Artificial pancreas: past, present, future - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Artificial pancreas: past, present, future
Claudio Cobelli et al. Diabetes. 2011 Nov.
No abstract available
Figures
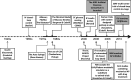
FIG. 1.
The Biostator (courtesy of William Clarke, University of Virginia).
FIG. 2.
Key milestones in the timeline of AP progress. EU, Europe; IP, intraperitoneal; NIH, National Institutes of Health; SC, subcutaneous.
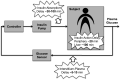
FIG. 3.
Block diagram of closed-loop glucose control. Three major delays are indicated: insulin absorption (regular and ultrafast insulin), insulin action on peripheral tissues and on the liver, and sensing in the interstitium.
FIG. 4.
A: The concept of MPC. At each step, future glucose levels are predicted and insulin delivery strategy is mapped several steps ahead. Then, the first insulin delivery step is implemented, and the situation is reassessed with new glucose data. The process is very similar to a chess game in which several moves are planned ahead, and after the implementation of the first move the position is reassessed given the response of the opponent. B: The critical stage of the famous chess game between Leonid Stein (white) and Lajos Portisch (black), Stockholm, 1962 (courtesy of Leon Fahri, University of Virginia).
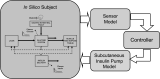
FIG. 5.
Principal component of the type 1 diabetes simulator: a model of the glucose-insulin system, a model of the sensor, a model of the insulin pump and subcutaneous insulin kinetics, and the controller to be tested.
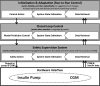
FIG. 6.
Modular architecture for sequential AP development.
Similar articles
- Insulin Infusion Sets and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensors: Where the Artificial Pancreas Meets the Patient.
Forlenza GP. Forlenza GP. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017 Apr;19(4):206-208. doi: 10.1089/dia.2017.0048. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28418732 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - The artificial pancreas: how close are we to closing the loop?
Clarke WL, Kovatchev B. Clarke WL, et al. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2007 Jun;4(4):314-6. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17643078 No abstract available. - Closing the Loop.
Nimri R, Yakoob H, Schoenberg B, Dassau E. Nimri R, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016 Feb;18 Suppl 1:S29-42. doi: 10.1089/dia.2016.2504. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26836427 Review. No abstract available. - Semi-closed-loop insulin delivery systems: early experience with low-glucose insulin suspend pumps.
Pickup JC. Pickup JC. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011 Jul;13(7):695-8. doi: 10.1089/dia.2011.0103. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21668344 No abstract available. - Automated insulin pump suspension for hypoglycaemia mitigation: development, implementation and implications.
Davis T, Salahi A, Welsh JB, Bailey TS. Davis T, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Dec;17(12):1126-32. doi: 10.1111/dom.12542. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. PMID: 26179879 Review.
Cited by
- Reinforcement Learning: A Paradigm Shift in Personalized Blood Glucose Management for Diabetes.
Dénes-Fazakas L, Szilágyi L, Kovács L, De Gaetano A, Eigner G. Dénes-Fazakas L, et al. Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 21;12(9):2143. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092143. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335656 Free PMC article. - Data-driven blood glucose level prediction in type 1 diabetes: a comprehensive comparative analysis.
Nemat H, Khadem H, Elliott J, Benaissa M. Nemat H, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 19;14(1):21863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70277-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39300118 Free PMC article. - Equivalent Electrical Circuit Approach to Enhance a Transducer for Insulin Bioavailability Assessment.
Mancino F, Nouri H, Moccaldi N, Arpaia P, Kanoun O. Mancino F, et al. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2024 Jul 8;12:533-541. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2024.3425269. eCollection 2024. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2024. PMID: 39155919 Free PMC article. - Advancements in Insulin Pumps: A Comprehensive Exploration of Insulin Pump Systems, Technologies, and Future Directions.
Rimon MTI, Hasan MW, Hassan MF, Cesmeci S. Rimon MTI, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 15;16(7):944. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070944. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065641 Free PMC article. Review. - Enhanced blood glucose levels prediction with a smartwatch.
Pikulin S, Yehezkel I, Moskovitch R. Pikulin S, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Jul 18;19(7):e0307136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307136. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39024327 Free PMC article.
References
- Kadish AH. Automation control of blood sugar. I. A servomechanism for glucose monitoring and control. Am J Med Electron 1964;3:82–86 - PubMed
- Albisser AM, Leibel BS, Ewart TG, Davidovac Z, Botz CK, Zingg W. An artificial endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 1974;23:389–396 - PubMed
- Pfeiffer EF, Thum C, Clemens AH. The artificial beta cell—a continuous control of blood sugar by external regulation of insulin infusion (glucose controlled insulin infusion system). Horm Metab Res 1974;6:339–342 - PubMed
- Mirouze J, Selam JL, Pham TC, Cavadore D. Evaluation of exogenous insulin homoeostasis by the artificial pancreas in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetologia 1977;13:273–278 - PubMed
- Kraegen EW, Campbell LV, Chia YO, Meler H, Lazarus L. Control of blood glucose in diabetics using an artificial pancreas. Aust N Z J Med 1977;7:280–286 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous