Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics
Jean-Claude Martinou et al. Dev Cell. 2011.
Abstract
Mitochondria participate in apoptosis through a range of mechanisms that vary between vertebrates and invertebrates. In vertebrates, they release intermembrane space proteins, such as cytochrome c, to promote caspase activation in the cytosol. This process is the result of the loss of integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane caused by proapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family. This event is always accompanied by a fissioning of the organelle. Fission of mitochondria has also been reported to participate in apoptosis in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans. However, in these organisms, mitochondrial membrane permeabilization does not occur and the mechanism by which mitochondrial dynamics participates in cell death remains elusive.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
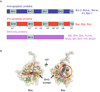
Figure 1. Structure of Bcl-2 family proteins
A) The Bcl-2 family is divided into three groups based on their Bcl-2 Homology domains (BH). Pro- and antiapoptotic proteins contain 4 BH domains, while BH3-only proteins, as their name indicates, contain only the BH3 domain. B) Structure of Bax showing the alpha-helix 9 (transmembrane domain) embedded in the hydrophobic groove (left structure). A 180° rotation (structure on the right) shows the alpha-helices 1 and 6. The red circle represents the binding site for the Bim BH3 domain.
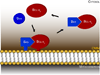
Figure 2. Bax moves back and forth from the cytosol to the mitochondrial outer membrane
In healthy cells, Bax (blue) and Bclx-L (red) are translocated from the cytosol to the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) where they attach loosely. The triangle in Bax represents its BH3 domain, which needs to be exposed in order for Bcl-xL-mediated retrotranslocation to occur. OMM: outer mitochondrial membrane.
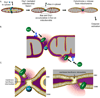
Figure 3. Model for Bax activation and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization: the role of membrane hemifission and hemifusion intermediates
A) During apoptosis, Drp1 and Bax are recruited to mitochondrial foci. As a result MOMP occurs concomitantly with mitochondrial fission. The release of cytochrome c promotes caspase activation in the cytosol. A magnification of what occurs at the level of mitochondrial fission sites is shown in (B). According to the ‘embeded together model’, tBid first inserts in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) to expose its BH3 domain. Upon interaction with the Bid BH3 domain, Bax is in turn recruited to the OMM where it inserts and oligomerizes. This process does not occur randomly at the OMM surface. Bax mainly oligomerizes at mitochondrial fission sites and at contact sites between the OMM and the IMM. C) (Left) A detailed structure of the hemifission intermediate that forms before fission of the organelle. The membrane forms a non bilayer structure that represents a privileged site for the formation of a membrane hole. Upon its oligomerization in the OMM, Bax forms a lipidic pore or triggers the formation of a hole at the edge of the hemifission intermediate. (Right) A detailed structure of the membrane at OMM and inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) contact sites. The model postulates that Bax forms a pore in the membrane at the edges of membrane hemifusion intermediates that may form between the OMM and the IMM.
Similar articles
- Intersection of mitochondrial fission and fusion machinery with apoptotic pathways: Role of Mcl-1.
Morciano G, Pedriali G, Sbano L, Iannitti T, Giorgi C, Pinton P. Morciano G, et al. Biol Cell. 2016 Oct;108(10):279-293. doi: 10.1111/boc.201600019. Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27234233 Review. - The role of mitochondria in apoptosis*.
Wang C, Youle RJ. Wang C, et al. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:95-118. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134850. Annu Rev Genet. 2009. PMID: 19659442 Free PMC article. Review. - Apoptosis: bombarding the mitochondria.
Parone P, Priault M, James D, Nothwehr SF, Martinou JC. Parone P, et al. Essays Biochem. 2003;39:41-51. doi: 10.1042/bse0390041. Essays Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14585073 Review. - Bax- or Bak-induced mitochondrial fission can be uncoupled from cytochrome C release.
Sheridan C, Delivani P, Cullen SP, Martin SJ. Sheridan C, et al. Mol Cell. 2008 Aug 22;31(4):570-585. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.002. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18722181 - Where killers meet--permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane during apoptosis.
Bender T, Martinou JC. Bender T, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Jan 1;5(1):a011106. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011106. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23284044 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates mitochondrial intermembrane space proteins.
Bragoszewski P, Gornicka A, Sztolsztener ME, Chacinska A. Bragoszewski P, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2136-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01579-12. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23508107 Free PMC article. - Regulation of retinal endothelial cell apoptosis through activation of the IGFBP-3 receptor.
Zhang Q, Soderland C, Steinle JJ. Zhang Q, et al. Apoptosis. 2013 Mar;18(3):361-8. doi: 10.1007/s10495-012-0793-3. Apoptosis. 2013. PMID: 23291901 Free PMC article. - Modeling pathogenic mutations of human twinkle in Drosophila suggests an apoptosis role in response to mitochondrial defects.
Sanchez-Martinez A, Calleja M, Peralta S, Matsushima Y, Hernandez-Sierra R, Whitworth AJ, Kaguni LS, Garesse R. Sanchez-Martinez A, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043954. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952820 Free PMC article. - Enhanced antitumor effects of BPD-MA-mediated photodynamic therapy combined with adriamycin on breast cancer in mice.
Tong ZS, Miao PT, Liu TT, Jia YS, Liu XD. Tong ZS, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Oct;33(10):1319-24. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.45. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22842729 Free PMC article. - Mechanism of transcription initiation by the yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase.
Deshpande AP, Patel SS. Deshpande AP, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep-Oct;1819(9-10):930-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22353467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Abdelwahid E, Yokokura T, Krieser RJ, Balasundaram S, Fowle WH, White K. Mitochondrial disruption in Drosophila apoptosis. Dev Cell. 2007;12:793–806. - PubMed
- Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod JJ, Mazzei G, et al. Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science. 1997;277:370–372. - PubMed
- Ardail D, Privat JP, Egret-Charlier M, Levrat C, Lerme F, Louisot P. Mitochondrial contact sites. Lipid composition and dynamics. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:18797–18802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases