Reduced serum vitamin D-binding protein levels are associated with type 1 diabetes - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Oct;60(10):2566-70.
doi: 10.2337/db11-0576. Epub 2011 Aug 15.
Zhao Han, Lindsey Bierschenk, M V Prasad Linga-Reddy, Hongjie Wang, Michael Clare-Salzler, Michael Haller, Desmond Schatz, Courtney Myhr, Jin-Xiong She, Clive Wasserfall, Mark Atkinson
Affiliations
- PMID: 21844098
- PMCID: PMC3178281
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0576
Reduced serum vitamin D-binding protein levels are associated with type 1 diabetes
Dustin Blanton et al. Diabetes. 2011 Oct.
Abstract
Objective: Previous studies have noted a specific association between type 1 diabetes and insufficient levels of vitamin D, as well as polymorphisms within genes related to vitamin D pathways. Here, we examined whether serum levels or genotypes of the vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP), a molecule key to the biologic actions of vitamin D, specifically associate with the disorder.
Research design and methods: A retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of VDBP levels used samples from 472 individuals of similar age and sex distribution, including 153 control subjects, 203 patients with type 1 diabetes, and 116 first-degree relatives of type 1 diabetic patients. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) typing for VDBP polymorphisms (SNP rs4588 and rs7041) was performed on this cohort to determine potential genetic correlations. In addition, SNP analysis of a second sample set of banked DNA samples from 1,502 type 1 diabetic patients and 1,880 control subjects also was used to determine genotype frequencies.
Results: Serum VDBP levels were highest in healthy control subjects (median 423.5 µg/mL [range 193.5-4,345.0; interquartile range 354.1-]586), intermediate in first-degree relatives (402.9 µg/mL [204.7-4,850.0; 329.6-492.4]), and lowest in type 1 diabetic patients (385.3 µg/mL [99.3-1,305.0; 328.3-473.0]; P = 0.003 vs. control subjects). VDBP levels did not associate with serum vitamin D levels, age, or disease duration. However, VDBP levels were, overall, lower in male subjects (374.7 µg/mL [188.9-1,602.0; 326.9-449.9]) than female subjects (433.4 µg/mL [99.3-4,850.0; 359.4-567.8]; P < 0.0001). It is noteworthy that no differences in genotype frequencies of the VDBP polymorphisms were associated with serum VDBP levels or between type 1 diabetic patients and control subjects.
Conclusions: Serum VDBP levels are decreased in those with type 1 diabetes. These studies suggest that multiple components in the metabolic pathway of vitamin D may be altered in type 1 diabetes and, collectively, have the potential to influence disease pathogenesis.
Figures
FIG. 1.
Serum levels of VDBP. A: VDBP levels in control subjects (n = 153), first-degree relatives (n = 116), and type 1 diabetic patients (n = 203). B: There is no association between VDBP levels and disease duration by linear regression analysis. C: Serum VDBP in male (n = 233) and female (n = 238) subjects and the total of all study groups. Medians with interquartile ranges are shown.
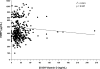
FIG. 2.
Linear regression of serum 25-OH vitamin D levels and VDBP levels. There was no significant correlation between these two parameters in the study cohort (n = 386).
Similar articles
- Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Polymorphisms (rs4588 and rs7041) and VDBP Levels in Total Hip Replacement Outcomes.
Rozmus D, Fiedorowicz E, Płomiński J, Cieślińska A. Rozmus D, et al. Nutrients. 2025 Jan 21;17(3):378. doi: 10.3390/nu17030378. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940236 Free PMC article. - Critically Ill Children Have Low Vitamin D-Binding Protein, Influencing Bioavailability of Vitamin D.
Madden K, Feldman HA, Chun RF, Smith EM, Sullivan RM, Agan AA, Keisling SM, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Randolph AG. Madden K, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Nov;12(11):1654-61. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201503-160OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 26356094 Free PMC article. - Upregulation of Irisin and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Concentrations by Increasing Maternal 25-Hydrovitamin D Concentrations in Combination with Specific Genotypes of Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms.
Karras SN, Dursun E, Alaylıoglu M, Gezen-Ak D, Al Anouti F, Pilz S, Pludowski P, Jude E, Kotsa K. Karras SN, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Dec 26;14(1):90. doi: 10.3390/nu14010090. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 35010965 Free PMC article. - rs7041 and rs4588 Polymorphisms in Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene (VDBP) and the Risk of Diseases.
Rozmus D, Płomiński J, Augustyn K, Cieślińska A. Rozmus D, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 15;23(2):933. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020933. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055118 Free PMC article. Review. - Vitamin D-Binding Protein in Pregnancy and Reproductive Health.
Fernando M, Ellery SJ, Marquina C, Lim S, Naderpoor N, Mousa A. Fernando M, et al. Nutrients. 2020 May 20;12(5):1489. doi: 10.3390/nu12051489. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32443760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Investigation of Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphism Impact on Coronary Artery Disease and Relationship with Longevity: Own Data and a Review.
Stakisaitis D, Lesauskaitė V, Girdauskaitė M, Janulionis E, Ulys A, Benetis R. Stakisaitis D, et al. Int J Endocrinol. 2016;2016:8347379. doi: 10.1155/2016/8347379. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Int J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27143969 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D and immunity.
Lucas RM, Gorman S, Geldenhuys S, Hart PH. Lucas RM, et al. F1000Prime Rep. 2014 Dec 1;6:118. doi: 10.12703/P6-118. eCollection 2014. F1000Prime Rep. 2014. PMID: 25580272 Free PMC article. Review. - The role of vitamin D in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection: An update.
Shah Alam M, Czajkowsky DM, Aminul Islam M, Ataur Rahman M. Shah Alam M, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Aug;97:107686. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107686. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33930705 Free PMC article. Review. - Correlation between urine vitamin D-binding protein and early-stage renal damage in Type 2 diabetes.
Huang Y, Chen S, Dai Q, Zhang H, Liu Y. Huang Y, et al. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Jan 28;48(1):40-48. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.210701. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 36935176 Free PMC article. Chinese, English. - Alterations in circulating levels of vitamin D binding protein, total and bioavailability of vitamin D in diabetic retinopathy patients.
Maghbooli Z, Ebrahimi Meimand S, Malek Hosseini AA, Shirvani A. Maghbooli Z, et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Jul 1;22(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01084-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35778716 Free PMC article.
References
- Alizadeh BZ, Koeleman BP. Genetic polymorphisms in susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Clin Chim Acta 2008;387:9–17 - PubMed
- Mathieu C, Gysemans C, Giulietti A, Bouillon R. Vitamin D and diabetes. Diabetologia 2005;48:1247–1257 - PubMed
- Pozzilli P, Manfrini S, Crinò A, et al. ; IMDIAB Group Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Horm Metab Res 2005;37:680–683 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical