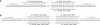Double indexing overcomes inaccuracies in multiplex sequencing on the Illumina platform - PubMed (original) (raw)
Double indexing overcomes inaccuracies in multiplex sequencing on the Illumina platform
Martin Kircher et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan.
Abstract
Due to the increasing throughput of current DNA sequencing instruments, sample multiplexing is necessary for making economical use of available sequencing capacities. A widely used multiplexing strategy for the Illumina Genome Analyzer utilizes sample-specific indexes, which are embedded in one of the library adapters. However, this and similar multiplex approaches come with a risk of sample misidentification. By introducing indexes into both library adapters (double indexing), we have developed a method that reveals the rate of sample misidentification within current multiplex sequencing experiments. With ~0.3% these rates are orders of magnitude higher than expected and may severely confound applications in cancer genomics and other fields requiring accurate detection of rare variants. We identified the occurrence of mixed clusters on the flow as the predominant source of error. The accuracy of sample identification is further impaired if indexed oligonucleotides are cross-contaminated or if indexed libraries are amplified in bulk. Double-indexing eliminates these problems and increases both the scope and accuracy of multiplex sequencing on the Illumina platform.
Figures
Figure 1.
(A) Regular Illumina multiplex library design. The grafting sequences (P5 and P7) are used for template immobilization and amplification. Three distinct sequence reads (forward read, index read, reverse read) are primed from different adapter sites. (B) Double-index library design with an additional index incorporated into the second adapter. Here, four distinct sequence reads are performed.
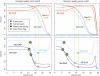
Figure 2.
Changes in the fraction of false (blue) and correct (red) index pairs when applying two different types of base quality filters on the index reads (minimum accepted quality score and average quality score). The fraction remaining after PF is indicated by a green ‘sun’ symbol. Black circles denote the fraction of reads remaining when considering quality score cutoffs that remove just a little bit less raw data than the Pass Filter flag (green lines, ~20% of the data). Both filter criteria remove considerably more false pairs. While no-CAP, SP-CAP and MP-CAP show similar trajectories, the fraction of false pairs is always considerably higher for the MP-CAP experiment, in which samples have been enriched and amplified in a multiplex setup. Quality score cutoffs for the SP-CAP experiment are lower than for the other two experiments due to the 40% higher cluster density of this experiment.
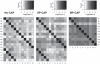
Figure 3.
Heat map with the counts observed for all index combinations in the experiments no-CAP, SP-CAP and MP-CAP after applying a minimum quality score filter of 15 to the index reads. Only indexes that were actually used in the experiments are plotted; forward indexes on the horizontal and reverse indexes on the vertical axis. Color frequencies are provided for each of the experiments in the top right graphs.
Similar articles
- A novel ultra high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing library preparation method for the Illumina HiSeq platform.
de Muinck EJ, Trosvik P, Gilfillan GD, Hov JR, Sundaram AYM. de Muinck EJ, et al. Microbiome. 2017 Jul 6;5(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0279-1. Microbiome. 2017. PMID: 28683838 Free PMC article. - Incorporation of unique molecular identifiers in TruSeq adapters improves the accuracy of quantitative sequencing.
Hong J, Gresham D. Hong J, et al. Biotechniques. 2017 Nov 1;63(5):221-226. doi: 10.2144/000114608. Biotechniques. 2017. PMID: 29185922 Free PMC article. - Report on the effects of fragment size, indexing, and read length on HLA sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq.
Profaizer T, Coonrod EM, Delgado JC, Kumánovics A. Profaizer T, et al. Hum Immunol. 2015 Dec;76(12):897-902. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Hum Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26303189 - Massively parallel sequencing approaches for characterization of structural variation.
Koboldt DC, Larson DE, Chen K, Ding L, Wilson RK. Koboldt DC, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;838:369-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-507-7_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22228022 Free PMC article. Review. - Best Practices for Illumina Library Preparation.
Bronner IF, Quail MA. Bronner IF, et al. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019 Jun;102(1):e86. doi: 10.1002/cphg.86. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31216112 Review.
Cited by
- Evidence for early dispersal of domestic sheep into Central Asia.
Taylor WTT, Pruvost M, Posth C, Rendu W, Krajcarz MT, Abdykanova A, Brancaleoni G, Spengler R, Hermes T, Schiavinato S, Hodgins G, Stahl R, Min J, Alisher Kyzy S, Fedorowicz S, Orlando L, Douka K, Krivoshapkin A, Jeong C, Warinner C, Shnaider S. Taylor WTT, et al. Nat Hum Behav. 2021 Sep;5(9):1169-1179. doi: 10.1038/s41562-021-01083-y. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Nat Hum Behav. 2021. PMID: 33833423 - Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe.
Haak W, Lazaridis I, Patterson N, Rohland N, Mallick S, Llamas B, Brandt G, Nordenfelt S, Harney E, Stewardson K, Fu Q, Mittnik A, Bánffy E, Economou C, Francken M, Friederich S, Pena RG, Hallgren F, Khartanovich V, Khokhlov A, Kunst M, Kuznetsov P, Meller H, Mochalov O, Moiseyev V, Nicklisch N, Pichler SL, Risch R, Rojo Guerra MA, Roth C, Szécsényi-Nagy A, Wahl J, Meyer M, Krause J, Brown D, Anthony D, Cooper A, Alt KW, Reich D. Haak W, et al. Nature. 2015 Jun 11;522(7555):207-11. doi: 10.1038/nature14317. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25731166 Free PMC article. - Genomic portrait and relatedness patterns of the Iron Age Log Coffin culture in northwestern Thailand.
Carlhoff S, Kutanan W, Rohrlach AB, Posth C, Stoneking M, Nägele K, Shoocongdej R, Krause J. Carlhoff S, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 22;14(1):8527. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44328-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38135688 Free PMC article. - Redefining the treponemal history through pre-Columbian genomes from Brazil.
Majander K, Pla-Díaz M, du Plessis L, Arora N, Filippini J, Pezo-Lanfranco L, Eggers S, González-Candelas F, Schuenemann VJ. Majander K, et al. Nature. 2024 Mar;627(8002):182-188. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06965-x. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38267579 Free PMC article. - Taxon Appearance From Extraction and Amplification Steps Demonstrates the Value of Multiple Controls in Tick Microbiota Analysis.
Lejal E, Estrada-Peña A, Marsot M, Cosson JF, Rué O, Mariadassou M, Midoux C, Vayssier-Taussat M, Pollet T. Lejal E, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 9;11:1093. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01093. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32655509 Free PMC article.
References
- Shendure J, Porreca GJ, Reppas NB, Lin X, McCutcheon JP, Rosenbaum AM, Wang MD, Zhang K, Mitra RD, Church GM. Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome. Science. 2005;309:1728–1732. - PubMed
- Harris TD, Buzby PR, Babcock H, Beer E, Bowers J, Braslavsky I, Causey M, Colonell J, Dimeo J, Efcavitch JW, et al. Single-molecule DNA sequencing of a viral genome. Science. 2008;320:106–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources