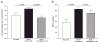Siglec-F inhibition reduces esophageal eosinophilia and angiogenesis in a mouse model of eosinophilic esophagitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Siglec-F inhibition reduces esophageal eosinophilia and angiogenesis in a mouse model of eosinophilic esophagitis
Eitan Rubinstein et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011 Oct.
Abstract
Objectives: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a disorder characterized histologically by tissue eosinophilia. Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec-F) is a receptor highly expressed on mouse eosinophils and mediates eosinophilic apoptosis. We investigated whether administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab would reduce esophageal eosinophilic inflammation and remodeling in a mouse model of egg ovalbumin (OVA)-induced EoE.
Subjects and methods: Three groups of mice were studied (no OVA, OVA + anti-Siglec-F Ab, and OVA + isotype control Ab). Mice were sensitized intraperitoneally and then challenged chronically with intraesophageal OVA. Levels of esophageal eosinophils and features of remodeling (angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor expression, deposition of fibronectin, basal zone hyperplasia, and fibrosis) were quantitated by immunohistochemistry and image analysis.
Results: Administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced levels of esophageal eosinophils, down to levels noted in non-OVA-challenged mice. The anti-Siglec-F Ab also reduced features of OVA-induced remodeling, including angiogenesis, basal zone hyperplasia, and fibronectin deposition. The reduced angiogenesis in anti-Siglec-F Ab-treated mice was associated with reduced numbers of vascular endothelial growth factor-positive cells in the esophagus. The anti-Siglec-F antibody did not significantly reduce esophageal fibrosis as assessed by trichrome staining.
Conclusions: Administration of an anti-Siglec-F antibody significantly decreased the number of eosinophils in the esophagus in a mouse model of OVA-induced EoE. The reduction in eosinophilic inflammation was associated with a significant decrease in levels of angiogenesis, deposition of fibronectin, and basal zone hyperplasia. Studies in this pre-clinical model of EoE suggest that Siglec-F (and its human paralog Siglec-8) may be novel therapeutic targets to reduce eosinophilic inflammation in EoE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
FIGURE 1
Experimental egg OVA EoE protocol. Mice were sensitized intraperitoneally (ip) on day 0 and day 14 and challenged intraesophageally (IE) on days 28, 30, 32, 35, 37, 39, 42, 44, 46, 49, 51, and 53. One hour before each OVA challenge, an anti-Siglec-F or isotype control antibody was administered ip. Mice were sacrificed 24 hours after last administration of intraesophageal OVA (day 54) and their esophagi were analyzed.
FIGURE 2
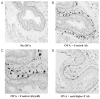
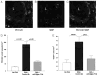
Eosinophils in the esophagus. Hematoxylin and anti-mouse major basic protein immunostain of esophagus. A, No OVA. B, OVA + control Ab. C, OVA + control Ab (40× magnification of panel B). D, OVA + anti-Siglec-F Ab.
FIGURE 3
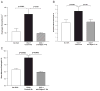
Eosinophil quantitation in esophagus, peripheral blood, and bone marrow. A, Esophagus. The number of eosinophils per square millimeter of esophageal lamina propria was quantitated. Intraesophageal OVA challenge induced a significant accumulation of eosinophils (OVA vs no OVA, P<0.0001). Administration of an anti-Siglec-F antibody to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the number of esophageal eosinophils (_P_= 0.003) to levels similar to those in the no-OVA group (n = 8 mice/group). B, Peripheral blood. The number of eosinophils was quantitated in Wright-Giemsa-stained peripheral blood. A significant increase in the percentage of eosinophils was noted in mice challenged with OVA compared to the non-OVA–exposed group (_P_= 0.0006). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the degree of peripheral blood eosinophilia compared to the group challenged with OVA and administered a control Ab (_P_= 0.04) (n = 16 mice/group). C, Bone marrow. The number of eosinophils was quantitated in Wright-Giemsa-stained bone marrow. A significant increase in the percentage of eosinophils was noted in OVA-challenged mice compared to the non-OVA-exposed group (_P_= 0.0002). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the degree of bone marrow eosinophilia compared to the group challenged with OVA and administered a control Ab (_P_= 0.0002) (n = 8 mice/group).
FIGURE 4
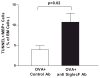
Effect of anti-Siglec-F antibody (Ab) on apoptosis. Bone marrow from mice chronically challenged with oral ovalbumin (OVA) and treated with either an anti-Siglec-F or control Ab was processed for TUNEL staining and the number of TUNEL-positive cells quantitated by immunohistology. The number of TUNEL-positive cells in mice chronically challenged with oral OVA was significantly increased in the bone marrow of anti-Siglec-F Ab compared to control Ab-treated mice (_P_= 0.02).
FIGURE 5
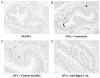
Angiogenesis in the esophagus. Hematoxylin and PECAM immunostain of esophagus. A, No OVA. B, OVA + control Ab. C, OVA + control Ab (40× magnification of panel B). D, OVA + anti-Siglec-F Ab.
FIGURE 6
OVA-induced angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the esophagus. A–C, Detection of cells expressing PECAM and major basic protein (MBP). Esophageal sections from wild-type mice that had been subjected to chronic oral OVA challenge were immunostained with both an anti-PECAM Ab (immunofluoresce green) and an anti-MBP Ab (immunofluoresce red). L indicates esophageal lumen. Arrow in A points to PECAM-positive blood vessel and * indicates PECAM-positive cells, which do not colocalize with MBP (B and C). D, Angiogenesis. A significant increase in the number of small blood vessels was noted in the lamina propria of mice challenged with OVA compared to the non-OVA-exposed group (P<0.001). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the number of small vessels compared with mice challenged with OVA and administered a control Ab (P<0.001). E, VEGF-positive cells. A significant increase in the number of VEGF-positive cells was noted in OVA-challenged mice compared to the non-OVA-exposed group (P<0.004). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the number of VEGF-positive cells compared with the group challenged with OVA and administered a control Ab (P<0.02) (n = 8 mice/group).
FIGURE 7
Esophageal fibronectin deposition and TGF-β1-positive cells. A, Fibronectin. A significant increase in lamina propria fibronectin deposition was noted in OVA-challenged mice compared to the non-OVA-exposed group (_P_= 0.05). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice significantly reduced the amount of fibronectin deposition compared with the group challenged with OVA and administered a control Ab (_P_= 0.0005). B, TGF-β1-positive cells. A significant increase in the number of TGF-β1-positive cells was noted in OVA-challenged mice compared with the non-OVA-exposed group (_P_= 0.0001). The administration of an anti-Siglec-F Ab to OVA-challenged mice resulted in a nonsignificant trend to reduced numbers of TGF-β1-positive cells (_P_= 0.18) (n = 8 mice/group).
Similar articles
- Anti-Siglec-F antibody reduces allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation and airway remodeling.
Song DJ, Cho JY, Lee SY, Miller M, Rosenthal P, Soroosh P, Croft M, Zhang M, Varki A, Broide DH. Song DJ, et al. J Immunol. 2009 Oct 15;183(8):5333-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801421. Epub 2009 Sep 25. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19783675 Free PMC article. - Smad3-deficient mice have reduced esophageal fibrosis and angiogenesis in a model of egg-induced eosinophilic esophagitis.
Cho JY, Doshi A, Rosenthal P, Beppu A, Miller M, Aceves S, Broide D. Cho JY, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014 Jul;59(1):10-6. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000343. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24590208 Free PMC article. - Targeting AMCase reduces esophageal eosinophilic inflammation and remodeling in a mouse model of egg induced eosinophilic esophagitis.
Cho JY, Rosenthal P, Miller M, Pham A, Aceves S, Sakuda S, Broide DH. Cho JY, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Jan;18(1):35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.10.026. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24239745 Free PMC article. - Remodeling and fibrosis in chronic eosinophil inflammation.
Aceves SS. Aceves SS. Dig Dis. 2014;32(1-2):15-21. doi: 10.1159/000357004. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Dig Dis. 2014. PMID: 24603375 Free PMC article. Review. - Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis.
Cheng E, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Cheng E, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Dec 1;303(11):G1175-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00313.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23019192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Siglec-8 antibody reduces eosinophils and mast cells in a transgenic mouse model of eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Youngblood BA, Brock EC, Leung J, Falahati R, Bochner BS, Rasmussen HS, Peterson K, Bebbington C, Tomasevic N. Youngblood BA, et al. JCI Insight. 2019 Oct 3;4(19):e126219. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.126219. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31465299 Free PMC article. - Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis.
Davis BP. Davis BP. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Aug;55(1):19-42. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8665-9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29332138 Review. - Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for eosinophilic esophagitis.
Zaidi AK, Mussarat A, Mishra A. Zaidi AK, et al. Clin Pract (Lond). 2014;11(3):351-367. doi: 10.2217/cpr.14.31. Clin Pract (Lond). 2014. PMID: 25400904 Free PMC article. - The extremely narrow-caliber esophagus is a treatment-resistant subphenotype of eosinophilic esophagitis.
Eluri S, Runge TM, Cotton CC, Burk CM, Wolf WA, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES. Eluri S, et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Jun;83(6):1142-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.11.019. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26608127 Free PMC article. - Divergent Siglec-F(eights) of mouse and human eosinophil death.
Jacobsen EA. Jacobsen EA. J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jul;108(1):9-11. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5CE0520-108R. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32557797 Free PMC article.
References
- Sant’Anna AM, Rolland S, Fournet JC, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: symptoms, histology and pH probe results. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39:373–7. - PubMed
- Rothenberg ME, Mishra A, Collins MH, et al. Pathogenesis and clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:891–4. - PubMed
- Parfitt JR, Gregor JC, Suskin NG, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: distinguishing features from gastroesophageal reflux disease: a study of 41 patients. Mod Pathol. 2006;19:90–6. - PubMed
- Ohno I, Nitta Y, Yamauchi K, et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF beta 1) gene expression by eosinophils in asthmatic airway inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996;15:404–9. - PubMed
- Horiuchi T, Weller PF. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor by human eosinophils: upregulation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997;17:70–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI 38425/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI038425/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI070535/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 70535/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI038425/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057345/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL057345/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI 72115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK07202-33/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical