Activation of cell stress response pathways by Shiga toxins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Activation of cell stress response pathways by Shiga toxins
Vernon L Tesh. Cell Microbiol. 2012 Jan.
Abstract
Shiga toxin-producing bacteria cause widespread outbreaks of bloody diarrhoea that may progress to life-threatening systemic complications. Shiga toxins (Stxs), the main virulence factors expressed by the pathogens, are ribosome-inactivating proteins which inhibit protein synthesis by removing an adenine residue from 28S rRNA. Recently, Stxs were shown to activate multiple stress-associated signalling pathways in mammalian cells. The ribotoxic stress response is activated following the depurination reaction localized to the α-sarcin/ricin loop of eukaryotic ribosomes. The unfolded protein response (UPR) may be initiated by toxin unfolding within the endoplasmic reticulum, and maintained by production of truncated, misfolded proteins following intoxication. Activation of the ribotoxic stress response leads to signalling through MAPK cascades, which appears to be critical for activation of innate immunity and regulation of apoptosis. Precise mechanisms linking ribosomal damage with MAPK activation require clarification but may involve recognition of ribosomal conformational changes and binding of protein kinases to ribosomes, which activate MAP3Ks and MAP2Ks. Stxs appear capable of activating all ER membrane localized UPR sensors. Prolonged signalling through the UPR induces apoptosis in some cell types. The characterization of stress responses activated by Stxs may identify targets for the development of interventional therapies to block cell damage and disease progression.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
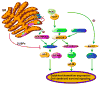
Fig. 1. Induction of the ribotoxic stress response by Stxs
Following retrotranslocation of Stx A1-fragment (green circle) across the ER membrane, the depurination reaction involving a single adenine residue within the α-sarcin/ricin loop of the 28S rRNA ribosomal subunit (blue circles) may induce a sufficient conformational change to allow the serine/threonine protein kinase PKR to bind. Additional kinases may also recognize changes in ribosomal tertiary structure. Stxs appear to be capable of activating all three MAPKs: JNK1,2, the p38 MAPK isoforms, and ERK1,2. Upstream molecules transducing signals from intoxicated ribosomes to activate MAPKs remain to be fully characterized, but include the MAP3Ks, ASK-1 and ZAK, and the MAP2Ks, SEK1/MKK4 and MKK3/6. Downstream signaling molecules activated by the MAPKs regulate cytokine/chemokine gene expression at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels, and activate apoptosis and cell survival pathways. Dual specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) are also activated by the ribotoxic stress response, suggesting that signals to ultimately down-regulate the response are initiated following intoxication.
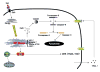
Fig. 2. Prolonged activation of the UPR by Stxs leads to apoptosis
Unfolded Stx A1-fragments and/or the presence of truncated, misfolded proteins within the ER of intoxicated monocytic THP-1 cells leads to increased phosphorylation of ER stress sensors PERK and IRE1, and cleavage of the sensor ATF6 from the 90 kDa precursor form to the active 50 kDa transcription factor. Expression of the transcription factor CHOP is up-regulated, which in turn, down-regulates expression of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2, and up-regulates expression of the apoptosis inducing factor TRAIL and its receptor DR5. Release of Ca2+ from ER stores also activates calpains which may directly cleave procaspase-8. Reproduced from Lee et al., Cellular Microbiology 10(3):770–780 [2008] with permission of the authors and Wiley-Blackwell Publishers.
Similar articles
- Shiga toxins: intracellular trafficking to the ER leading to activation of host cell stress responses.
Lee MS, Cherla RP, Tesh VL. Lee MS, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jun;2(6):1515-35. doi: 10.3390/toxins2061515. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069648 Free PMC article. Review. - Ribosome depurination by ricin leads to inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HAC1 mRNA splicing on the ribosome.
Pierce M, Vengsarkar D, McLaughlin JE, Kahn JN, Tumer NE. Pierce M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 22;294(47):17848-17862. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009128. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31624149 Free PMC article. - Shiga Toxins Induce Apoptosis and ER Stress in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.
Park JY, Jeong YJ, Park SK, Yoon SJ, Choi S, Jeong DG, Chung SW, Lee BJ, Kim JH, Tesh VL, Lee MS, Park YJ. Park JY, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2017 Oct 13;9(10):319. doi: 10.3390/toxins9100319. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29027919 Free PMC article. - The induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins and ricin.
Tesh VL. Tesh VL. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:137-78. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_155. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22130961 Review.
Cited by
- Crosstalk between Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Tubular Epithelial Cells Modulates Pro-Inflammatory Responses Induced by Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin.
Álvarez RS, Jancic C, Garimano N, Sacerdoti F, Paton AW, Paton JC, Ibarra C, Amaral MM. Álvarez RS, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 7;11(11):648. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110648. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31703347 Free PMC article. - A novel polysaccharide derived from algae extract inhibits cancer progression via JNK, not via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Xie P, Horio F, Fujii I, Zhao J, Shinohara M, Matsukura M. Xie P, et al. Int J Oncol. 2018 May;52(5):1380-1390. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4297. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29512724 Free PMC article. - Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in the era of terminal complement inhibition: an observational cohort study.
Brocklebank V, Walsh PR, Smith-Jackson K, Hallam TM, Marchbank KJ, Wilson V, Bigirumurame T, Dutt T, Montgomery EK, Malina M, Wong EKS, Johnson S, Sheerin NS, Kavanagh D. Brocklebank V, et al. Blood. 2023 Oct 19;142(16):1371-1386. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018833. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37369098 Free PMC article. - The endoplasmic reticulum in plant immunity and cell death.
Eichmann R, Schäfer P. Eichmann R, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2012 Aug 22;3:200. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00200. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22936941 Free PMC article. - A comprehensive coverage insurance for cells: revealing links between ribosome collisions, stress responses and mRNA surveillance.
De S, Mühlemann O. De S, et al. RNA Biol. 2022;19(1):609-621. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2065116. Epub 2021 Dec 31. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 35491909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alisi A, Spaziani A, Anticoli S, Ghidinelli M, Balsano C. PKR is a novel functional direct player that coordinates skeletal muscle differentiation via p38MAPK/AKT pathways. Cell Signal. 2008;20:534–542. - PubMed
- Allison HE. Stx-phages: drivers and mediators of the evolution of STEC and STEC-like pathogens. Future Microbiol. 2007;2:165–174. - PubMed
- Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:487–508. - PubMed
- Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:326–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources