The modular neuroarchitecture of social judgments on faces - PubMed (original) (raw)
The modular neuroarchitecture of social judgments on faces
Danilo Bzdok et al. Cereb Cortex. 2012 Apr.
Abstract
Face-derived information on trustworthiness and attractiveness crucially influences social interaction. It is, however, unclear to what degree the functional neuroanatomy of these complex social judgments on faces reflects genuine social versus basic emotional and cognitive processing. To disentangle social from nonsocial contributions, we assessed commonalities and differences between the functional networks activated by judging social (trustworthiness, attractiveness), emotional (happiness), and cognitive (age) facial traits. Relative to happiness and age evaluations, both trustworthiness and attractiveness judgments selectively activated the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and inferior frontal gyrus, forming a core social cognition network. Moreover, they also elicited a higher amygdalar response than even the emotional control condition. Both social judgments differed, however, in their top-down modulation of face-sensitive regions: trustworthiness judgments recruited the posterior superior temporal sulcus, whereas attractiveness judgments recruited the fusiform gyrus. Social and emotional judgments converged and, therefore, likely interact in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Social and age judgments, on the other hand, commonly engaged the anterior insula, inferior parietal cortex, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which appear to subserve more cognitive aspects in social evaluation. These findings demonstrate the modularity of social judgments on human faces by separating the neural correlates of social, face-specific, emotional, and cognitive processing facets.
Figures
Figure 1.
Timeline of screens within one block of the fMRI experiment. During the actual trials participants were required to compare the face pair based on 4 different questions: “(Who do you regard as) More trustworthy?,” “More attractive?,” “Happier?,” and “Older?.” The face pair was presented for 3 s, with an additional double arrow between the 2 faces during the last second of presentation to prompt a response if not already given (ISI, interstimulus interval).
Figure 2.
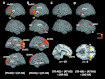
Main effects of social judgments. Medial and lateral views of T1 MNI single-subject template for common activation in social judgments, relative to emotional and cognitive judgments. The significance threshold is set at P < 0.001 with a cluster-forming threshold of P < 0.05 (for subcortical and cerebellar activation, see also
Supplementary Fig. S2
).
Figure 3.
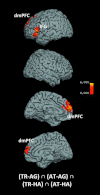
Emotional and cognitive aspects in social judgments. Medial and lateral views of T1 MNI single-subject template for common activation in social judgments when not parceling out (A) emotion decision–related activation and (B) cognitive decision–related activation. Lateral and section views of T1 MNI single-subject template for (C) conjunction across trustworthiness [TR], attractiveness [AT], and happiness [HA] judgments, relative to age [AG] judgments, to specifically depict the convergence of social and emotional processes during social judgments (sagittal section at x = −10); (D) conjunction across trustworthiness, attractiveness, and age judgments, relative to happiness judgments, to specifically depict convergence of social and cognitive processes during social judgments (axial section at z = −9). The significance threshold is set at P < 0.001 with a cluster-forming threshold of P < 0.05 (for subcortical and cerebellar activation, see also
Supplementary Fig. S3
).
Figure 4.
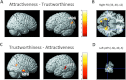
Neural differences between trustworthiness and attractiveness judgments. Activation for attractiveness versus trustworthiness judgments (A/B) and vice versa (C/D) superimposed on a T1 MNI single-subject template. (B) Horizontal section through cluster maximum in the right FG (z = −12) in the attractiveness–trustworthiness contrast, (D) sagittal section through cluster maximum in the left pSTS (x = −66) in the trustworthiness–attractiveness contrast. Coordinates in MNI space. The significance threshold is set at P < 0.001 with a cluster-forming threshold of P < 0.05. TR, trustworthiness; AT, attractiveness; HA, happiness; AG, age judgments.
Figure 5.
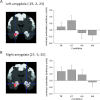
Amygdalar response across social, emotional, and cognitive facial judgments. Small volume–corrected analysis of the difference _F_-test across conditions using an anatomical template for the (A) left amygdala and (B) right amygdala. Activity significant at voxel-level P < 0.05 (family-wise error corrected) is shown on 2 coronal sections through the T1 MNI single-subject template at (A) y = −2 and (B) y = −5. Coordinates in MNI space. Two histograms, added for purely illustrative purposes, depicting BOLD signal changes across conditions in the cluster peak voxel in the (A) left and (B) right amygdala. TR, trustworthiness; AT, attractiveness; HA, happiness; AG, age judgments. The asterisk indicates significant differences between conditions (P < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Neural correlates of explicit social judgments on vocal stimuli.
Hensel L, Bzdok D, Müller VI, Zilles K, Eickhoff SB. Hensel L, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2015 May;25(5):1152-62. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht307. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 24243619 Free PMC article. - Similar patterns of brain activation abnormalities during emotional and non-emotional judgments of faces in a schizophrenia family study.
Spilka MJ, Goghari VM. Spilka MJ, et al. Neuropsychologia. 2017 Feb;96:164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 14. Neuropsychologia. 2017. PMID: 28093278 - Neural correlates of recognition memory for emotional faces and scenes.
Keightley ML, Chiew KS, Anderson JA, Grady CL. Keightley ML, et al. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2011 Jan;6(1):24-37. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsq003. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20194514 Free PMC article. - Evaluating faces on trustworthiness: an extension of systems for recognition of emotions signaling approach/avoidance behaviors.
Todorov A. Todorov A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Mar;1124:208-24. doi: 10.1196/annals.1440.012. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18400932 Review. - Brain systems for assessing the affective value of faces.
Said CP, Haxby JV, Todorov A. Said CP, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011 Jun 12;366(1571):1660-70. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0351. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21536552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- "Calculating faces": can face perception paradigms enrich dyscalculia research?
Baulina M, Kosonogov V. Baulina M, et al. Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1218124. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1218124. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38235284 Free PMC article. Review. - Social cognitive regions of human association cortex are selectively connected to the amygdala.
Edmonds D, Salvo JJ, Anderson N, Lakshman M, Yang Q, Kay K, Zelano C, Braga RM. Edmonds D, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 9:2023.12.06.570477. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.06.570477. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38106046 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Evolution of cortical geometry and its link to function, behaviour and ecology.
Schwartz E, Nenning KH, Heuer K, Jeffery N, Bertrand OC, Toro R, Kasprian G, Prayer D, Langs G. Schwartz E, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 20;14(1):2252. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37574-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37080952 Free PMC article. - Social belonging: brain structure and function is linked to membership in sports teams, religious groups, and social clubs.
Kieckhaefer C, Schilbach L, Bzdok D. Kieckhaefer C, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2023 Apr 4;33(8):4405-4420. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac351. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 36161309 Free PMC article. - Task Modulation of Single-Neuron Activity in the Human Amygdala and Hippocampus.
Cao R, Todorov A, Brandmeir NJ, Wang S. Cao R, et al. eNeuro. 2022 Jan 19;9(1):ENEURO.0398-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0398-21.2021. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 34933946 Free PMC article.
References
- Aggleton JP, Mishkin M. The amygdala sensory gateway to the emotions. In: Plutchick R, Kellerman H, editors. Emotion: theory, research and experience. Biological foundation of emotion. Orlando (FL): Academic Press; 1986. pp. 281–299.
- Akiyama T, Kato M, Muramatsu T, Saito F, Nakachi R, Kashima H. A deficit in discriminating gaze direction in a case with right superior temporal gyrus lesion. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44:161–170. - PubMed
- Amaral DG, Price JL. Amygdalo-cortical projections in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis) J Comp Neurol. 1984;230:465–496. - PubMed
- Amodio DM, Frith CD. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:268–277. - PubMed