Phase II trial of modified FOLFOX6 and erlotinib in patients with metastatic or advanced adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus and gastro-oesophageal junction - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2011 Sep 6;105(6):760-5.
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.280. Epub 2011 Aug 2.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21811258
- PMCID: PMC3171005
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.280
Clinical Trial
Phase II trial of modified FOLFOX6 and erlotinib in patients with metastatic or advanced adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus and gastro-oesophageal junction
Z A Wainberg et al. Br J Cancer. 2011.
Abstract
Background: There is increased recognition that cancers of the upper GI tract comprise distinct epidemiological and molecular entities. Erlotinib has shown activity in patients with adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus/gastro-oesophageal junction (GEJ), but not in distal gastric cancer. mFOLFOX6 is one of several active regimens used to treat adenocarcinoma of the Eso/GEJ. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of mFOLFOX6 and erlotinib in patients with metastatic or advanced Eso/GEJ cancers.
Methods: Patients with previously untreated advanced or metastatic Eso/GEJ adenocarcinoma are treated with oxaliplatin 85 mg m(-2), 5-FU 400 mg m(-2), LV 400 mg m(-2) on day 1, 5-FU 2400 mg m(-2) over 48 h and erlotinib 150 mg PO daily. Treatment was repeated every 14 days. The primary objective was response rate (RR), secondary objectives include toxicity, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and to correlate clinical outcome with expression patterns and molecular alterations in the epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent pathways.
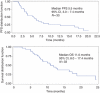
Results: A total of 33 patients were treated and evaluable: there were two complete responses, 15 partial responses for an objective RR of 51.5% (95% CI, 34.5-68.6%). Median PFS was 5.5 months (95% CI, 3.1-7.5 months) and median OS was 11.0 months (95% CI, 8.0-17.4 months). The most common grade 3-4 toxicities were: diarrhoea (24%), nausea/vomiting (11%), skin rash (8%) and peripheral neuropathy (8%). The frequency of alterations was KRAS mutations (8%), EGFR mutations (0%) and HER2 amplification (19%).
Conclusion: In patients with Eso/GEJ adenocarcinoma, mFOLFOX6 and erlotinib is active, has an acceptable toxicity profile and FOLFOX ± erlotinib could be considered for further development.
Figures
Figure 1
Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) (Kaplan–Meier estimates).
Similar articles
- TFOX versus FOLFOX in first-line treatment of patients with advanced HER2-negative gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (PRODIGE 51- FFCD-GASTFOX): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial.
Zaanan A, Bouché O, de la Fouchardière C, Le Malicot K, Pernot S, Louvet C, Artru P, Le Brun Ly V, Aldabbagh K, Khemissa-Akouz F, Lecomte T, Castanie H, Laly M, Botsen D, Roth G, Samalin E, Muller M, Breysacher G, Manfredi S, Phelip JM, Taieb J. Zaanan A, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2025 Jun;26(6):732-744. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(25)00130-5. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Lancet Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40286809 Clinical Trial. - A phase II study of FOLFOX combined with nab-paclitaxel in the treatment of metastatic or advanced unresectable gastric, gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: a Big Ten Cancer Research Consortium trial.
Dreyer MS, Mulcahy M, Kocherginsky M, Chen Y, Hochster HS, Kasi PM, Kircher S, Lou E, Ma Y, Uboha NV, Benson AB 3rd. Dreyer MS, et al. Oncologist. 2024 Dec 6;29(12):1044-1050. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae236. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 39293067 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab in combination with oxaliplatin and fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for patients with HER2-positive metastatic gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma patients: a retrospective study.
Soularue É, Cohen R, Tournigand C, Zaanan A, Louvet C, Bachet JB, Hentic O, Samalin E, Chibaudel B, de Gramont A, André T; for GERCOR. Soularue É, et al. Bull Cancer. 2015 Apr;102(4):324-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2014.08.001. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Bull Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25744576 - A Phase II Study of the c-Met Inhibitor Tivantinib in Combination with FOLFOX for the Treatment of Patients with Previously Untreated Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Distal Esophagus, Gastroesophageal Junction, or Stomach.
Pant S, Patel M, Kurkjian C, Hemphill B, Flores M, Thompson D, Bendell J. Pant S, et al. Cancer Invest. 2017 Aug 9;35(7):463-472. doi: 10.1080/07357907.2017.1337782. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Cancer Invest. 2017. PMID: 28662341 Clinical Trial. - Total neoadjuvant therapy in oesophageal and gastro-oesophageal junctional adenocarcinoma.
Clements HA, Underwood TJ, Petty RD. Clements HA, et al. Br J Cancer. 2024 Jan;130(1):9-18. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02458-w. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37898721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Small-molecule inhibitors of the receptor tyrosine kinases: promising tools for targeted cancer therapies.
Hojjat-Farsangi M. Hojjat-Farsangi M. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Aug 8;15(8):13768-801. doi: 10.3390/ijms150813768. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25110867 Free PMC article. Review. - Gastric cancer and trastuzumab: first biologic therapy in gastric cancer.
Gunturu KS, Woo Y, Beaubier N, Remotti HE, Saif MW. Gunturu KS, et al. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2013 Mar;5(2):143-51. doi: 10.1177/1758834012469429. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23450234 Free PMC article. - Exploring the chemotherapeutic potential of currently used kinase inhibitors: An update.
Naik RR, Shakya AK. Naik RR, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1064472. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1064472. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36699049 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex difference in EGFR pathways in mouse kidney-potential impact on the immune system.
Liu F, Jiao Y, Jiao Y, Garcia-Godoy F, Gu W, Liu Q. Liu F, et al. BMC Genet. 2016 Nov 24;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12863-016-0449-3. BMC Genet. 2016. PMID: 27881077 Free PMC article. - Recent Trends and Advancements in the Diagnosis and Management of Gastric Cancer.
Haque E, Esmail A, Muhsen I, Salah H, Abdelrahim M. Haque E, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;14(22):5615. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225615. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, Rethwisch V, Seipelt G, Homann N, Wilhelm G, Schuch G, Stoehlmacher J, Derigs HG, Hegewisch-Becker S, Grossmann J, Pauligk C, Atmaca A, Bokemeyer C, Knuth A, Jager E (2008) Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol 26(9): 1435–1442 - PubMed
- Alimandi M, Romano A, Curia MC, Muraro R, Fedi P, Aaronson SA, Di Fiore PP, Kraus MH (1995) Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene 10(9): 1813–1821 - PubMed
- Altiok S, Mezzadra H, Jagannath S, Tsottles N, Rudek MA, Abdallah N, Berman D, Forastiere A, Gibson MK (2010) A novel pharmacodynamic approach to assess and predict tumor response to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib in patients with esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol 36(1): 19–27 - PMC - PubMed
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD (2008) Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(10): 1626–1634 - PubMed
- Arber N, Shapira I, Ratan J, Stern B, Hibshoosh H, Moshkowitz M, Gammon M, Fabian I, Halpern Z (2000) Activation of c-K-ras mutations in human gastrointestinal tumors. Gastroenterology 118(6): 1045–1050 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous