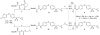Selective water-soluble gelatinase inhibitor prodrugs - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Oct 13;54(19):6676-90.
doi: 10.1021/jm200566e. Epub 2011 Sep 6.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21866961
- PMCID: PMC3190643
- DOI: 10.1021/jm200566e
Selective water-soluble gelatinase inhibitor prodrugs
Major Gooyit et al. J Med Chem. 2011.
Abstract
SB-3CT (1), a selective and potent thiirane-based gelatinase inhibitor, is effective in animal models of cancer metastasis and stroke; however, it is limited by poor aqueous solubility and extensive metabolism. We addressed these issues by blocking the primary site of metabolism and capitalizing on a prodrug strategy to achieve >5000-fold increased solubility. The amide prodrugs were quantitatively hydrolyzed in human blood to a potent gelatinase inhibitor, ND-322 (3). The arginyl amide prodrug (ND-478, 5d) was metabolically stable in mouse, rat, and human liver microsomes. Both 5d and 3 were nonmutagenic in the Ames II mutagenicity assay. The prodrug 5d showed moderate clearance of 0.0582 L/min/kg, remained mostly in the extracellular fluid compartment (Vd = 0.0978 L/kg), and had a terminal half-life of >4 h. The prodrug 5d had superior pharmacokinetic properties than those of 3, making the thiirane class of selective gelatinase inhibitors suitable for intravenous administration in the treatment of acute gelatinase-dependent diseases.
Figures
Figure 1
Ex vivo hydrolysis of 5d in human blood generates 3.
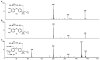
Figure 2
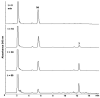
Reconstructed ion chromatogram following 60-min incubation of 5d with rat S9 liver microsomes.
Figure 3
Product ion mass spectra of (A) metabolite M1 (MH+, m/z 406) (B) M2 (MH+, m/z 250) and (C) M3 (MH+, m/z 364).
Figure 4
Product ion mass spectra of (A) metabolite M4 and (B) M5 (Inset: Reconstructed ion chromatogram of m/z 338 (MH + 16)+, following 30-min incubation of 3 with rat liver microsomes).
Figure 5
Identification of M4 by comparison of HPLC retention time to synthetic standards. (A) Reconstructed ion chromatogram of m/z 338 following 30-min incubation of 3 with rat liver microsomes and (B) HPLC chromatogram of a mixture of synthetic standards 13 and 14 using UV absorbance at 245 nm.
Figure 6
Product ion mass spectra of (A) metabolite M4, (B) synthetic standard 13, and (C) synthetic standard 14.
Figure 7
Metabolism pathway of 5d. Active gelatinase inhibitors are boxed; the major pathway is represented by a thick arrow, minor pathways are depicted by thin arrows, minute pathways are represented by broken thin arrows. The crossed red arrow indicates the absence of 14.
Figure 8
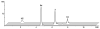
Plasma concentration-time curves of 3 after a single bolus intravenous dose of 5d and 3 to mice.
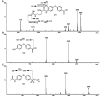
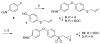
Scheme 1
Synthesis of 3_a_ a Reagents and condition: (a) (i) Cs2CO3, room temperature, 2 h; (ii) Zn, AcOH, 0 °C to room temperature, 2 h, 79%. (b) Boc2O, Et3N, MeOH, 60 °C, 2 h, 82%. (c) _m_-CPBA, CH2Cl2, room temperature, 72 h, 81%. (d) thiourea, MeOH/CH2Cl2, room temperature, 18 h, 72%. (e) 4 N HCl in 1,4-dioxane, ethyl acetate/CH2Cl2, 0 °C to room temperature, 48 h, 82%.
Scheme 2
Syntheses of the Ester and Amide Prodrugs_a_ a Reagents and condition: (a) DMAP, _i_Pr2EtN, CH2Cl2, room temperature, 3 h, 72 - 81%. (b) 4 N HCl in 1,4-dioxane, ethyl acetate/CH2Cl2, 0 °C to room temperature, 48 h, 71-79%. (c) THF, −20 °C to room temperature, 1 h, 61-79%.
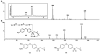
Scheme 3
Syntheses of 13 and the _N_-Hydroxylamine 14 Derivative.a a Reagents and condition: (a) Cs2CO3, DMF, room temperature, 24 h, 88%. (b) Fe, NH4Cl, MeOH/H2O, reflux, 2 h, 83%. (c) Boc2O, Et3N, MeOH, room temperature, 24 h, 76%. (d) KOH, MeOH, reflux, 4 h; then epichlorohydrin, room temperature, 10 min, 68%. (e) _m_-CPBA, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to room temperature, 10 min, 89%. (f) thiourea, MeOH/CH2Cl2, room temperature, 24 h, 83%. (g) HCl, MeOH, reflux, 1 h, 95%. (h) Zn, NH4Cl, CH2Cl2/H2O, room temperature, 0.5 h, 69%.
Similar articles
- Synthesis, kinetic characterization and metabolism of diastereomeric 2-(1-(4-phenoxyphenylsulfonyl)ethyl)thiiranes as potent gelatinase and MT1-MMP inhibitors.
Gooyit M, Lee M, Hesek D, Boggess B, Oliver AG, Fridman R, Mobashery S, Chang M. Gooyit M, et al. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2009 Dec;74(6):535-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00898.x. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2009. PMID: 19824893 Free PMC article. - Synthesis of chiral ND-322, ND-364 and ND-364 derivatives as selective inhibitors of human gelatinase.
Yan Y, Chen X, Yang X, Zhang J, Xu W, Zhang Y. Yan Y, et al. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Oct 15;23(20):6632-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.09.013. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26386821 - Metabolism of (4-phenoxyphenylsulfonyl) methylthiirane, a selective gelatinase inhibitor.
Celenza G, Villegas-Estrada A, Lee M, Boggess B, Forbes C, Wolter WR, Suckow MA, Mobashery S, Chang M. Celenza G, et al. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008 Mar;71(3):187-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00632.x. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008. PMID: 18221479 - Conformational analyses of thiirane-based gelatinase inhibitors.
Lee M, Hesek D, Shi Q, Noll BC, Fisher JF, Chang M, Mobashery S. Lee M, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 May 15;18(10):3064-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.11.131. Epub 2007 Dec 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008. PMID: 18083555 Free PMC article. - Is prodrug design an approach to increase water solubility?
Sanches BMA, Ferreira EI. Sanches BMA, et al. Int J Pharm. 2019 Sep 10;568:118498. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118498. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31301465 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular design of a highly selective and strong protein inhibitor against matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2).
Higashi S, Hirose T, Takeuchi T, Miyazaki K. Higashi S, et al. J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 29;288(13):9066-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.441758. Epub 2013 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23395821 Free PMC article. - Structure-Activity Relationship for Thiirane-Based Gelatinase Inhibitors.
Lee M, Ikejiri M, Klimpel D, Toth M, Espahbodi M, Hesek D, Forbes C, Kumarasiri M, Noll BC, Chang M, Mobashery S. Lee M, et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jun 14;3(6):490-495. doi: 10.1021/ml300050b. Epub 2012 May 2. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22737278 Free PMC article. - A Review of Immunomodulatory Reprogramming by Probiotics in Combating Chronic and Acute Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs).
Srivastava P, Sondak T, Sivashanmugam K, Kim KS. Srivastava P, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 10;14(11):2436. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112436. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365254 Free PMC article. Review. - Water-Soluble MMP-9 Inhibitor Reduces Lesion Volume after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury.
Lee M, Chen Z, Tomlinson BN, Gooyit M, Hesek D, Juárez MR, Nizam R, Boggess B, Lastochkin E, Schroeder VA, Wolter WR, Suckow MA, Cui J, Mobashery S, Gu Z, Chang M. Lee M, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Oct 21;6(10):1658-64. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00140. Epub 2015 Aug 14. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26241578 Free PMC article.
References
- Moses MA. The regulation of neovascularization by matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Stem Cells. 1997;15:180–189. - PubMed
- Nguyen M, Arkell J, Jackson CJ. Human endothelial gelatinases and angiogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001;33:960–970. - PubMed
- Stamenkovic I. Extracellular matrix remodelling: the role of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Pathol. 2003;200:448–464. - PubMed
- Sorokin L. The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:712–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information