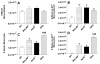Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 prevents early atherosclerosis by limiting lesional apoptosis and inflammatory Ly-6Chigh monocytosis: evidence that the effects are not apolipoprotein E dependent - PubMed (original) (raw)
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 prevents early atherosclerosis by limiting lesional apoptosis and inflammatory Ly-6Chigh monocytosis: evidence that the effects are not apolipoprotein E dependent
Patricia G Yancey et al. Circulation. 2011.
Abstract
Background: We previously demonstrated that macrophage low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR)-related protein 1 (LRP1) deficiency increases atherosclerosis despite antiatherogenic changes including decreased uptake of remnants and increased secretion of apolipoprotein E (apoE). Thus, our objective was to determine whether the atheroprotective effects of LRP1 require interaction with apoE, one of its ligands with multiple beneficial effects.
Methods and results: We examined atherosclerosis development in mice with specific deletion of macrophage LRP1 (apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-)) and in LDLR(-/-) mice reconstituted with apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) bone marrow. The combined absence of apoE and LRP1 promoted atherogenesis more than did macrophage apoE deletion alone in both apoE-producing LDLR(-/-) mice (+88%) and apoE(-/-) mice (+163%). The lesions of both mouse models with apoE(-/-) LRP1(-/-) macrophages had increased macrophage content. In vitro, apoE and LRP1 additively inhibit macrophage apoptosis. Furthermore, there was excessive accumulation of apoptotic cells in lesions of both LDLR(-/-) mice (+110%) and apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) mice (+252%). The apoptotic cell accumulation was partially due to decreased efferocytosis as the ratio of free to cell-associated apoptotic nuclei was 3.5-fold higher in lesions of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice. Lesion necrosis was also increased (6 fold) in apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice. Compared with apoE(-/-) mice, the spleens of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) mice contained 1.6- and 2.4-fold more total and Ly6-C(high) monocytes. Finally, there were 3.6- and 2.4-fold increases in Ly6-C(high) and CC-chemokine receptor 2-positive cells in lesions of apoE(-/-) MΦLRP1(-/-) versus apoE(-/-) mice, suggesting that accumulation of apoptotic cells enhances lesion development and macrophage content by promoting the recruitment of inflammatory monocytes.
Conclusion: Low-density lipoprotein receptor protein 1 exerts antiatherogenic effects via pathways independent of apoE involving macrophage apoptosis and monocyte recruitment.
Figures
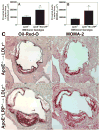
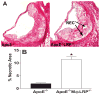
Figure 1. Atherosclerosis in LDLR−/− mice transplanted with BM from apoE−/− or apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice
Quantitation of the mean Oil-red-O (A) and MOMA-2 (B) stained cross-sectional area of proximal aortas from LDLR−/− mice transplanted with either apoE−/− (n=10) or apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− (n=10) BM. *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. C. Representative images show Oil-red-O and MOMA-2 stain in aortic root sections.
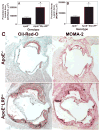
Figure 2. Atherosclerosis in apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice
Quantitation of the mean Oil-red-O (A) and MOMA-2 (B) stained cross-sectional area of proximal aortas from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice (n=12 per group). *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. C. Images show Oil-redO and MOMA-2 stain in aortic root sections.
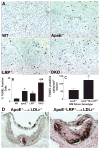
Figure 3. In vitro macrophage apoptosis and atherosclerotic lesion apoptosis
A and B. Images show TUNEL positive (red) and negatively stained macrophages after 16h with DMEM (A). Quantitation of the percent TUNEL positive cells in WT, apoE−/−, LRP−/−, and apoE−/−LRP−/−cultures (n=6 per group). (B). *, #, and & denotes statistically significances compared to WT, apoE−/−, and LRP−/− cells, respectively, p<0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post test. C. Quantitation of apoptotic cells in proximal aorta sections from apoE−/− (n=6) or apoE−/−MΦLRP−/−(n=7) BM recipient LDLr−/− mice. *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. D. Images show TUNEL staining (dark red) of nuclei in aortic root sections.
Figure 4. Macrophage apoptosis and efferocytosis in lesions of apoE−/− and apoE−/− MΦLRP−/− mice
A Micrographs show nuclei (Hoechst, blue), nuclei + TUNEL positive staining (red), and merged images of macrophage cytoplasm (green), nuclei, and TUNEL in aortic root sections from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice. Quantitation of the number of apoptotic cells (B) and of the ratio of free versus macrophage associated TUNEL positive cells (C) in proximal aorta sections of lesions from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice (n=6 per group). *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test.
Figure 5. Necrosis in lesions of apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice
A Images show hematoxylin and eosin staining of aortic root sections from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice. NEC denotes necrotic area. B. Quantitation of the percent necrotic area in the aortic lesions from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice (n=6 per group). *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test.
Figure 6. Total and Ly-6Chigh monocytes in blood and spleens of WT, MΦLRP−/−, apoE−/−, and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice
A-D WT (n=10), MΦLRP−/− (n=8), apoE−/− (n=10), and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− (n=10) mice were fed a western type diet for 8 weeks and then blood (A-B) and spleen (C-D) total (A,C) and Ly-6Chigh monocytes (B,D) were measured by flow cytometry analysis. A-D. *, #, and & denotes statistically significances compared to WT, apoE−/−, and MΦLRP−/− mice, respectively, p<0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post test.
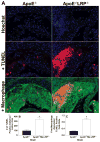
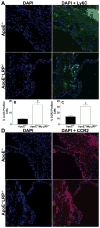
Figure 7. Ly-6C and CCR2 positive cells in lesions of apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice
A and D Representative images show nuclei (blue, Dapi) and merged images of Ly-6C (A, green) and CCR positive staining (D, red) and nuclei. B and C. Quantitation of the percent Ly-6C (B) and CCR2 (C) positive cells in aortic root sections from apoE−/− and apoE−/−MΦLRP−/− mice (n=6 per group). *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test.
Similar articles
- The Dual Role of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 in Atherosclerosis.
Chen J, Su Y, Pi S, Hu B, Mao L. Chen J, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 28;8:682389. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.682389. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34124208 Free PMC article. Review. - Loss of Macrophage Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 Confers Resistance to the Antiatherogenic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibition.
Zhu L, Giunzioni I, Tavori H, Covarrubias R, Ding L, Zhang Y, Ormseth M, Major AS, Stafford JM, Linton MF, Fazio S. Zhu L, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Aug;36(8):1483-95. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307736. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27365402 Free PMC article. - Deletion of Macrophage Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) Accelerates Atherosclerosis Regression and Increases C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 (CCR7) Expression in Plaque Macrophages.
Mueller PA, Zhu L, Tavori H, Huynh K, Giunzioni I, Stafford JM, Linton MF, Fazio S. Mueller PA, et al. Circulation. 2018 Oct 23;138(17):1850-1863. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031702. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29794082 Free PMC article. - Interleukin-3/granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promotes stem cell expansion, monocytosis, and atheroma macrophage burden in mice with hematopoietic ApoE deficiency.
Wang M, Subramanian M, Abramowicz S, Murphy AJ, Gonen A, Witztum J, Welch C, Tabas I, Westerterp M, Tall AR. Wang M, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 May;34(5):976-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303097. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24651678 Free PMC article. - Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1: role in the regulation of vascular integrity.
Strickland DK, Au DT, Cunfer P, Muratoglu SC. Strickland DK, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Mar;34(3):487-98. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301924. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24504736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Macrophage LRP1 (Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1) Is Required for the Effect of CD47 Blockade on Efferocytosis and Atherogenesis-Brief Report.
Mueller PA, Kojima Y, Huynh KT, Maldonado RA, Ye J, Tavori H, Pamir N, Leeper NJ, Fazio S. Mueller PA, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022 Jan;42(1):e1-e9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316854. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022. PMID: 34758632 Free PMC article. - Reduced size and macrophage content of advanced atherosclerotic lesions in mice with bone marrow specific deficiency of alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
Lee RH, Vazquez G. Lee RH, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 31;10(3):e0124584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124584. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25826262 Free PMC article. - The Dual Role of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 in Atherosclerosis.
Chen J, Su Y, Pi S, Hu B, Mao L. Chen J, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 28;8:682389. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.682389. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34124208 Free PMC article. Review. - Overexpression of microRNA-155 enhances the efficacy of dendritic cell vaccine against breast cancer.
Hodge J, Wang F, Wang J, Liu Q, Saaoud F, Wang Y, Singh UP, Chen H, Luo M, Ai W, Fan D. Hodge J, et al. Oncoimmunology. 2020 Feb 9;9(1):1724761. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1724761. eCollection 2020. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32117588 Free PMC article. - Immunization with the Gly1127-Cys1140 amino acid sequence of the LRP1 receptor reduces atherosclerosis in rabbits. Molecular, immunohistochemical and nuclear imaging studies.
Bornachea O, Benitez-Amaro A, Vea A, Nasarre L, de Gonzalo-Calvo D, Escola-Gil JC, Cedo L, Iborra A, Martínez-Martínez L, Juarez C, Camara JA, Espinet C, Borrell-Pages M, Badimon L, Castell J, Llorente-Cortés V. Bornachea O, et al. Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(7):3263-3280. doi: 10.7150/thno.37305. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194867 Free PMC article.
References
- Linton MF, Atkinson JB, Fazio S. Prevention of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by bone marrow transplantation. Science. 1995;267:1034–1037. - PubMed
- Fazio S, Babaev V, Burleigh M, Major A, Hasty A, Linton M. Physiologic expression of macrophage apoE in the artery wall reduces atherosclerosis in severely hyperlipidemic mice. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1602–1609. - PubMed
- Overton CD, Yancey PG, Major AS, Linton MF, Fazio S. Deletion of Macrophage LDL Receptor-Related Protein Increases Atherogenesis in the Mouse. Circ Res. 2007;100:670–677. - PubMed
- Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988;240:622–630. - PubMed
- Williams DL, Dawson PA, Newman TC, Rudel LL. Apolipoprotein E synthesis in peripheral tissues of nonhuman primates. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:2444–2451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL057986-11A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057986-11A1W1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086988/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086988/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057986/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086988-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL57986/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous