The neurobiology of cognitive control in successful cocaine abstinence - PubMed (original) (raw)
The neurobiology of cognitive control in successful cocaine abstinence
Colm G Connolly et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012.
Abstract
Introduction: Extensive evidence demonstrates that current cocaine abusers show hypoactivity in anterior cingulate and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and respond poorly relative to drug-naïve controls on tests of executive function. Relatively little is known about the cognitive sequelae of long-term abstinence in cocaine addicts.
Methods: Here, we use a GO-NOGO task in which successful performance necessitated withholding a prepotent response to assay cognitive control in short- and long-term abstinent cocaine users (1-5 weeks and 40-102 weeks, respectively).
Results: We report significantly greater activity in prefrontal, cingulate, cerebellar and inferior frontal gyrii in abstinent cocaine users for both successful response inhibitions and errors of commission. Moreover, this relative hyperactivity was present in both abstinent groups, which, in the presence of comparable behavioral performance, suggests a functional compensation.
Conclusions: Differences between the short- and long-abstinence groups in the patterns of functional recruitment suggest different cognitive control demands at different stages in abstinence. Short-term abstinence showed increased inhibition-related dorsolateral and inferior frontal activity indicative of the need for increased inhibitory control while long-term abstinence showed increased error-related ACC activity indicative of heightened behavioral monitoring. The results suggest that the integrity of prefrontal systems that underlie cognitive control functions may be an important characteristic of successful long-term abstinence.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
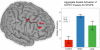
Figure 1
Regions in the left and right inferior frontal gyrii for STOPS analysis. Group-wise differences are shown in the charts. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
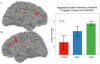
Figure 2
Three regions, located in RMFG, and two in RSFG, used in the aggregate STOPS DLPFC cluster, the mean activity in which was aggregated and weighted by volume. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
Figure 3
Four regions, located in left and right cingulate gyrii, used in the aggregate ERROR cingulate gyrus cluster, the mean activity in which was aggregated and scaled by volume. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
Similar articles
- Cingulate hypoactivity in cocaine users during a GO-NOGO task as revealed by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging.
Kaufman JN, Ross TJ, Stein EA, Garavan H. Kaufman JN, et al. J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 27;23(21):7839-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-21-07839.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12944513 Free PMC article. - The influence of monetary punishment on cognitive control in abstinent cocaine-users.
Hester R, Bell RP, Foxe JJ, Garavan H. Hester R, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013 Nov 1;133(1):86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.05.027. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013. PMID: 23791040 Free PMC article. - Inhibitory behavioral control: A stochastic dynamic causal modeling study comparing cocaine dependent subjects and controls.
Ma L, Steinberg JL, Cunningham KA, Lane SD, Bjork JM, Neelakantan H, Price AE, Narayana PA, Kosten TR, Bechara A, Moeller FG. Ma L, et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 24;7:837-47. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.015. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26082893 Free PMC article. - [Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)].
Emond V, Joyal C, Poissant H. Emond V, et al. Encephale. 2009 Apr;35(2):107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19393378 Review. French. - The neurobiology of successful abstinence.
Garavan H, Brennan KL, Hester R, Whelan R. Garavan H, et al. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;23(4):668-74. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.029. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23510740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Multimodal evidence of regional midcingulate gray matter volume underlying conflict monitoring.
Parvaz MA, Maloney T, Moeller SJ, Malaker P, Konova AB, Alia-Klein N, Goldstein RZ. Parvaz MA, et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Jun 2;5:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.05.011. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 24918068 Free PMC article. - Fronto-striatal circuits in response-inhibition: Relevance to addiction.
Morein-Zamir S, Robbins TW. Morein-Zamir S, et al. Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.012. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25218611 Free PMC article. Review. - Development of the Alcohol Quality of Life Scale (AQoLS): a new patient-reported outcome measure to assess health-related quality of life in alcohol use disorder.
Luquiens A, Whalley D, Crawford SR, Laramée P, Doward L, Price M, Hawken N, Dorey J, Owens L, Llorca PM, Falissard B, Aubin HJ. Luquiens A, et al. Qual Life Res. 2015 Jun;24(6):1471-81. doi: 10.1007/s11136-014-0865-7. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Qual Life Res. 2015. PMID: 25407634 - Emotion recognition in individuals with cocaine use disorder: the role of abstinence length and the social brain network.
Rabin RA, Parvaz MA, Alia-Klein N, Goldstein RZ. Rabin RA, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Apr;239(4):1019-1033. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05868-x. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34089343 Free PMC article. - Differential Activation of the Left and Right Cerebral Hemispheres of Individuals Who Use or are Dependent on Drugs of Abuse.
Gordon HW. Gordon HW. J Drug Abuse. 2018;4(2):10. doi: 10.21767/2471-853X.100077. Epub 2018 Jul 25. J Drug Abuse. 2018. PMID: 30090867 Free PMC article.
References
- Aharonovich E, Hasin DS, Brooks AC, Liu X, Bisaga A, Nunes EV. Cognitive deficits predict low treatment retention in cocaine dependent patients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;81:313–322. - PubMed
- Alterman A, McKay J, Mulvaney F, McLellan A. Prediction of attrition from day hospital treatment in lower socioeconomic cocaine-dependent men. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1996;40:227–233. - PubMed
- Ardila A, Rosselli M, Strumwasser S. Neuropsychological deficits in chronic cocaine abusers. Int. J. Neurosci. 1991;57:73–79. - PubMed
- Aron AR, Fletcher PC, Bullmore ET, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW. Stop-signal inhibition disrupted by damage to right inferior frontal gyrus in humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2003;6:115–116. - PubMed
- Bartzokis G, Beckson M, Lu PH, Nuechterlein KH, Edwards N, Mintz J. Age-related changes in frontal and temporal lobe volumes in men - a magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2000;58:461–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical