Exaggerated activation of dorsal anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive interference: a monozygotic twin study of posttraumatic stress disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Sep;168(9):979-85.
doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.09121812. Epub 2011 Jul 1.
George Bush, Mohammed R Milad, Natasha B Lasko, Kathryn Handwerger Brohawn, Katherine C Hughes, Michael L Macklin, Andrea L Gold, Rachel D Karpf, Scott P Orr, Scott L Rauch, Roger K Pitman
Affiliations
- PMID: 21724666
- PMCID: PMC3773363
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.09121812
Exaggerated activation of dorsal anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive interference: a monozygotic twin study of posttraumatic stress disorder
Lisa M Shin et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Sep.
Abstract
Objective: Neuroimaging studies have revealed functional abnormalities in the anterior cingulate cortex in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The goal of this study was to determine whether hyperresponsivity of the dorsal anterior cingulate in PTSD is an acquired characteristic or a familial risk factor.
Method: Using a case-control twin design, the authors studied combat-exposed veterans with PTSD (N=12) and their identical combat-unexposed co-twins (N=12), as well as combat-exposed veterans without PTSD (N=14) and their identical combat-unexposed co-twins (N=14). Participants underwent functional MRI during completion of the Multi-Source Interference Task, which reliably activates the dorsal anterior cingulate.
Results: Combat-exposed veterans with PTSD and their unexposed co-twins had significantly greater activation in the dorsal anterior cingulate and tended to have larger response time difference scores, as compared to combat-exposed veterans without PTSD and their co-twins. Dorsal anterior cingulate activation in the exposed twins was positively correlated with their PTSD symptom severity. Dorsal anterior cingulate activation in the unexposed twins was positively correlated with their combat-exposed co-twins' PTSD symptom severity, but not with depression or alcohol use severity in the combat-exposed co-twins.
Conclusions: Hyperresponsivity in the dorsal anterior cingulate appears to be a familial risk factor for the development of PTSD following psychological trauma.
Figures
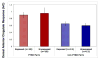
Figure 1
Functional MRI data extracted from the maximum voxels in the dorsal anterior cingulate of individual subjects and displayed per group. These data show a main effect of PTSD Diagnosis, F(1, 20)=8.9, p=.007, consistent with the whole-brain voxelwise analyses. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
Comment in
- Imaging a brighter future.
Pine DS, Freedman R. Pine DS, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Sep;168(9):885-7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11050788. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21890801 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Evidence for acquired pregenual anterior cingulate gray matter loss from a twin study of combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder.
Kasai K, Yamasue H, Gilbertson MW, Shenton ME, Rauch SL, Pitman RK. Kasai K, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Mar 15;63(6):550-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.06.022. Epub 2007 Sep 7. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17825801 Free PMC article. - Imaging a brighter future.
Pine DS, Freedman R. Pine DS, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Sep;168(9):885-7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11050788. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21890801 No abstract available. - Resting metabolic activity in the cingulate cortex and vulnerability to posttraumatic stress disorder.
Shin LM, Lasko NB, Macklin ML, Karpf RD, Milad MR, Orr SP, Goetz JM, Fischman AJ, Rauch SL, Pitman RK. Shin LM, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009 Oct;66(10):1099-107. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.138. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19805700 Free PMC article. - Twin studies of posttraumatic stress disorder: differentiating vulnerability factors from sequelae.
Kremen WS, Koenen KC, Afari N, Lyons MJ. Kremen WS, et al. Neuropharmacology. 2012 Feb;62(2):647-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21443892 Free PMC article. Review. - Cingulate subregions in posttraumatic stress disorder, chronic stress, and treatment.
Hinojosa CA, Kaur N, VanElzakker MB, Shin LM. Hinojosa CA, et al. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;166:355-370. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64196-0.00020-0. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31731922 Review.
Cited by
- Diminished rostral anterior cingulate cortex activation during trauma-unrelated emotional interference in PTSD.
Offringa R, Handwerger Brohawn K, Staples LK, Dubois SJ, Hughes KC, Pfaff DL, Vanelzakker MB, Davis FC, Shin LM. Offringa R, et al. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2013 May 14;3(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-3-10. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2013. PMID: 23672953 Free PMC article. - Biological studies of post-traumatic stress disorder.
Pitman RK, Rasmusson AM, Koenen KC, Shin LM, Orr SP, Gilbertson MW, Milad MR, Liberzon I. Pitman RK, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Nov;13(11):769-87. doi: 10.1038/nrn3339. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23047775 Free PMC article. Review. - Tempering aversive/traumatic memories with cannabinoids: a review of evidence from animal and human studies.
Lisboa SF, Vila-Verde C, Rosa J, Uliana DL, Stern CAJ, Bertoglio LJ, Resstel LB, Guimaraes FS. Lisboa SF, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):201-226. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5127-x. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30604182 Review. - Neural processing correlates of assaultive violence exposure and PTSD symptoms during implicit threat processing: a network-level analysis among adolescent girls.
Cisler JM, Scott Steele J, Smitherman S, Lenow JK, Kilts CD. Cisler JM, et al. Psychiatry Res. 2013 Dec 30;214(3):238-46. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Psychiatry Res. 2013. PMID: 23969000 Free PMC article. - Voxel-wise resting-state MEG source magnitude imaging study reveals neurocircuitry abnormality in active-duty service members and veterans with PTSD.
Huang MX, Yurgil KA, Robb A, Angeles A, Diwakar M, Risbrough VB, Nichols SL, McLay R, Theilmann RJ, Song T, Huang CW, Lee RR, Baker DG. Huang MX, et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Aug 7;5:408-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.08.004. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25180160 Free PMC article.
References
- Vogt BA, Finch DM, Olson CR. Functional heterogeneity in cingulate cortex: the anterior executive and posterior evaluative regions. Cereb Cortex. 1992;2:435–43. - PubMed
- Bishop S, Duncan J, Brett M, Lawrence AD. Prefrontal cortical function and anxiety: controlling attention to threat-related stimuli. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:184–8. - PubMed
- Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI. Cognitive and emotional influence in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2000;4:215–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical