Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2011 Sep 18;43(10):977-83.
doi: 10.1038/ng.943.
Collaborators, Affiliations
- PMID: 21926972
- PMCID: PMC3637176
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.943
Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4
Psychiatric GWAS Consortium Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Nat Genet. 2011.
Erratum in
- Nat Genet. 2012 Sep;44(9):1072. Fullerton, Janice M [added]; Hyoun, Phil L [corrected to Lee, Phil H]; Meng, Fan Guo [corrected to Meng, Fan]
Abstract
We conducted a combined genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 7,481 individuals with bipolar disorder (cases) and 9,250 controls as part of the Psychiatric GWAS Consortium. Our replication study tested 34 SNPs in 4,496 independent cases with bipolar disorder and 42,422 independent controls and found that 18 of 34 SNPs had P < 0.05, with 31 of 34 SNPs having signals with the same direction of effect (P = 3.8 × 10(-7)). An analysis of all 11,974 bipolar disorder cases and 51,792 controls confirmed genome-wide significant evidence of association for CACNA1C and identified a new intronic variant in ODZ4. We identified a pathway comprised of subunits of calcium channels enriched in bipolar disorder association intervals. Finally, a combined GWAS analysis of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder yielded strong association evidence for SNPs in CACNA1C and in the region of NEK4-ITIH1-ITIH3-ITIH4. Our replication results imply that increasing sample sizes in bipolar disorder will confirm many additional loci.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL STATEMENT
We have no competing financial interests.
Figures
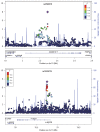
Figure 1
Results are shown as –log10(P value) for genotyped and imputed SNPs. The most associated SNP in the primary analysis is shown as the small purple triangle. The most associated SNP in the combined analysis is shown as the large purple triangle. The color of the remaining markers reflects r2 with the most associated SNP. The recombination rate from CEU HapMap (second y axis) is plotted in light blue.
Similar articles
- Genome-wide significant associations in schizophrenia to ITIH3/4, CACNA1C and SDCCAG8, and extensive replication of associations reported by the Schizophrenia PGC.
Hamshere ML, Walters JT, Smith R, Richards AL, Green E, Grozeva D, Jones I, Forty L, Jones L, Gordon-Smith K, Riley B, O'Neill FA, Kendler KS, Sklar P, Purcell S, Kranz J; Schizophrenia Psychiatric Genome-wide Association Study Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium+; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Morris D, Gill M, Holmans P, Craddock N, Corvin A, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC. Hamshere ML, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Jun;18(6):708-12. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.67. Epub 2012 May 22. Mol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22614287 Free PMC article. - Replication of bipolar disorder susceptibility alleles and identification of two novel genome-wide significant associations in a new bipolar disorder case-control sample.
Green EK, Hamshere M, Forty L, Gordon-Smith K, Fraser C, Russell E, Grozeva D, Kirov G, Holmans P, Moran JL, Purcell S, Sklar P, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC, Jones L; WTCCC; Jones IR, Craddock N. Green EK, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2013 Dec;18(12):1302-7. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.142. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23070075 Free PMC article. - Identification of risk loci with shared effects on five major psychiatric disorders: a genome-wide analysis.
Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Lancet. 2013 Apr 20;381(9875):1371-1379. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62129-1. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23453885 Free PMC article. - What is the impact of genome-wide supported risk variants for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder on brain structure and function? A systematic review.
Gurung R, Prata DP. Gurung R, et al. Psychol Med. 2015;45(12):2461-80. doi: 10.1017/S0033291715000537. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Psychol Med. 2015. PMID: 25858580 Review. - Genetics of bipolar disorder.
Craddock N, Sklar P. Craddock N, et al. Lancet. 2013 May 11;381(9878):1654-62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60855-7. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23663951 Review.
Cited by
- From trans to cis: transcriptional regulatory networks in neocortical development.
Shibata M, Gulden FO, Sestan N. Shibata M, et al. Trends Genet. 2015 Feb;31(2):77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.12.004. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Trends Genet. 2015. PMID: 25624274 Free PMC article. Review. - DNA methylation meta-analysis reveals cellular alterations in psychosis and markers of treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
Hannon E, Dempster EL, Mansell G, Burrage J, Bass N, Bohlken MM, Corvin A, Curtis CJ, Dempster D, Di Forti M, Dinan TG, Donohoe G, Gaughran F, Gill M, Gillespie A, Gunasinghe C, Hulshoff HE, Hultman CM, Johansson V, Kahn RS, Kaprio J, Kenis G, Kowalec K, MacCabe J, McDonald C, McQuillin A, Morris DW, Murphy KC, Mustard CJ, Nenadic I, O'Donovan MC, Quattrone D, Richards AL, Rutten BP, St Clair D, Therman S, Toulopoulou T, Van Os J, Waddington JL; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC); CRESTAR consortium; Sullivan P, Vassos E, Breen G, Collier DA, Murray RM, Schalkwyk LS, Mill J. Hannon E, et al. Elife. 2021 Feb 26;10:e58430. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58430. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33646943 Free PMC article. - Genetic and functional analyses implicate microRNA 499A in bipolar disorder development.
Tielke A, Martins H, Pelzl MA, Maaser-Hecker A, David FS, Reinbold CS, Streit F, Sirignano L, Schwarz M, Vedder H, Kammerer-Ciernioch J, Albus M, Borrmann-Hassenbach M, Hautzinger M, Hünten K, Degenhardt F, Fischer SB, Beins EC, Herms S, Hoffmann P, Schulze TG, Witt SH, Rietschel M, Cichon S, Nöthen MM, Schratt G, Forstner AJ. Tielke A, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 7;12(1):437. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02176-6. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36207305 Free PMC article. - Predicting Cognitive Executive Functioning with Polygenic Risk Scores for Psychiatric Disorders.
Benca CE, Derringer JL, Corley RP, Young SE, Keller MC, Hewitt JK, Friedman NP. Benca CE, et al. Behav Genet. 2017 Jan;47(1):11-24. doi: 10.1007/s10519-016-9814-2. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Behav Genet. 2017. PMID: 27743041 Free PMC article. - Identification of Susceptible Loci and Enriched Pathways for Bipolar II Disorder Using Genome-Wide Association Studies.
Kao CF, Chen HW, Chen HC, Yang JH, Huang MC, Chiu YH, Lin SK, Lee YC, Liu CM, Chuang LC, Chen CH, Wu JY, Lu RB, Kuo PH. Kao CF, et al. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Dec 3;19(12):pyw064. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw064. Print 2016 Dec. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27450446 Free PMC article.
References
- Craddock N, Sklar P. Genetics of bipolar disorder: successful start to a long journey. Trends Genet. 2009;25:99–105. - PubMed
- Cardno AG, et al. Heritability estimates for psychotic disorders: the Maudsley twin psychosis series. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:162–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH078151/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH080372/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071681/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083738/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081804/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MH080372/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54RR025204/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH094421/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH078151/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0701003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0701007/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093500-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G1000708/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MH081804/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080403/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG005827/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous