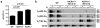CTCF-binding elements mediate control of V(D)J recombination - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Sep 11;477(7365):424-30.
doi: 10.1038/nature10495.
Hye Suk Yoon, Andrew Franklin, Suvi Jain, Anja Ebert, Hwei-Ling Cheng, Erica Hansen, Orion Despo, Claudia Bossen, Christian Vettermann, Jamie G Bates, Nicholas Richards, Darienne Myers, Harin Patel, Michael Gallagher, Mark S Schlissel, Cornelis Murre, Meinrad Busslinger, Cosmas C Giallourakis, Frederick W Alt
Affiliations
- PMID: 21909113
- PMCID: PMC3342812
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10495
CTCF-binding elements mediate control of V(D)J recombination
Chunguang Guo et al. Nature. 2011.
Abstract
Immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) variable region exons are assembled from V(H), D and J(H) gene segments in developing B lymphocytes. Within the 2.7-megabase mouse Igh locus, V(D)J recombination is regulated to ensure specific and diverse antibody repertoires. Here we report in mice a key Igh V(D)J recombination regulatory region, termed intergenic control region 1 (IGCR1), which lies between the V(H) and D clusters. Functionally, IGCR1 uses CTCF looping/insulator factor-binding elements and, correspondingly, mediates Igh loops containing distant enhancers. IGCR1 promotes normal B-cell development and balances antibody repertoires by inhibiting transcription and rearrangement of D(H)-proximal V(H) gene segments and promoting rearrangement of distal V(H) segments. IGCR1 maintains ordered and lineage-specific V(H)(D)J(H) recombination by suppressing V(H) joining to D segments not joined to J(H) segments, and V(H) to DJ(H) joins in thymocytes, respectively. IGCR1 is also required for feedback regulation and allelic exclusion of proximal V(H)-to-DJ(H) recombination. Our studies elucidate a long-sought Igh V(D)J recombination control region and indicate a new role for the generally expressed CTCF protein.
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
Figures
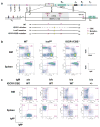
Figure 1. Mutation of IGCR1 CBEs impairs B cell development
(a) Murine 129SV IgH locus (accession number: AJ851868) schematic showing 4.1 kb IGCR1 region in WT compared to IGCR1 deleted, loxP inserted, or CBE mutated configuration. (b) Flow cytometry analysis of IgM- bone marrow (BM) and IgM+ splenic B cell populations in WT, loxPI/I, and IGCR1/CBE-/- mice. In BM the B220intCD43+ pro-B and B220+CD43- pre-B cell populations are indicated. (c) Expression of IgMa and IgMb allotypic markers in BM and spleen from WT IgMa/IgMa (pure 129SV), WT IgMb/IgMb (pure C57BL/6), WT F1 (IgMa/IgMb), and heterozygous mutant IGCR1/CBE- IgMa/ WT IgMb mice.
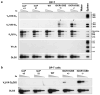
Figure 2. IGCR1 mutations alter VH usage, germline transcription and rearrangement order
(a) PCR analyses of indicated VH family rearrangements in pro-B cells from indicated mice compared to a DLG5 loading control. Results are typical of four experiments. Bands corresponding to rearrangements to various JHs are indicated on right. (b) RT-PCR analysis of indicated germline VH transcripts in three independent WT and IGCR1-/- A-MuLV virus transformed RAG2-/- pro-B cell lines. N=nonspliced sense/antisense and S=spliced sense. (c) ChIP-qPCR analyses of H3K4me2 and H3K9ac histone modifications at indicated VHs in 129SV Rag2−/− (black) and Rag2−/− IGCR1−/− (red) A-MuLV-transformed pro-B lines. The 5′ region (5′), body (G) and 3′ region (3′) of VH81X and body (G) of VHQ52.2.4 were analyzed. Average values and standard deviations of three experiments with one line shown are representative of results from both. (d) Semi-quantitative PCR analyses of direct VH-D rearrangements in sorted pro-B cells from indicated mice. The PCR assays utilized for panels a, b, and d are diagrammed in Supp. Figs. 6a, 7a, and 8a.
Figure 3. IGCR1/CBE Mutations lead to VHDJH and VHD rearrangements in thymocytes
(a) PCR analyses of VH family rearrangements in sorted DP thymocytes and total splenic B cells from indicated mice with DLG5 as a loading control. Bands corresponding to rearrangements to various JHs are indicated on right. Igκ rearrangement (VκJκ) served as a control for B cell contamination. (b) Semi-quantitative PCR analyses of direct VH-D rearrangements in sorted DP-T cells from indicated mice. Assays are diagrammed in Supp. Figs. 6a and 8a.
Figure 4. IGCR1 is required to allow feedback regulation of proximal VH to DJH recombination
(a) Mean percentage of splenic B cells with VHDJH rearrangements on both IgH alleles as determined by analyses of hybridomas from three independent sets of WT, IGCR1+/-, and IGCR1-/- mice (Supp. Table 5). Error bars represent standard deviation. _p_-values were calculated by student t-test. (b) IgH VHDJH rearrangements in splenic B cells from two independent WT and VB1-8 knock-in mice carrying either a WT (IGCR1+/+ VB1-8 KI) or an IGCR1 deleted (IGCR1+/- VB1-8 KI) second allele. Bands corresponding to rearrangements to various JHs are indicated on right. DLG5 is the loading control.
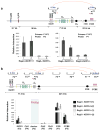
Figure 5. IGCR1 mediates long distance IgH chromosomal loops
(a) Schematic of chromosome interactions between IGCR1-containing and 3′_IgHC_BE-containing KpnI restriction fragments in 3C assays. Interactions between IGCR1 and 3′_IgH_CBE locales in 129SV RAG2-/- and RAG2-/-IGCR1-/- A-MuLV transformed pro-B cells were quantified by real time PCR (Taqman) using probe (P2) (left) and a probe (P1) (right). (b) Schematic of chromosome interactions between iEμ-containing KpnI restriction fragment and indicated KpnI restriction fragments in other IgH locales. Interactions between iEμ and IGCR1, iEμ and 3′_IgH_RR locales, iEμ and 3′_IgH_CBE locales in RAG2-/- and RAG2-/-IGCR1-/- A-MuLV transformed pro-B cells were quantified by real time PCR using a probe (P3) from the iEμ locale. F1-F8 indicate primers used for PCR. K indicates _Kpn_I sites. Red arcs indicate interactions detected in RAG2-/- cells. The average association frequency of three independent 3C experiments with 2 independent A-MuLV transformed lines from each genotype is shown with standard deviation indicated.
Similar articles
- CTCF-binding elements 1 and 2 in the Igh intergenic control region cooperatively regulate V(D)J recombination.
Lin SG, Guo C, Su A, Zhang Y, Alt FW. Lin SG, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 10;112(6):1815-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424936112. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25624508 Free PMC article. - Elements between the IgH variable (V) and diversity (D) clusters influence antisense transcription and lineage-specific V(D)J recombination.
Giallourakis CC, Franklin A, Guo C, Cheng HL, Yoon HS, Gallagher M, Perlot T, Andzelm M, Murphy AJ, Macdonald LE, Yancopoulos GD, Alt FW. Giallourakis CC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 21;107(51):22207-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015954107. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21123744 Free PMC article. - Contribution of the IGCR1 regulatory element and the 3 'Igh CBEs to Regulation of Igh V(D)J Recombination.
Liang Z, Zhao L, Yongxin Ye A, Lin SG, Zhang Y, Guo C, Dai HQ, Ba Z, Alt FW. Liang Z, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 25:2023.04.21.537836. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.21.537836. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37163018 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Cis-regulatory elements and epigenetic changes control genomic rearrangements of the IgH locus.
Perlot T, Alt FW. Perlot T, et al. Adv Immunol. 2008;99:1-32. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00601-9. Adv Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19117530 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.
Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Jung D, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115830. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16551259 Review.
Cited by
- Chromatin architecture, CCCTC-binding factor, and V(D)J recombination: managing long-distance relationships at antigen receptor loci.
Shih HY, Krangel MS. Shih HY, et al. J Immunol. 2013 May 15;190(10):4915-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300218. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23645930 Free PMC article. Review. - Skewed primary Igκ repertoire and V-J joining in C57BL/6 mice: implications for recombination accessibility and receptor editing.
Aoki-Ota M, Torkamani A, Ota T, Schork N, Nemazee D. Aoki-Ota M, et al. J Immunol. 2012 Mar 1;188(5):2305-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103484. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22287713 Free PMC article. - Targeting the oncogene B lymphoma deregulator IgH 3' regulatory region does not impede the in vivo inflammatory response in mice.
Saad F, Saintamand A, Rouaud P, Denizot Y. Saad F, et al. Oncoscience. 2014 Sep 19;1(9):591-8. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.81. eCollection 2014. Oncoscience. 2014. PMID: 25594069 Free PMC article. - Assembly and Expression of Shark Ig Genes.
Hsu E. Hsu E. J Immunol. 2016 May 1;196(9):3517-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600164. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27183649 Free PMC article. Review. - Antibody repertoire diversification through VH gene replacement in mice cloned from an IgA plasma cell.
Kumar R, Bach MP, Mainoldi F, Maruya M, Kishigami S, Jumaa H, Wakayama T, Kanagawa O, Fagarasan S, Casola S. Kumar R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 3;112(5):E450-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417988112. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25609671 Free PMC article.
References
- Schatz DG. Antigen receptor genes and the evolution of a recombinase. Semin Immunol. 2004;16:245–56. - PubMed
- Yancopoulos GD, et al. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal VH gene segments in pre-B-cell lines. Nature. 1984;311:727–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL48702/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI40227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- K08 AI070839/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA054198-20/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020047-27/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI040227/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020047-28/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL048702/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009151/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020047-29/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI20047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases