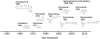Current concepts in antifungal pharmacology - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Current concepts in antifungal pharmacology
Russell E Lewis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011 Aug.
Abstract
The introduction of new antifungal agents (eg, echinocandins, second-generation triazoles) in the past decade has transformed the management of invasive mycoses to the point that drug toxicity is no longer the major limiting factor in treatment. Yet, many of these newer antifungal agents have important limitations in their spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetics, and unique predisposition for pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions and unusual toxicities associated with long-term use. This article reviews key pharmacological aspects of systemic antifungal agents as well as evolving strategies, such as pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic optimization and therapeutic drug monitoring, to improve the safety and efficacy of systemic antifungal therapy.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
Timeline of systemic antifungal drugs.
FIGURE 2.
Sites of action and mechanisms of systemic antifungal agents. FKS1, FKS2 catalytic subunits of the glucan synthase complex are the putative target binding site of echinocandins. Rho is a cell wall–regulating protein. *Isavuconazole is still in phase 3 trials.
FIGURE 3.
Spectrum of action of systemic antifungal agents. Solid blocks represent species in which the antifungal agent has demonstrated microbiological and clinical efficacy. Blocks with dotted lines indicate fungal genera/species in which resistance is common. AMB = amphotericin; ANID = anidulafungin; CAS = caspofungin; 5-FC = flucytosine; FLU = fluconazole; ITRA = itraconazole; MICA = micafungin; POSA = posaconazole; VORI = voriconazole.
FIGURE 4.
Common toxicities of antifungal agents. CNS = central nervous system; 5-FC = flucytosine; GI = gastrointestinal; IV = intravenous; QTc = corrected QT interval.
Similar articles
- Pharmacology and clinical use of voriconazole.
Thompson GR 3rd, Lewis JS 2nd. Thompson GR 3rd, et al. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010 Jan;6(1):83-94. doi: 10.1517/17425250903463878. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 19947892 Review. - Posaconazole: a new broad-spectrum antifungal agent.
Kwon DS, Mylonakis E. Kwon DS, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007 Jun;8(8):1167-78. doi: 10.1517/14656566.8.8.1167. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17516880 Review. - Caspofungin: pharmacology, safety and therapeutic potential in superficial and invasive fungal infections.
Groll AH, Walsh TJ. Groll AH, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 Aug;10(8):1545-58. doi: 10.1517/13543784.10.8.1545. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11772269 Review. - [New systemic antifungal drugs: mechanisms of action, drug interactions and side effects].
Schäfer-Korting M. Schäfer-Korting M. Mycoses. 2003;46 Suppl 1:28-31. Mycoses. 2003. PMID: 12955850 Review. German. - Update on antifungal agents for paediatric patients.
Groll AH, Tragiannidis A. Groll AH, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Sep;16(9):1343-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03334.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20678177 Review.
Cited by
- Preliminary Characterization of NP339, a Novel Polyarginine Peptide with Broad Antifungal Activity.
Duncan V, Smith D, Simpson L, Lovie E, Katvars L, Berge L, Robertson J, Smith S, Munro C, Mercer D, O'Neil D. Duncan V, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Jul 16;65(8):e0234520. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02345-20. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34031048 Free PMC article. - The Therapy of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Paracoccidioidomycosis: What Are the New Experimental Approaches?
González Á. González Á. J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Oct 11;6(4):217. doi: 10.3390/jof6040217. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050568 Free PMC article. Review. - Application of Probiotic Yeasts on Candida Species Associated Infection.
Kunyeit L, K A AA, Rao RP. Kunyeit L, et al. J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;6(4):189. doi: 10.3390/jof6040189. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992993 Free PMC article. Review. - Osteoarticular Mycoses.
Gamaletsou MN, Rammaert B, Brause B, Bueno MA, Dadwal SS, Henry MW, Katragkou A, Kontoyiannis DP, McCarthy MW, Miller AO, Moriyama B, Pana ZD, Petraitiene R, Petraitis V, Roilides E, Sarkis JP, Simitsopoulou M, Sipsas NV, Taj-Aldeen SJ, Zeller V, Lortholary O, Walsh TJ; International Consortium for Osteoarticular Mycoses. Gamaletsou MN, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022 Dec 21;35(4):e0008619. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00086-19. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36448782 Free PMC article. Review. - Antifungal susceptibility patterns of opportunistic fungi in the genera Verruconis and Ochroconis.
Seyedmousavi S, Samerpitak K, Rijs AJ, Melchers WJ, Mouton JW, Verweij PE, de Hoog GS. Seyedmousavi S, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jun;58(6):3285-92. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00002-14. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24687495 Free PMC article.
References
- Dutcher JD. The discovery and development of amphotericin B. Dis Chest. 1968;54(suppl 1):296-298 - PubMed
- Rex JH, Bennett JE, Sugar AM, et al. ; Candidemia Study Group; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group A randomized trial comparing fluconazole with amphotericin B for the treatment of candidemia in patients without neutropenia. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(20):1325-1330 - PubMed
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE. Antifungal drug resistance of pathogenic fungi. Lancet. 2002;359(9312):1135-1144 - PubMed
- Smith D, van de Velde V, Woestenborghs R, et al. The pharmacokinetics of oral itraconazole in AIDS patients. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1992;44(7): 618-619 - PubMed
- Marr KA, Crippa F, Leisenring W, et al. Itraconazole versus fluconazole for prevention of fungal infections in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplants. Blood. 2004;103(4):1527-1533 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous