Extracellular TG2: emerging functions and regulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Extracellular TG2: emerging functions and regulation
Alexey M Belkin. FEBS J. 2011 Dec.
Abstract
Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) is a ubiquitously expressed member of the transglutaminase family of Ca(2+)-dependent crosslinking enzymes. Unlike other family members, TG2 is a multifunctional protein, which has several other well documented enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions. A significant body of evidence accumulated over the last decade reveals multiple and complex activities of this protein on the cell surface and in the extracellular matrix (ECM), including its role in the regulation of cell-ECM interactions and outside-in signaling by several types of transmembrane receptors. Moreover, recent findings indicate a dynamic regulation of the levels and functions of extracellular TG2 by several complementary mechanisms. This review summarizes and assesses recent research into the emerging functions and regulation of extracellular TG2.
© 2011 The Author Journal compilation © 2011 FEBS.
Figures
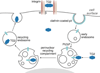
Fig. 1
Several types of TG2-containing adhesive / signaling complexes present on the cell surface. Solid black lines indicate TG2-mediated activation of cytoplasmic targets by transmembrane signaling receptors. Dotted black line marks binding of activated PKCα to the integrin cytoplasmic tails, which causes their redistribution on the cell surface. Red dashed line outlines the activation of syndecan-2 by intracellular PKCα, and green dashed line - syndecan-2-mediated activation of ROCK, which induces stress fiber and focal adhesion formation. Blue dashed line marks nuclear translocation of β-catenin which leads to its complex formation with Tcf/Lef and activation of gene transcription. Curved black line indicates the principal pathway of surface TG2 internalization.
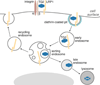
Fig. 2
The unconventional pathway of cytoplasmic TG2 secretion involves phospholipid-dependent delivery into recycling endosomes. Solid lines mark the major endosomal recycling pathway which operates via the perinuclear recycling endosomal compartment. Dashed line indicates the PI(3)P-dependent recruitment of cytoplasmic TG2 to the membranes of the perinuclear recycling compartment.
Fig. 3
The constitutive LRP1-dependent internalization and lysosomal degradation of cell surface TG2. Solid lines mark the major endosomal recycling and lysosomal degradative pathways.
Similar articles
- Physiological, pathological, and structural implications of non-enzymatic protein-protein interactions of the multifunctional human transglutaminase 2.
Kanchan K, Fuxreiter M, Fésüs L. Kanchan K, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Aug;72(16):3009-35. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1909-z. Epub 2015 May 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25943306 Free PMC article. Review. - Crosslinking and G-protein functions of transglutaminase 2 contribute differentially to fibroblast wound healing responses.
Stephens P, Grenard P, Aeschlimann P, Langley M, Blain E, Errington R, Kipling D, Thomas D, Aeschlimann D. Stephens P, et al. J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 1;117(Pt 15):3389-403. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01188. Epub 2004 Jun 15. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15199098 - Transglutaminase 2 interacts with syndecan-4 and CD44 at the surface of human macrophages to promote removal of apoptotic cells.
Nadella V, Wang Z, Johnson TS, Griffin M, Devitt A. Nadella V, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1853(1):201-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.020. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25449226 - Transglutaminase 2 as a novel activator of LRP6/β-catenin signaling.
Deasey S, Nurminsky D, Shanmugasundaram S, Lima F, Nurminskaya M. Deasey S, et al. Cell Signal. 2013 Dec;25(12):2646-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.016. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23993960 Free PMC article. - The role of tissue transglutaminase in cell-matrix interactions.
Zemskov EA, Janiak A, Hang J, Waghray A, Belkin AM. Zemskov EA, et al. Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1057-76. doi: 10.2741/1863. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146797 Review.
Cited by
- Transglutaminase 2 has opposing roles in the regulation of cellular functions as well as cell growth and death.
Tatsukawa H, Furutani Y, Hitomi K, Kojima S. Tatsukawa H, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 2;7(6):e2244. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.150. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27253408 Free PMC article. Review. - Application of a Fluorescence Anisotropy-Based Assay to Quantify Transglutaminase 2 Activity in Cell Lysates.
Hauser S, Sommerfeld P, Wodtke J, Hauser C, Schlitterlau P, Pietzsch J, Löser R, Pietsch M, Wodtke R. Hauser S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 19;23(9):4475. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094475. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562866 Free PMC article. - Cell-Impermeable Inhibitors Confirm That Intracellular Human Transglutaminase 2 Is Responsible for the Transglutaminase-Associated Cancer Phenotype.
Gates EWJ, Calvert ND, Cundy NJ, Brugnoli F, Navals P, Kirby A, Bianchi N, Adhikary G, Shuhendler AJ, Eckert RL, Keillor JW. Gates EWJ, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12546. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612546. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628729 Free PMC article. - Assessment of α9β1 ıntegrın as a new dıagnostıc and therapeutıc target ın Behcet's dısease.
Ellergezen P, Coşkun BN, Çeçen GS, Bozkurt ZY, Ağca H, Dalkılıç HE, Çavun S. Ellergezen P, et al. Clin Exp Med. 2023 Dec;23(8):5345-5353. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01173-3. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37728818 - Hepatic Localization of Macrophage Phenotypes during Fibrogenesis and Resolution of Fibrosis in Mice and Humans.
Beljaars L, Schippers M, Reker-Smit C, Martinez FO, Helming L, Poelstra K, Melgert BN. Beljaars L, et al. Front Immunol. 2014 Sep 8;5:430. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00430. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25250030 Free PMC article.
References
- Lorand L, Graham RM. Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:140–156. - PubMed
- Iismaa SE, Mearns BM, Lorand L, Graham RM. Transglutaminases and disease: lessons from genetically engineered mouse models and inherited disorders. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:991–1023. - PubMed
- Kiraly R, Demeny M, Fesus L. Protein transamidation by transglutaminase 2 in cells: a disputed Ca2+-dependent action of a multifunctional protein. FEBS J. 2011 submitted. - PubMed
- Walther DJ, Stahlberg S, Vowinckel J. Novel roles for primeval chemicals: from monoamines in transglutaminase-mediated posttranslational protein modification to mono-aminylation deregulation diseases. FEBS J. 2011 submitted. - PubMed
- Kuo F-T, Kojima S. new insights into functions and localization of nuclear transglutaminase 2. FEBS J. 2011 submitted. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous