Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.75.
Andreas Wilm, David Dineen, Toby J Gibson, Kevin Karplus, Weizhong Li, Rodrigo Lopez, Hamish McWilliam, Michael Remmert, Johannes Söding, Julie D Thompson, Desmond G Higgins
Affiliations
- PMID: 21988835
- PMCID: PMC3261699
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2011.75
Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega
Fabian Sievers et al. Mol Syst Biol. 2011.
Abstract
Multiple sequence alignments are fundamental to many sequence analysis methods. Most alignments are computed using the progressive alignment heuristic. These methods are starting to become a bottleneck in some analysis pipelines when faced with data sets of the size of many thousands of sequences. Some methods allow computation of larger data sets while sacrificing quality, and others produce high-quality alignments, but scale badly with the number of sequences. In this paper, we describe a new program called Clustal Omega, which can align virtually any number of protein sequences quickly and that delivers accurate alignments. The accuracy of the package on smaller test cases is similar to that of the high-quality aligners. On larger data sets, Clustal Omega outperforms other packages in terms of execution time and quality. Clustal Omega also has powerful features for adding sequences to and exploiting information in existing alignments, making use of the vast amount of precomputed information in public databases like Pfam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
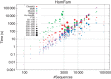
Alignment time for Clustal Omega (red), MAFFT (blue), MUSCLE (green) and Kalign (purple) against the number of sequences of HomFam test sets. Average sequence length is rendered by point size. Both axes have logarithmic scales. Clustal Omega and Kalign were run with default flags over the entire range. MUSCLE was run with –maxiters 2 for _N_>3000 sequences. MAFFT was run with --parttree for _N_>10 000 sequences.
Figure 2
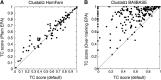
EPA for HomFam and BAliBASE. Points represent TC scores of Clustal Omega alignment with EPA versus TC scores of default Clustal Omega alignment (without EPA). Points above bisectrix represent beneficial effect of EPA, points below deleterious effect. Average improvement in (A) 2.5%. HMMs taken from Pfam, benchmarking carried out using corresponding structure-based alignment in Homstrad. Average improvement in (B) over 30%. Here, test sets and EPA-HMMs were both derived from BAliBASE reference alignments.
Figure 3
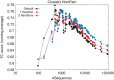
Iteration of HomFam alignments. Points represent cumulative running averages of TC scores. Clustal Omega default results in black, results after 1 iteration in red, after 2 iterations in blue. Iterations are combined HMM/guide tree iterations; x axis, logarithmic and y axis, linear scale.
Similar articles
- Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences.
Sievers F, Higgins DG. Sievers F, et al. Protein Sci. 2018 Jan;27(1):135-145. doi: 10.1002/pro.3290. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Protein Sci. 2018. PMID: 28884485 Free PMC article. - Using CLUSTAL for multiple sequence alignments.
Higgins DG, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ. Higgins DG, et al. Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:383-402. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)66024-8. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8743695 - The Clustal Omega Multiple Alignment Package.
Sievers F, Higgins DG. Sievers F, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2231:3-16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1036-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33289883 - Multiple sequence alignments.
Wallace IM, Blackshields G, Higgins DG. Wallace IM, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Jun;15(3):261-6. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.04.002. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 15963889 Review. - Towards the accurate alignment of over a million protein sequences: Current state of the art.
Santus L, Garriga E, Deorowicz S, Gudyś A, Notredame C. Santus L, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023 Jun;80:102577. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102577. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37012200 Review.
Cited by
- Sustainable production of the drug precursor tyramine by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Poethe SS, Junker N, Meyer F, Wendisch VF. Poethe SS, et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 30;108(1):499. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13319-8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39476177 Free PMC article. - Evolution of the pheV-tRNA integrated genomic island in Escherichia coli.
Nhu NTK, Forde BM, Ben Zakour NL, Phan MD, Roberts LW, Beatson SA, Schembri MA. Nhu NTK, et al. PLoS Genet. 2024 Oct 24;20(10):e1011459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011459. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39446883 Free PMC article. - A putative, novel coli surface antigen 8B (CS8B) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.
Njoroge SM, Boinett CJ, Madé LF, Ouko TT, Fèvre EM, Thomson NR, Kariuki S. Njoroge SM, et al. Pathog Dis. 2015 Oct;73(7):ftv047. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv047. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26187892 Free PMC article. - Variants in GCNA, X-linked germ-cell genome integrity gene, identified in men with primary spermatogenic failure.
Hardy JJ, Wyrwoll MJ, Mcfadden W, Malcher A, Rotte N, Pollock NC, Munyoki S, Veroli MV, Houston BJ, Xavier MJ, Kasak L, Punab M, Laan M, Kliesch S, Schlegel P, Jaffe T, Hwang K, Vukina J, Brieño-Enríquez MA, Orwig K, Yanowitz J, Buszczak M, Veltman JA, Oud M, Nagirnaja L, Olszewska M, O'Bryan MK, Conrad DF, Kurpisz M, Tüttelmann F, Yatsenko AN; GEMINI Consortium. Hardy JJ, et al. Hum Genet. 2021 Aug;140(8):1169-1182. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02287-y. Epub 2021 May 7. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33963445 Free PMC article. - Molecular evolution of translin superfamily proteins within the genomes of eubacteria, archaea and eukaryotes.
Gupta GD, Kale A, Kumar V. Gupta GD, et al. J Mol Evol. 2012 Dec;75(5-6):155-67. doi: 10.1007/s00239-012-9534-z. Epub 2012 Nov 28. J Mol Evol. 2012. PMID: 23188094
References
- Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S (2007) k-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. pp 1027–1035
- Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20: 426–427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases