Effect of honey on Streptococcus mutans growth and biofilm formation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effect of honey on Streptococcus mutans growth and biofilm formation
Hani M Nassar et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jan.
Abstract
Because of the tradition of using honey as an antimicrobial medicament, we investigated the effect of natural honey (NH) on Streptococcus mutans growth, viability, and biofilm formation compared to that of an artificial honey (AH). AH contained the sugars at the concentrations reported for NH. NH and AH concentrations were obtained by serial dilution with tryptic soy broth (TSB). Several concentrations of NH and AH were tested for inhibition of bacterial growth, viability, and biofilm formation after inoculation with S. mutans UA159 in 96-well microtiter plates to obtain absorbance and CFU values. Overall, NH supported significantly less (P < 0.05) bacterial growth than AH at 25 and 12.5% concentrations. At 50 and 25% concentrations, both honey groups provided significantly less bacterial growth and biofilm formation than the TSB control. For bacterial viability, the results for all honey concentrations except 50% NH were not significantly different from those for the TSB control. NH was able to decrease the maximum velocity of S. mutans growth compared to AH. In summary, NH demonstrated more inhibition of bacterial growth, viability, and biofilm formation than AH. This study highlights the potential antibacterial properties of NH and could suggest that the antimicrobial mechanism of NH is not solely due to its high sugar content.
Figures
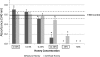
Fig 1
S. mutans planktonic and biofilm cell growth absorbance values for NH and AH concentrations. The absorbance values of the 50% NH- and 50% AH-treated cultures as well as the 25% NH-treated culture were below 0.001. Horizontal lines, means and SEs of the TSB control; error bars, SEs; asterisks, significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) from the TSB control; boxed concentrations, significant difference between NH and AH groups for a specific concentration.
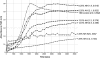
Fig 2
S. mutans growth curves for NH and AH concentrations compared to the TSB control. The graph shows absorbance values over a period of 12.5 h (45,000 s). Numbers in brackets next to groups indicate mean _V_max and mean maximum absorbance, respectively. An asterisk indicates that _V_max and maximum absorbance could not be calculated due to the influence of the high absorbance values of NH at 25% (N/A, not available). Note that there was no bacterial growth at this concentration.
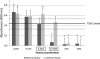
Fig 3
S. mutans biofilm formation absorbance values for NH and AH concentrations after staining with crystal violet. Horizontal lines, means and SEs of the TSB control; error bars, SEs; asterisks, significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) from TSB control; boxed concentrations, significant difference between NH and AH groups for a specific concentration.
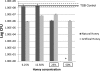
Fig 4
S. mutans viability presented as numbers of CFU in a logarithmic scale of selected concentrations of NH and AH. The viability of the 50% NH-treated sample was almost zero. Horizontal lines, means and SEs of the TSB control; error bars, SEs; asterisks, significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) from the TSB control; boxed concentrations, significant difference between NH and AH groups for a specific concentration.
Fig 5
S. mutans XTT viability assay absorbance values for NH, AH, and TSBS. Horizontal lines, means and SEs of the 1% TSBS control; error bars, SEs; asterisks, significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) from the 1% TSBS control. Groups with different letters were significantly different (P ≤ 0.05). Comparisons were made between solutions with the same concentration.
Similar articles
- In vitro Cariostatic effects of cinnamon water extract on nicotine-induced Streptococcus mutans biofilm.
Alshahrani AM, Gregory RL. Alshahrani AM, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Feb 11;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-2840-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32046702 Free PMC article. - Effect of Commonly Prescribed Liquid Medications on Streptococcus mutans Biofilm. An in vitro study.
Clark SA, Vinson LA, Eckert G, Gregory RL. Clark SA, et al. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017;41(2):141-146. doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-41.2.141. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017. PMID: 28288290 - Effect of γ-lactones and γ-lactams compounds on Streptococcus mutans biofilms.
Sordi MB, Moreira TA, Montero JFD, Barbosa LC, Benfatti CAM, Magini RS, Pimenta AL, Souza JCM. Sordi MB, et al. J Appl Oral Sci. 2018;26:e20170065. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2017-0065. Epub 2018 Feb 22. J Appl Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 29489934 Free PMC article. - Antibacterial activity of disodium succinoyl glycyrrhetinate, a derivative of glycyrrhetinic acid against Streptococcus mutans.
Yamashita T, Kawada-Matsuo M, Katsumata T, Watanabe A, Oogai Y, Nishitani Y, Miyawaki S, Komatsuzawa H. Yamashita T, et al. Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Jul;63(7):251-260. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12717. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31166029 - Antibacterial activities of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) against planktonic and biofilm growing Streptococcus mutans.
Sun M, Dong J, Xia Y, Shu R. Sun M, et al. Microb Pathog. 2017 Jun;107:212-218. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.03.040. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28373143
Cited by
- Biofilm sensitivity of seven Streptococcus mutans strains to different fluoride levels.
Nassar HM, Gregory RL. Nassar HM, et al. J Oral Microbiol. 2017 Jun 12;9(1):1328265. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2017.1328265. eCollection 2017. J Oral Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28748032 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of Brazilian organic honey against oral microorganisms.
Romário-Silva D, Franchin M, Alencar SM, Bueno-Silva B, de Cássia Orlandi Sardi J, da Silva ACB, Cruz-Vieira F, da Silva PV, Rosalen PL. Romário-Silva D, et al. Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;55(3):2285-2292. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01343-9. Epub 2024 May 15. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38744770 - Potential antibacterial activity of some Saudi Arabia honey.
Hegazi AG, Guthami FM, Gethami AF, Allah FM, Saleh AA, Fouad EA. Hegazi AG, et al. Vet World. 2017 Feb;10(2):233-237. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.233-237. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28344408 Free PMC article. - Effects of artificial honey and epigallocatechin-3-gallate on streptococcus pyogenes.
Jiang X, Lin A, Li S, Shi Y, Zhou F, Felix Gomez GG, Gregory RL, Zhang C, Chen S, Huang R. Jiang X, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2022 Aug 26;22(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02611-0. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36028794 Free PMC article. - The Antibacterial Properties of Polish Honey against _Streptococcus mutans_-A Causative Agent of Dental Caries.
Grabek-Lejko D, Hyrchel T. Grabek-Lejko D, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;12(11):1640. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111640. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998842 Free PMC article.
References
- Allen KL, Molan PC, Reid GM. 1991. A survey of the antibacterial activity of some New Zealand honeys. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 43:817–822 - PubMed
- Aristotle 1910 (350 BC). Historia animalium. In Smith JA, Ross WD. (ed), The works of Aristotle. Oxford University, Oxford, United Kingdom: (Translated by Thompson DAW.)
- Autio-Gold J. 2008. The role of chlorhexidine in caries prevention. Oper. Dent. 33:710–716 - PubMed
- Badet C, Quero F. 2011. The in vitro effect of manuka honeys on growth and adherence of oral bacteria. Anaerobe 17:19–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical