittmann M, Emery P, Tsokos GC, Vital EM. Psarras A, et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 1;11(1):6149. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19918-z. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33262343 Free PMC article. - The genetics of lupus: a functional perspective.
Guerra SG, Vyse TJ, Cunninghame Graham DS. Guerra SG, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 29;14(3):211. doi: 10.1186/ar3844. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22640752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM. Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2006;28:119–130. - PubMed
- Rönnblom LE, Alm GV, Oberg KE. Possible induction of systemic lupus erythematosus by interferon-alpha treatment in a patient with a malignant carcinoid tumour. J. Intern. Med. 1990;227:207–210. - PubMed
- Niewold TB, Swedler WI. Systemic lupus erythematosus arising during interferon-alpha therapy for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis associated with hepatitis C. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005;24:178–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- L30 AI071651-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK042086/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060861/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060861-01/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous