A critical review of habit learning and the Basal Ganglia - PubMed (original) (raw)
A critical review of habit learning and the Basal Ganglia
Carol A Seger et al. Front Syst Neurosci. 2011.
Abstract
The current paper briefly outlines the historical development of the concept of habit learning and discusses its relationship to the basal ganglia. Habit learning has been studied in many different fields of neuroscience using different species, tasks, and methodologies, and as a result it has taken on a wide range of definitions from these various perspectives. We identify five common but not universal, definitional features of habit learning: that it is inflexible, slow or incremental, unconscious, automatic, and insensitive to reinforcer devaluation. We critically evaluate for each of these how it has been defined, its utility for research in both humans and non-human animals, and the evidence that it serves as an accurate description of basal ganglia function. In conclusion, we propose a multi-faceted approach to habit learning and its relationship to the basal ganglia, emphasizing the need for formal definitions that will provide directions for future research.
Keywords: automaticity; basal ganglia; habit learning; reward.
Figures
Figure 1
The fractionation of long-term memory proposed by Squire and Zola-Morgan. Redrawn based on Squire and Zola-Morgan (1991).
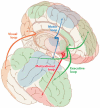
Figure 2
Corticostriatal loops.
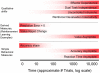
Figure 3
Comparison of various possible criteria for habit learning that develop across learning on the basis of approximate point in training at which learning becomes habitual. Note that only criteria that can develop across training are included; criteria that are required across the entire time course of learning (unconscious, inflexible) are not. Top section: Qualitative criteria including two operational definitions of automaticity, and reinforcer devaluation. Middle and Bottom section: possible operational definitions of slow or incremental. Middle: Criteria based on computational modeling. This approach is illustrated using reinforcement-learning measures (reward prediction error, and value, or reward prediction) although other approaches can also be used. Bottom: Commonly used simple behavioral measures of learning.
Similar articles
- The Aristotelian conception of habit and its contribution to human neuroscience.
Bernacer J, Murillo JI. Bernacer J, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 Nov 3;8:883. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00883. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25404908 Free PMC article. - Cortical and basal ganglia contributions to habit learning and automaticity.
Ashby FG, Turner BO, Horvitz JC. Ashby FG, et al. Trends Cogn Sci. 2010 May;14(5):208-15. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Trends Cogn Sci. 2010. PMID: 20207189 Free PMC article. Review. - Habit learning in Tourette syndrome: a translational neuroscience approach to a developmental psychopathology.
Marsh R, Alexander GM, Packard MG, Zhu H, Wingard JC, Quackenbush G, Peterson BS. Marsh R, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004 Dec;61(12):1259-68. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.12.1259. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15583117 - Habit learning in hierarchical cortex-basal ganglia loops.
Baladron J, Hamker FH. Baladron J, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2020 Dec;52(12):4613-4638. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14730. Epub 2020 May 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32237250 - Brain substrates for automatic retrieval of value memory in the primate basal ganglia.
Kim HF. Kim HF. Mol Brain. 2021 Nov 16;14(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00871-x. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34784931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Comparative Perspective on the Cerebello-Cerebral System and Its Link to Cognition.
Magielse N, Heuer K, Toro R, Schutter DJLG, Valk SL. Magielse N, et al. Cerebellum. 2023 Dec;22(6):1293-1307. doi: 10.1007/s12311-022-01495-0. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Cerebellum. 2023. PMID: 36417091 Free PMC article. Review. - Impaired acquisition of goal-directed action in healthy aging.
de Wit S, van de Vijver I, Ridderinkhof KR. de Wit S, et al. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014 Jun;14(2):647-58. doi: 10.3758/s13415-014-0288-5. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24796599 - Ethanol seeking by Long Evans rats is not always a goal-directed behavior.
Mangieri RA, Cofresí RU, Gonzales RA. Mangieri RA, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042886. Epub 2012 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22870342 Free PMC article. - Changes in global functional network properties predict individual differences in habit formation.
Wang X, Zwosta K, Wolfensteller U, Ruge H. Wang X, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 Mar;44(4):1565-1578. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26158. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 36413054 Free PMC article. - Acquisition of habitual visual attention and transfer to related tasks.
Salovich NA, Remington RW, Jiang YV. Salovich NA, et al. Psychon Bull Rev. 2018 Jun;25(3):1052-1058. doi: 10.3758/s13423-017-1341-5. Psychon Bull Rev. 2018. PMID: 28698989 Free PMC article.
References
- Anderson J. R. (1982). Acquisition of cognitive skill. Psychol. Rev. 89, 369–40610.1037/0033-295X.89.4.369 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources