Antiviral Properties of ISG15 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 Oct;2(10):2154-2168.
doi: 10.3390/v2102154. Epub 2010 Sep 28.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21994614
- PMCID: PMC3185569
- DOI: 10.3390/v2102154
Antiviral Properties of ISG15
Deborah J Lenschow. Viruses. 2010 Oct.
Abstract
The type I interferon system plays a critical role in limiting the spread of viral infection. Viruses induce the production of interferon (IFN), which after binding to the IFN-α/β receptor (IFNAR), and triggering of the JAK/STAT signaling cascade, results in the induction of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). These ISGs function to inhibit viral replication and to regulate the host immune response. Among these ISGs, the ubiquitin-like molecule, ISG15, is one of the most strongly induced proteins. Similar to ubiquitin, through an IFN induced conjugation cascade, ISG15 is covalently linked to a variety of cellular proteins, suggesting regulation of different cellular processes. Studies performed over the past several years have shown that ISG15 plays a central role in the host's antiviral response against many viruses. Mice lacking ISG15 display increased susceptibility to multiple viruses. Furthermore, several viruses have developed immune evasion strategies that directly target the ISG15 pathway. Work is now underway to determine the mechanism by which ISG15 functions as an antiviral molecule, such that therapies targeting this pathway can be developed in the future.
Keywords: ISG15; antiviral; interferon; ubiquitin-like molecule.
Figures
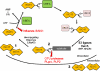
Figure 1
ISG15 conjugation cascade. Following exposure to IFN a cell will upregulate free intracellular ISG15 (1), conjugate ISG15 to target proteins (2), and release ISG15 into the extracellular space (3). Shown in red are the immune evasion strategies utilized by viruses to circumvent the ISG15 pathway.
Similar articles
- Identification of interferon-stimulated gene 15 as an antiviral molecule during Sindbis virus infection in vivo.
Lenschow DJ, Giannakopoulos NV, Gunn LJ, Johnston C, O'Guin AK, Schmidt RE, Levine B, Virgin HW 4th. Lenschow DJ, et al. J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):13974-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.13974-13983.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254333 Free PMC article. - Protein interferon-stimulated gene 15 conjugation delays but does not overcome coronavirus proliferation in a model of fulminant hepatitis.
Ma XZ, Bartczak A, Zhang J, He W, Shalev I, Smil D, Chen L, Phillips J, Feld JJ, Selzner N, Levy G, McGilvray I. Ma XZ, et al. J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):6195-204. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03801-13. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24648452 Free PMC article. - IFN-stimulated gene 15 functions as a critical antiviral molecule against influenza, herpes, and Sindbis viruses.
Lenschow DJ, Lai C, Frias-Staheli N, Giannakopoulos NV, Lutz A, Wolff T, Osiak A, Levine B, Schmidt RE, García-Sastre A, Leib DA, Pekosz A, Knobeloch KP, Horak I, Virgin HW 4th. Lenschow DJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 23;104(4):1371-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607038104. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17227866 Free PMC article. - ISG15 in antiviral immunity and beyond.
Perng YC, Lenschow DJ. Perng YC, et al. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018 Jul;16(7):423-439. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0020-5. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29769653 Free PMC article. Review. - How ISG15 combats viral infection.
Freitas BT, Scholte FEM, Bergeron É, Pegan SD. Freitas BT, et al. Virus Res. 2020 Sep;286:198036. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198036. Epub 2020 May 31. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32492472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) restricts Zika virus replication in primary human corneal epithelial cells.
Singh PK, Singh S, Farr D, Kumar A. Singh PK, et al. Ocul Surf. 2019 Jul;17(3):551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Ocul Surf. 2019. PMID: 30905842 Free PMC article. - One Step Ahead: Herpesviruses Light the Way to Understanding Interferon-Stimulated Genes (ISGs).
Gonzalez-Perez AC, Stempel M, Chan B, Brinkmann MM. Gonzalez-Perez AC, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 7;11:124. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00124. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117146 Free PMC article. Review. - Zebrafish ISG15 exerts a strong antiviral activity against RNA and DNA viruses and regulates the interferon response.
Langevin C, van der Aa LM, Houel A, Torhy C, Briolat V, Lunazzi A, Harmache A, Bremont M, Levraud JP, Boudinot P. Langevin C, et al. J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(18):10025-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01294-12. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23824820 Free PMC article. - Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Viral Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 Interacts with a Member of the Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 Pathway.
Jacobs SR, Stopford CM, West JA, Bennett CL, Giffin L, Damania B. Jacobs SR, et al. J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11572-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01482-15. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26355087 Free PMC article. - The ESCRT-Related ATPase Vps4 Is Modulated by Interferon during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.
Cabrera JR, Manivanh R, North BJ, Leib DA. Cabrera JR, et al. mBio. 2019 Mar 5;10(2):e02567-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02567-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30837340 Free PMC article.
References
- Narasimhan J, Wang M, Fu Z, Klein JM, Haas AL, Kim JJ. Crystal structure of the interferon-induced ubiquitin-like protein ISG15. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:27356–27365. - PubMed
- Potter JL, Narasimhan J, Mende-Mueller L, Haas AL. Precursor processing of pro-ISG15/UCRP, an interferon-beta-induced ubiquitin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:25061–25068. - PubMed
- D’Cunha J, Ramanujam S, Wagner RJ, Witt PL, Knight E, Jr, Borden EC. In vitro and in vivo secretion of human ISG15, an IFN-induced immunomodulatory cytokine. J Immunol. 1996;157:4100–4108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous