Impact of tissue plasminogen activator on the neurovascular unit: from clinical data to experimental evidence - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Impact of tissue plasminogen activator on the neurovascular unit: from clinical data to experimental evidence
Denis Vivien et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Nov.
Abstract
About 15 million strokes occur each year worldwide. As the number one cause of morbidity and acquired disability, stroke is a major drain on public health-care funding, due to long hospital stays followed by ongoing support in the community or nursing-home care. Although during the last 10 years we have witnessed a remarkable progress in the understanding of the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke, reperfusion induced by recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA-Actilyse) remains the only approved acute treatment by the health authorities. The objective of the present review is to provide an overview of our present knowledge about the impact of tPA on the neurovascular unit during acute ischemic stroke.
Figures
Figure 1
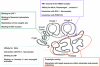
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) is a ‘JANUS' protease. tPA is a five domain serine protease including a Finger domain, an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, two kringle domains, and a catalytic domain. Pleiotropic functions of tPA as related to the specificity of each of these domains. LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1; NMDA receptor, _N_-methyl--aspartate receptor; PDGF-CC, platelet-derived growth factor-CC.
Figure 2
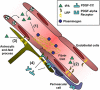
Effect of exogenous and endogenous tPA at the blood–brain barrier (BBB). (1) Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA)-mediated plasminogen activation promotes clot lysis and subsequent blood flow restoration. (2) tPA interacts with endothelial LRPs, leading to NF_κ_B activation and MMPs overexpression. (3) tPA can shed the ectodomain of astrocytic LRP receptors, inducing detachment of astrocytic end-feet processes. (4) tPA bound to LRP can activate latent PDGF-CC. Active PDGF-CC binds PDGF-Rα on perivascular cells leading to BBB opening. LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; MMPs, metalloproteinases; PDGF-CC, platelet-derived growth factor-CC.
Figure 3
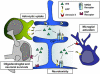
Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) in the brain parenchyma. In the brain parenchyma, tPA, released by neurons, was reported to potentiate NMDA receptors signaling to display either neurotrophic or neurotoxic effects, to reduce apoptotic neuronal and oligodendroglial deaths, to activate microglia after binding to annexin II and LRP and to be cleared from the extracellular space by astrocytes through an LRP-dependent mechanism. LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; NMDA, _N_-methyl--aspartate receptor; EGF, epidermal growth factor.
Similar articles
- Intravenously administered tissue plasminogen activator useful in milder strokes? A meta-analysis.
Yeo LLL, Ho R, Paliwal P, Rathakrishnan R, Sharma VK. Yeo LLL, et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014 Sep;23(8):2156-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 Aug 10. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 25113080 - Randomised trials of endovascular treatment of stroke are needed.
Schott AM. Schott AM. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Jan;9(1):30-1. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70350-3. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20083032 No abstract available. - Randomised trials of endovascular treatment of stroke are needed.
Ciccone A, Sterzi R. Ciccone A, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Jan;9(1):30; author reply 31-2. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70349-7. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20083033 No abstract available. - Optimizing the management of acute ischaemic stroke: a review of the utilization of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
Eissa A, Krass I, Bajorek BV. Eissa A, et al. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012 Dec;37(6):620-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2012.01366.x. Epub 2012 Jun 19. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012. PMID: 22708668 Review. - Plasmin-dependent modulation of the blood-brain barrier: a major consideration during tPA-induced thrombolysis?
Niego B, Medcalf RL. Niego B, et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Aug;34(8):1283-96. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.99. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 24896566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Brazilian Angiology and Vascular Surgery Society Guidelines for the treatment of extracranial cerebrovascular disease.
Ristow AVB, Massière B, Meirelles GV, Casella IB, Morales MM, Moreira RCR, Procópio RJ, Oliveira TF, de Araujo WJB, Joviliano EE, de Oliveira JCP. Ristow AVB, et al. J Vasc Bras. 2024 May 31;23:e20230094. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.202300942. eCollection 2024. J Vasc Bras. 2024. PMID: 39099701 Free PMC article. - Targeting vascular inflammation in ischemic stroke: Recent developments on novel immunomodulatory approaches.
Shekhar S, Cunningham MW, Pabbidi MR, Wang S, Booz GW, Fan F. Shekhar S, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 15;833:531-544. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.028. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29935175 Free PMC article. Review. - Sub-acute systemic erythropoietin administration reduces ischemic brain injury in an age-dependent manner.
Thériault P, Le Béhot A, ElAli A, Rivest S. Thériault P, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):35552-35561. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9652. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248662 Free PMC article. - Impact of Bradykinin Generation During Thrombolysis in Ischemic Stroke.
Gauberti M, Potzeha F, Vivien D, Martinez de Lizarrondo S. Gauberti M, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Jul 3;5:195. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00195. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30018956 Free PMC article. Review. - A concerted appeal for international cooperation in preclinical stroke research.
Dirnagl U, Hakim A, Macleod M, Fisher M, Howells D, Alan SM, Steinberg G, Planas A, Boltze J, Savitz S, Iadecola C, Meairs S. Dirnagl U, et al. Stroke. 2013 Jun;44(6):1754-60. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.000734. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23598526 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Adams HPJ, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, Grubb RL, Higashida RT, Jauch EC, Kidwell C, Lyden PD, Morgenstern LB, Qureshi AI, Rosenwasser RH, Scott PA, Wijdicks EFM. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Circulation. 2007;115:e478–e534. - PubMed
- Adams HPJ, Leira EC, Torner JC, Barnathan E, Padgett L, Effron MB, Hacke W. Treating patients with ‘wake-up' stroke: the experience of the AbESTT-II trial. Stroke. 2008;39:3277–3282. - PubMed
- Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Brainin M, Castillo J, Ford GA, Kaste M, Lees KR, Toni D. Relationship of blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy, and outcome in ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis: retrospective analysis from Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-International Stroke Thrombolysis Register (SITS-ISTR) Stroke. 2009;40:2442–2449. - PubMed
- Ahmed N, Dávalos A, Eriksson N, Ford GA, Glahn J, Hennerici M, Mikulik R, Kaste M, Lees KR, Lindsberg PJ, Toni D. Association of admission blood glucose and outcome in patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: results from the Safe Implementation of Treatments in Stroke International Stroke Thrombolysis Register (SITS-ISTR) Arch Neurol. 2010;67:1123–1130. - PubMed
- Alexandrov AV, Molina CA, Grotta JC, Garami Z, Ford SR, Alvarez-Sabin J, Montaner J, Saqqur M, Demchuk AM, Moyé LA, Hill MD, Wojner AW. Ultrasound-enhanced systemic thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2170–2178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials