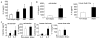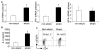Predisposition to the development of IL-9-secreting T cells in atopic infants - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Predisposition to the development of IL-9-secreting T cells in atopic infants
Weiguo Yao et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Dec.
No abstract available
Figures
Fig. 1
IL-9 concentration in anti-CD3- or allergen-stimulated PBMC from atopic and non-atopic patients. A. PBMCs were stimulated with anti-CD3 for 72 hours before supernatants were assayed for IL-9 concentration using ELISA. Samples were divided into non-atopic patients (n=34), or patients that had allergen-specific IgE for egg (n=20), cat (n=29) or house dust mite (n=28). B–C, IL-9 (B) or Th2 cytokine (C) concentration was determined in supernatants of PBMC stimulated for seven days of culture with cat dander extract- or house dust mite extract (10 μg/ml) using cells isolated from atopic (n=5–10, black bars) or non-atopic (n=10–11, white bars) patients. *:p<0.05 by Student’s t test.
Fig. 2
In vitro Th9 differentiation of naïve (CD4+ CD45RA+) T cells from atopic and non-atopic patients. A. IL9, PU.1 (SPI1), and IRF4 gene expression in Th9 cells derived from naïve CD4+ T cells isolated from non-atopic (n=11) and atopic patients (n=10) and cultured for five days with TGFβ and IL-4. B. IL-9 production from Th9 cells derived as in (A). C. The percentage of pSTAT6-positive cells was assessed at day 4 of differentiation under Th9 conditions in cultures from atopic and non-atopic patients (n=6). *:p<0.05 by Student’s t test.
Comment on
- Expired nitric oxide and airway reactivity in infants at risk for asthma.
Tepper RS, Llapur CJ, Jones MH, Tiller C, Coates C, Kimmel R, Kisling J, Katz B, Ding Y, Swigonski N. Tepper RS, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;122(4):760-765. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.022. Epub 2008 Aug 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18760452 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of airway reactivity and immune characteristics as risk factors for wheezing early in life.
Yao W, Barbé-Tuana FM, Llapur CJ, Jones MH, Tiller C, Kimmel R, Kisling J, Nguyen ET, Nguyen J, Yu Z, Kaplan MH, Tepper RS. Yao W, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Sep;126(3):483-8.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.028. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20816184 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Food allergen sensitization as a determinant of disturbed airway function in young infants: first step on the path to persistent asthma?
Teague WG. Teague WG. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;122(4):766-767. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.030. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19014768 No abstract available. - Expired nitric oxide and airway reactivity in infants at risk for asthma.
Tepper RS, Llapur CJ, Jones MH, Tiller C, Coates C, Kimmel R, Kisling J, Katz B, Ding Y, Swigonski N. Tepper RS, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Oct;122(4):760-765. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.022. Epub 2008 Aug 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18760452 Free PMC article. - Exhaled nitric oxide and respiratory symptoms in a community sample of school aged children.
Kovesi T, Dales R. Kovesi T, et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2008 Dec;43(12):1198-205. doi: 10.1002/ppul.20927. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2008. PMID: 19003883 - The atopic march: what's the evidence?
Ker J, Hartert TV. Ker J, et al. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009 Oct;103(4):282-9. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60526-1. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19852191 Free PMC article. Review. - Markers of airway inflammation in preschool wheezers.
Carlsen KH. Carlsen KH. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 1997 Oct;52(5):455-60. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 1997. PMID: 9510666 Review.
Cited by
- Microbiota, Oxidative Stress, and Skin Cancer: An Unexpected Triangle.
Azzimonti B, Ballacchino C, Zanetta P, Cucci MA, Monge C, Grattarola M, Dianzani C, Barrera G, Pizzimenti S. Azzimonti B, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;12(3):546. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030546. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978794 Free PMC article. Review. - ERG Functionally Overlaps with Other Ets Proteins in Promoting TH9 Cell Expression of Il9 during Allergic Lung Inflammation.
Kharwadkar R, Ulrich BJ, Chu M, Koh B, Hufford MM, Fu Y, Birdsey GM, Porse BT, Randi AM, Kaplan MH. Kharwadkar R, et al. J Immunol. 2023 Mar 1;210(5):537-546. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200113. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36637217 Free PMC article. - Differences in Inflammatory Cytokine Profile in Obesity-Associated Asthma: Effects of Weight Loss.
Bantulà M, Tubita V, Roca-Ferrer J, Mullol J, Valero A, Bobolea I, Pascal M, de Hollanda A, Vidal J, Picado C, Arismendi E. Bantulà M, et al. J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 29;11(13):3782. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133782. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35807067 Free PMC article. - Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiome in Inflammatory Skin Diseases.
Ni Q, Zhang P, Li Q, Han Z. Ni Q, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 7;10:849985. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.849985. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35321240 Free PMC article. Review. - Predictive biomarker modeling of pediatric atopic dermatitis severity based on longitudinal serum collection.
Engle SM, Chang CY, Ulrich BJ, Satterwhite A, Hayes T, Robling K, Sissons SE, Schmitz J, Tepper RS, Kaplan MH, Sims JT. Engle SM, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Nov 30;207(3):253-62. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxab009. Online ahead of print. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35020861 Free PMC article.
References
- Devos S, Cormont F, Vrtala S, Hooghe-Peters E, Pirson F, Snick J. Allergen-induced interleukin-9 production in vitro: correlation with atopy in human adults and comparison with interleukin-5 and interleukin-13. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006;36:174–82. - PubMed
- Erpenbeck VJ, Hohlfeld JM, Discher M, Krentel H, Hagenberg A, Braun A, et al. Increased expression of interleukin-9 messenger RNA after segmental allergen challenge in allergic asthmatics. Chest. 2003;123:370S. - PubMed
- Jenmalm MC, Van Snick J, Cormont F, Salman B. Allergen-induced Th1 and Th2 cytokine secretion in relation to specific allergen sensitization and atopic symptoms in children. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31:1528–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI057459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070448/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070448-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI070448/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL080071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057459-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070448-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080071-05/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States