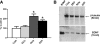Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment - PubMed (original) (raw)
Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment
Tali Kobilo et al. Learn Mem. 2011.
Abstract
Environmental enrichment (EE) increases dentate gyrus (DG) neurogenesis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. However, running is considered an element of EE. To dissociate effects of physical activity and enrichment on hippocampal neurogenesis and BDNF levels, young female C57Bl/6 mice were housed under control, running, enrichment, or enrichment plus running conditions, and injected with bromodeoxyuridine. Cell genesis was assessed after 12 d and differentiation was analyzed 1 mo later. In addition, locomotor activity in the open field and hippocampal mature BDNF peptide levels were measured. Open-field adaptation was improved in all groups, compared to controls, but more so with running. New cell proliferation, survival, neuron number, and neurotrophin levels were enhanced only when running was accessible. We conclude that exercise is the critical factor mediating increased BDNF levels and adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
Figures
Figure 1.
Housing of the experimental animals. Female C57Bl/6 mice (n = 10 per group) were housed in large cages (30″ × 33″ × 8″) as shown. (A) Control (CON). (B) Running (RUN); cage with 10 running wheels for voluntary physical activity. (C) Enriched environment only (EEO). (D) Enrichment and running (EER); the cage contained enrichment objects similar to C, as well as 10 running wheels. (E) Overview of the experimental cages.
Figure 2.
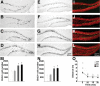
Dentate gyrus cell proliferation and neurogenesis, and open-field locomotion. Photomicrographs (A_–_L) and quantification (M,N) of BrdU-positive cells 1 d (A_–_D,M) and 4 wk (E_–_H,N) after the last BrdU injection in CON (A,E,I), EEO (B,F,J), RUN (C,G,K), and EER (D,H,L) mice. (I_–_L) Confocal images of BrdU-positive cells in CON (I), EEO (J), RUN (K), and EER (L) 4 wk after the last injection. Sections were immunofluorescent double-labeled for BrdU (green) and NeuN (red) indicating neuronal phenotype. (O) Open-field behavior was evaluated on day 30. RUN and EER groups habituated more rapidly to the open field than CON and EEO (P < 0.04). EEO differed significantly from CON (P < 0.01).
Figure 3.
Hippocampal BDNF levels. (A) Mature BDNF peptide levels were significantly increased in the hippocampi of mice in the running (RUN, n = 8) and enriched plus running (EER, n = 9) groups compared to the enriched only (EEO, n = 10) and control (CON, n = 8) groups. Specific comparisons showed that RUN, EER, and EEO groups differed (P < 0.04), as well as RUN, EER and CON groups (P < 0.01). (B) One replicate of the Western blot is shown for each condition, as well as recombinant mature human BDNF peptide as a positive control and β-tubulin as an endogenous control.
Similar articles
- Running throughout middle-age improves memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and BDNF levels in female C57BL/6J mice.
Marlatt MW, Potter MC, Lucassen PJ, van Praag H. Marlatt MW, et al. Dev Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;72(6):943-52. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22009. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22252978 Free PMC article. - Voluntary wheel running in mice increases the rate of neurogenesis without affecting anxiety-related behaviour in single tests.
Garrett L, Lie DC, Hrabé de Angelis M, Wurst W, Hölter SM. Garrett L, et al. BMC Neurosci. 2012 Jun 8;13:61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-61. BMC Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22682077 Free PMC article. - Running per se stimulates the dendritic arbor of newborn dentate granule cells in mouse hippocampus in a duration-dependent manner.
Dostes S, Dubreucq S, Ladevèze E, Marsicano G, Abrous DN, Chaouloff F, Koehl M. Dostes S, et al. Hippocampus. 2016 Mar;26(3):282-8. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22551. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26606164 - Effects of environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise on neurogenesis, learning and memory, and pattern separation: BDNF as a critical variable?
Bekinschtein P, Oomen CA, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ. Bekinschtein P, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Jul;22(5):536-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21767656 Review. - From neurotransmitters to neurotrophic factors to neurogenesis.
Hagg T. Hagg T. Neuroscientist. 2009 Feb;15(1):20-7. doi: 10.1177/1073858408324789. Neuroscientist. 2009. PMID: 19218228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Hidden Dangers of Sedentary Living: Insights into Molecular, Cellular, and Systemic Mechanisms.
Diniz DG, Bento-Torres J, da Costa VO, Carvalho JPR, Tomás AM, Galdino de Oliveira TC, Soares FC, de Macedo LDED, Jardim NYV, Bento-Torres NVO, Anthony DC, Brites D, Picanço Diniz CW. Diniz DG, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 6;25(19):10757. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910757. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409085 Free PMC article. Review. - Adult Neurogenesis, Context Encoding, and Pattern Separation: A Pathway for Treating Overgeneralization.
Chang WL, Hen R. Chang WL, et al. Adv Neurobiol. 2024;38:163-193. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62983-9_10. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39008016 Review. - Ageing, Cognitive Decline, and Effects of Physical Exercise: Complexities, and Considerations from Animal Models.
Caruso MG, Nicolas S, Lucassen PJ, Mul JD, O'Leary OF, Nolan YM. Caruso MG, et al. Brain Plast. 2024 May 14;9(1-2):43-73. doi: 10.3233/BPL-230157. eCollection 2024. Brain Plast. 2024. PMID: 38993577 Free PMC article. Review. - Comparison of the effect of postweaning social isolation, enriched environment, and exercise training on learning and memory functions in rats.
Ekinalan Kayhan H, Okudan N, Belviranli M. Ekinalan Kayhan H, et al. Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Jun 21;53(5):1412-1420. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5708. eCollection 2023. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38812994 Free PMC article. - Regenerative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Healing in Youth and Adolescent Athletes: The Emerging Age of Recovery Science.
Nyland J, Sirignano MN, Richards J, Krupp RJ. Nyland J, et al. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2024 Apr 23;9(2):80. doi: 10.3390/jfmk9020080. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2024. PMID: 38804446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bennett EL, Diamond MC, Krech D, Rosenzweig MR 1964. Chemical and anatomical plasticity brain. Science 30: 610–619 - PubMed
- Cotman CW, Berchtold NC 2002. Exercise: A behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity. Trends Neurosci 25: 295–301 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources