Effect of melatonin on nocturnal blood pressure: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Effect of melatonin on nocturnal blood pressure: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ehud Grossman et al. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011.
Abstract
Background: Patients with nocturnal hypertension are at higher risk for cardiovascular complications such as myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular insult. Published studies inconsistently reported decreases in nocturnal blood pressure with melatonin.
Methods: A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of exogenous melatonin in ameliorating nocturnal blood pressure was performed using a random effects model of all studies fitting the inclusion criteria, with subgroup analysis of fast-release versus controlled-release preparations.
Results: Seven trials (three of controlled-release and four of fast-release melatonin) with 221 participants were included. Meta-analysis of all seven studies did not reveal significant effects of melatonin versus placebo on nocturnal blood pressure. However, subgroup analysis revealed that controlled-release melatonin significantly reduced nocturnal blood pressure whereas fast-release melatonin had no effect. Systolic blood pressure decreased significantly with controlled-release melatonin (-6.1 mmHg; 95% confidence interval [CI] -10.7 to -1.5; P = 0.009) but not fast-release melatonin (-0.3 mmHg; 95% CI -5.9 to 5.30; P = 0.92). Diastolic blood pressure also decreased significantly with controlled-release melatonin (-3.5 mmHg; 95% CI -6.1 to -0.9; P = 0.009) but not fast-release melatonin (-0.2 mmHg; 95% CI -3.8 to 3.3; P = 0.89). No safety concerns were raised.
Conclusion: Add-on controlled-release melatonin to antihypertensive therapy is effective and safe in ameliorating nocturnal hypertension, whereas fast-release melatonin is ineffective. It is necessary that larger trials of longer duration be conducted in order to determine the long-term beneficial effects of controlled-release melatonin in patients with nocturnal hypertension.
Keywords: melatonin; meta-analysis; nocturnal blood pressure.
Figures
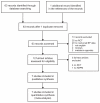
Figure 1
Flowchart of the study selection process.
Figure 2
Effect of FR and CR-melatonin on nocturnal systolic/diastolic BP. Effect of FR and CR-melatonin on systolic blood pressure (left panel) and diastolic blood pressure (right panel). The following parameters are reported: Mean difference (md); Confidence interval (Ci).
Similar articles
- Pharmacological interventions for hypertension in children.
Chaturvedi S, Lipszyc DH, Licht C, Craig JC, Parekh R. Chaturvedi S, et al. Evid Based Child Health. 2014 Sep;9(3):498-580. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1974. Evid Based Child Health. 2014. PMID: 25236305 Review. - Melatonin reduces night blood pressure in patients with nocturnal hypertension.
Grossman E, Laudon M, Yalcin R, Zengil H, Peleg E, Sharabi Y, Kamari Y, Shen-Orr Z, Zisapel N. Grossman E, et al. Am J Med. 2006 Oct;119(10):898-902. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.02.002. Am J Med. 2006. PMID: 17000226 Clinical Trial. - Prolonged melatonin administration decreases nocturnal blood pressure in women.
Cagnacci A, Cannoletta M, Renzi A, Baldassari F, Arangino S, Volpe A. Cagnacci A, et al. Am J Hypertens. 2005 Dec;18(12 Pt 1):1614-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.05.008. Am J Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 16364834 Clinical Trial. - Cochrane in context: pharmacological interventions for hypertension in children.
Chaturvedi S, Lipszyc DH, Licht C, Craig JC, Parekh RS. Chaturvedi S, et al. Evid Based Child Health. 2014 Sep;9(3):581-3. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1975. Evid Based Child Health. 2014. PMID: 25236306 Review. - Controlled-release oral melatonin supplementation for hypertension and nocturnal hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Lee EK, Poon P, Yu CP, Lee VW, Chung VC, Wong SY. Lee EK, et al. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022 May;24(5):529-535. doi: 10.1111/jch.14482. Epub 2022 Apr 7. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022. PMID: 35388609 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Melatonin and Vascular Function.
Mendes L, Queiroz M, Sena CM. Mendes L, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 20;13(6):747. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060747. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929187 Free PMC article. Review. - Hypotensive effects of melatonin in rats: Focus on the model, measurement, application, and main mechanisms.
Cvikova D, Sutovska H, Babarikova K, Molcan L. Cvikova D, et al. Hypertens Res. 2022 Dec;45(12):1929-1944. doi: 10.1038/s41440-022-01031-x. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 36123396 Review. - Cardioprotective Role of Melatonin in Acute Myocardial Infarction.
Fu Z, Jiao Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Shen M, Reiter RJ, Xi Q, Chen Y. Fu Z, et al. Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 29;11:366. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00366. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32411013 Free PMC article. Review. - Melatonin for Atypical Antipsychotic-Induced Metabolic Adverse Effects: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Kamath A, Rather ZA. Kamath A, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2018 Feb 21;2018:4907264. doi: 10.1155/2018/4907264. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29682546 Free PMC article. - Molecular clocks and the human condition: approaching their characterization in human physiology and disease.
Fitzgerald GA, Yang G, Paschos GK, Liang X, Skarke C. Fitzgerald GA, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Sep;17 Suppl 1(0 1):139-42. doi: 10.1111/dom.12526. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. PMID: 26332979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Cuspidi C, Meani S, Salerno M, et al. Cardiovascular target organ damage in essential hypertensives with or without reproducible nocturnal fall in blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2004;22(11):273–280. - PubMed
- Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Gatteschi C, et al. Blunted nocturnal fall in blood pressure in hypertensive women with future cardiovascular morbid events. Circulation. 1993;88(3):986–992. - PubMed
- Brzezinski A. Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(3):186–195. - PubMed
- Sewerynek E. Melatonin and the cardiovascular system. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2002;(Suppl 23):79–83. - PubMed
- Cagnacci A, Arangino S, Angiolucci M, Maschio E, Longu G, Melis G. Potentially beneficial cardiovascular effects of melatonin administration in women. J Pineal Res. 1997;22(1):16–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical