Personalized genomic medicine: lessons from the exome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
. 2011 Sep-Oct;104(1-2):189-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.06.022. Epub 2011 Jul 5.
Daniel E Pineda-Alvarez, Donald W Hadley, NISC Comparative Sequencing Program, Jamie K Teer, Praveen F Cherukuri, Nancy F Hansen, Pedro Cruz, Alice C Young, Robert W Blakesley, Brendan Lanpher, Stephanie Mayfield Gibson, Murat Sincan, Settara C Chandrasekharappa, James C Mullikin
Affiliations
- PMID: 21767969
- PMCID: PMC3171610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.06.022
Case Reports
Personalized genomic medicine: lessons from the exome
Benjamin D Solomon et al. Mol Genet Metab. 2011 Sep-Oct.
Abstract
While genomic sequencing methods are powerful tools in the discovery of the genetic underpinnings of human disease, incidentally-revealed novel genomic risk factors may be equally important, both scientifically, and as relates to direct patient care. We performed whole-exome sequencing on a child with VACTERL association who suffered severe post-surgical neonatal pulmonary hypertension, and identified a potential novel genetic risk factor for this complication: a heterozygous mutation in CPSI. Newborn screening results from this patient's monozygotic twin provided evidence that this mutation, in combination with an environmental trigger (in this case, surgery), may have resulted in pulmonary artery hypertension due to inadequate nitric oxide production. Identification of this genetic risk factor allows for targeted medical preventative measures in this patient as well as relatives with the same mutation, and illustrates the power of incidental medical information unearthed by whole-exome sequencing.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
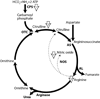
Fig.
Hypothesized explanation for pulmonary artery hypertension in the patient described here[–12, 14]. A loss-of-function mutation in the CPSI gene (1) leads to impaired production of citrulline (2) and arginine (3). The lack of availability of these precursors leads to decreased availability of nitric oxide (4), resulting in decreased pulmonary artery vasodilation, which becomes especially severe in concert with iatrogenic depletion of arginine and citrulline.
Similar articles
- Incidental medical information in whole-exome sequencing.
Solomon BD, Hadley DW, Pineda-Alvarez DE; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Kamat A, Teer JK, Cherukuri PF, Hansen NF, Cruz P, Young AC, Berkman BE, Chandrasekharappa SC, Mullikin JC. Solomon BD, et al. Pediatrics. 2012 Jun;129(6):e1605-11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-0080. Epub 2012 May 14. Pediatrics. 2012. PMID: 22585771 Free PMC article. - Incidentalome from Genomic Sequencing: A Barrier to Personalized Medicine?
Jamuar SS, Kuan JL, Brett M, Tiang Z, Tan WL, Lim JY, Liew WK, Javed A, Liew WK, Law HY, Tan ES, Lai A, Ng I, Teo YY, Venkatesh B, Reversade B, Tan EC, Foo R. Jamuar SS, et al. EBioMedicine. 2016 Feb 4;5:211-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.01.030. eCollection 2016 Mar. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27077130 Free PMC article. - Genomic and clinical profiling of a national nephrotic syndrome cohort advocates a precision medicine approach to disease management.
Bierzynska A, McCarthy HJ, Soderquest K, Sen ES, Colby E, Ding WY, Nabhan MM, Kerecuk L, Hegde S, Hughes D, Marks S, Feather S, Jones C, Webb NJ, Ognjanovic M, Christian M, Gilbert RD, Sinha MD, Lord GM, Simpson M, Koziell AB, Welsh GI, Saleem MA. Bierzynska A, et al. Kidney Int. 2017 Apr;91(4):937-947. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.10.013. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28117080 - Controversy and debate on clinical genomics sequencing-paper 1: genomics is not exceptional: rigorous evaluations are necessary for clinical applications of genomic sequencing.
Wilson BJ, Miller FA, Rousseau F. Wilson BJ, et al. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017 Dec;92:4-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.08.018. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28870871 Review. - An update on genomic-guided therapies for pediatric solid tumors.
Tsui PC, Lee YF, Liu ZWY, Ip LRH, Piao W, Chiang AKS, Lui VWY. Tsui PC, et al. Future Oncol. 2017 Jun;13(15):1345-1358. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0003. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28589766 Review.
Cited by
- VATER/VACTERL association: identification of seven new twin pairs, a systematic review of the literature, and a classical twin analysis.
Bartels E, Schulz AC, Mora NW, Pineda-Alvarez DE, Wijers CHW, Marcelis CM, Stressig R, Ritgen J, Schmiedeke E, Mattheisen M, Draaken M, Hoffmann P, Hilger AC, Dworschak GC, Baudisch F, Ludwig M, Bagci S, Müller A, Gembruch U, Geipel A, Berg C, Bartmann P, Nöthen MM, van Rooij IALM, Solomon BD, Reutter HM. Bartels E, et al. Clin Dysmorphol. 2012 Oct;21(4):191-195. doi: 10.1097/MCD.0b013e328358243c. Clin Dysmorphol. 2012. PMID: 22895008 Free PMC article. Review. - Exome Sequencing and High-Density Microarray Testing in Monozygotic Twin Pairs Discordant for Features of VACTERL Association.
Solomon BD, Pineda-Alvarez DE, Hadley DW, Hansen NF, Kamat A, Donovan FX, Chandrasekharappa SC, Hong SK, Roessler E, Mullikin JC; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. Solomon BD, et al. Mol Syndromol. 2013 Feb;4(1-2):27-31. doi: 10.1159/000345406. Mol Syndromol. 2013. PMID: 23653574 Free PMC article. - A genetic counselor's guide to using next-generation sequencing in clinical practice.
Facio FM, Lee K, O'Daniel JM. Facio FM, et al. J Genet Couns. 2014 Aug;23(4):455-62. doi: 10.1007/s10897-013-9662-7. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Genet Couns. 2014. PMID: 24151055 - Familial occurrence of the VATER/VACTERL association.
Hilger A, Schramm C, Draaken M, Mughal SS, Dworschak G, Bartels E, Hoffmann P, Nöthen MM, Reutter H, Ludwig M. Hilger A, et al. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012 Jul;28(7):725-9. doi: 10.1007/s00383-012-3073-y. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012. PMID: 22422375 Review. - A View on Genomic Medicine Activities in Africa: Implications for Policy.
Jongeneel CV, Kotze MJ, Bhaw-Luximon A, Fadlelmola FM, Fakim YJ, Hamdi Y, Kassim SK, Kumuthini J, Nembaware V, Radouani F, Tiffin N, Mulder N. Jongeneel CV, et al. Front Genet. 2022 Apr 27;13:769919. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.769919. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35571023 Free PMC article.
References
- Quan L, Smith DW. The VATER association. Vertebral defects, Anal atresia, T-E fistula with esophageal atresia, Radial and Renal dysplasia: a spectrum of associated defects. J. Pediatr. 1973;82:104–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases