POM121 and Sun1 play a role in early steps of interphase NPC assembly - PubMed (original) (raw)
POM121 and Sun1 play a role in early steps of interphase NPC assembly
Jessica A Talamas et al. J Cell Biol. 2011.
Abstract
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) assemble at the end of mitosis during nuclear envelope (NE) reformation and into an intact NE as cells progress through interphase. Although recent studies have shown that NPC formation occurs by two different molecular mechanisms at two distinct cell cycle stages, little is known about the molecular players that mediate the fusion of the outer and inner nuclear membranes to form pores. In this paper, we provide evidence that the transmembrane nucleoporin (Nup), POM121, but not the Nup107-160 complex, is present at new pore assembly sites at a time that coincides with inner nuclear membrane (INM) and outer nuclear membrane (ONM) fusion. Overexpression of POM121 resulted in juxtaposition of the INM and ONM. Additionally, Sun1, an INM protein that is known to interact with the cytoskeleton, was specifically required for interphase assembly and localized with POM121 at forming pores. We propose a model in which POM121 and Sun1 interact transiently to promote early steps of interphase NPC assembly.
Figures
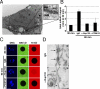
Figure 1.
POM121 is involved in the fusion of inner and outer nuclear membranes in vitro. (A) Transmission electron micrograph of a U2OS cell. Inset shows INM, ONM, and NPC. (B) Quantification of total mAb414 signal in nuclei assembled in vitro from Xenopus egg extracts for 30 min and then incubated for 60 min with either control IgG or inhibitory antibodies against Nup133 or POM121. Error bars are standard deviation. (C) Nuclei described in B were incubated in the presence of 500-kD and 70-kD fluorescent dextrans and imaged to assay for INM/ONM fusion. (D) TEM of in vitro assembled nuclei described in B. Arrows show NPCs (top) and NPC intermediates (bottom). Bars: (A and C) 5 µm; (D) 200 nm. N, nucleoplasm; C, cytoplasm.
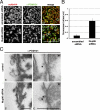
Figure 2.
POM121 is present at early NPC assembly intermediates. (A) Double immunofluorescence staining of the nuclear surface with mAb414 and α-POM121 antibodies in U2OS cells transfected with scrambled or Nup96-specific siRNA oligos. Circles indicate POM121 signal without mAb414. (B) Quantification of sites containing POM121 signal without mAb414 in control and Nup96-depleted U2OS cells. n = 8 nuclear surfaces per condition. Error bars are standard error. (C) TEM of immunogold labeling of POM121 in control and Nup96-depleted U2OS cells. Bars: (A) 2 µm; (C) 200 nm. N, nucleoplasm; C, cytoplasm.
Figure 3.
POM121 plays a role in juxtaposing inner and outer nuclear membranes. (A) Schematic representation of POM121 and truncation mutant fusion proteins. (B) POM121-GFP and Ndc1-GFP fusion plasmids were transfected into U2OS cells and immunostained with mAb414 to verify correct localization of the fusion proteins to the NE/NPCs. (C) Cross-sectional TEM of the NE in control or U2OS cells transfected with the GFP fusion proteins described in B. (D) Quantification of NPC width and transverse sectional lengths of reduced membrane spacing in control or cells expressing POM121-GFP or POM121 aa1–129-GFP. n > 9 measurements per condition. Horizontal bars are mean lengths. (E) POM121 aa1–129-GFP was transfected into U2OS cells and immunostained with either mAb414 or α-rtn4a. (F) Cross-sectional TEM of the NE in a U2OS cell transfected with POM121 aa1–129-GFP. (C and F) Right images are enlargements of the boxed areas on the left. Black arrows mark NPCs, and red arrows show areas of reduced membrane spacing. Bars: (A and E) 10 µm; (C and F) 200 nm. N, nucleoplasm; C, cytoplasm.
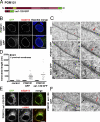
Figure 4.
Sun1 is required for interphase NPC assembly. (A) Double immunofluorescence staining of the nuclear surface with mAb414 and α-Sun1 antibodies in U2OS cells. Histogram of fluorescent signals shows partial overlap between mAb414 and α-Sun1 staining. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of U2OS cells shows efficient knockdown of POM121 and Sun1 by siRNA oligo transfection. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of the nuclear surface using mAb414 in U2OS cells transfected with either scrambled or siRNA oligos specific to POM121 or Sun1. (D) Quantification of total mAb414 fluorescence during G1 and G2 in U2OS cells treated with either scrambled or siRNA oligos specific to POM121 or Sun1. n > 167 nuclei per condition. Error bars are standard error. Bars, 10 µm.
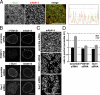
Figure 5.
Sun1 and POM121 collaborate during early steps of NPC assembly. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with POM121-3GFP and immunostained with mAb414 and α-Sun1 antibodies. Circles indicate loci at the nuclear surface containing GFP and Sun1 signal without mAb414. The box represents the area of zoomed in images on the right. (B) Quantification of NPCs and NPC intermediates overlapping with the Sun1 signal. n > 5 nuclear surfaces. Error bars are standard error. (C) Schematic representation of Sun1 and truncation mutant fusion proteins. C, carboxy terminus; N, amino terminus; ZnF, zinc finger. (D) Sun1-GFP, Sun1 aa1–330-GFP, and Sun1 aa1–221-GFP fusion plasmids were transfected into U2OS cells and immunostained with mAb414 to verify localization of the fusion proteins to the NE. (E) Quantification of total mAb414 fluorescence during G1 and G2 in control and U2OS cells transfected with Sun1 aa1–330-GFP. n > 60 nuclei per condition. Error bars are standard error. (F) Sun1 aa1–330-GFP and Sun1 aa1–221-GFP were transfected into U2OS cells that were immunostained with mAb414 and α-POM121 antibodies and imaged at the nuclear surface. Bars, 10 µm.
Similar articles
- The integral membrane nucleoporin pom121 functionally links nuclear pore complex assembly and nuclear envelope formation.
Antonin W, Franz C, Haselmann U, Antony C, Mattaj IW. Antonin W, et al. Mol Cell. 2005 Jan 7;17(1):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.12.010. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15629719 - Live imaging of single nuclear pores reveals unique assembly kinetics and mechanism in interphase.
Dultz E, Ellenberg J. Dultz E, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 Oct 4;191(1):15-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007076. Epub 2010 Sep 27. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20876277 Free PMC article. - Localization of Pom121 to the inner nuclear membrane is required for an early step of interphase nuclear pore complex assembly.
Funakoshi T, Clever M, Watanabe A, Imamoto N. Funakoshi T, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Apr;22(7):1058-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-07-0641. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21289085 Free PMC article. - Function and assembly of nuclear pore complex proteins.
Bodoor K, Shaikh S, Enarson P, Chowdhury S, Salina D, Raharjo WH, Burke B. Bodoor K, et al. Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;77(4):321-9. Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10546895 Review. - Nuclear pore biogenesis into an intact nuclear envelope.
Doucet CM, Hetzer MW. Doucet CM, et al. Chromosoma. 2010 Oct;119(5):469-77. doi: 10.1007/s00412-010-0289-2. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Chromosoma. 2010. PMID: 20721671 Review.
Cited by
- ESCRTs breach the nuclear border.
Webster BM, Lusk CP. Webster BM, et al. Nucleus. 2015;6(3):197-202. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1035844. Epub 2015 May 5. Nucleus. 2015. PMID: 25942571 Free PMC article. - Human telomeres are tethered to the nuclear envelope during postmitotic nuclear assembly.
Crabbe L, Cesare AJ, Kasuboski JM, Fitzpatrick JA, Karlseder J. Crabbe L, et al. Cell Rep. 2012 Dec 27;2(6):1521-9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.019. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23260663 Free PMC article. - G4C2 Repeat RNA Initiates a POM121-Mediated Reduction in Specific Nucleoporins in C9orf72 ALS/FTD.
Coyne AN, Zaepfel BL, Hayes L, Fitchman B, Salzberg Y, Luo EC, Bowen K, Trost H, Aigner S, Rigo F, Yeo GW, Harel A, Svendsen CN, Sareen D, Rothstein JD. Coyne AN, et al. Neuron. 2020 Sep 23;107(6):1124-1140.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.027. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32673563 Free PMC article. - Emerin Is Required for Proper Nucleus Reassembly after Mitosis: Implications for New Pathogenetic Mechanisms for Laminopathies Detected in EDMD1 Patients.
Dubińska-Magiera M, Kozioł K, Machowska M, Piekarowicz K, Filipczak D, Rzepecki R. Dubińska-Magiera M, et al. Cells. 2019 Mar 13;8(3):240. doi: 10.3390/cells8030240. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30871242 Free PMC article. - An inside-out origin for the eukaryotic cell.
Baum DA, Baum B. Baum DA, et al. BMC Biol. 2014 Oct 28;12:76. doi: 10.1186/s12915-014-0076-2. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 25350791 Free PMC article.
References
- Bodoor K., Shaikh S., Salina D., Raharjo W.H., Bastos R., Lohka M., Burke B. 1999. Sequential recruitment of NPC proteins to the nuclear periphery at the end of mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 112:2253–2264 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous