Atg8 transfer from Atg7 to Atg3: a distinctive E1-E2 architecture and mechanism in the autophagy pathway - PubMed (original) (raw)
Atg8 transfer from Atg7 to Atg3: a distinctive E1-E2 architecture and mechanism in the autophagy pathway
Asad M Taherbhoy et al. Mol Cell. 2011.
Abstract
Atg7 is a noncanonical, homodimeric E1 enzyme that interacts with the noncanonical E2 enzyme, Atg3, to mediate conjugation of the ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) Atg8 during autophagy. Here we report that the unique N-terminal domain of Atg7 (Atg7(NTD)) recruits a unique "flexible region" from Atg3 (Atg3(FR)). The structure of an Atg7(NTD)-Atg3(FR) complex reveals hydrophobic residues from Atg3 engaging a conserved groove in Atg7, important for Atg8 conjugation. We also report the structure of the homodimeric Atg7 C-terminal domain, which is homologous to canonical E1s and bacterial antecedents. The structures, SAXS, and crosslinking data allow modeling of a full-length, dimeric (Atg7~Atg8-Atg3)(2) complex. The model and biochemical data provide a rationale for Atg7 dimerization: Atg8 is transferred in trans from the catalytic cysteine of one Atg7 protomer to Atg3 bound to the N-terminal domain of the opposite Atg7 protomer within the homodimer. The studies reveal a distinctive E1~UBL-E2 architecture for enzymes mediating autophagy.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
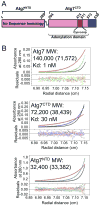
Figure 1. Homodimerization of Atg7 via Atg7CTD
A) Schematic of Atg7 showing positions of NTD and CTD [adenylation domain, Cys-loop, extreme C-terminal domain (ECTD)]. B) Sedimentation equilibrium AUC data for Atg7, Atg7CTD, and Atg7NTD. Molecular weight (MW) was determined using sedimentation velocity AUC, with theoretical values in parenthesis.
Figure 2. Structure of Atg7CTD: structural similarity among E1 adenylation domains
A) Structure of crystallographic Atg7CTD homodimer, with one protomer colored as in Figure 1A, and the other in gray. B) Structural comparison of Atg7CTD adenylation domain with those of MoeB, ThiF, and E1s for ubiquitin (UBA1), NEDD8 (NAE1-UBA3), and SUMO (SAE1-UBA2), depicted without Cys-loops/domains for clarity, with cognate UBLs in corresponding colors below (Huang et al., 2007; Lake et al., 2001; Lee and Schindelin, 2008; Lehmann et al., 2006; Lois and Lima, 2005; Noda et al., 2008). UBA1 (ubiquitin E1) is one polypeptide, but represented according to N- and C-terminal halves. Atg8's C-terminal tail is missing in the structure and is therefore depicted as a dashed line. PDB codes are shown below each structure. C) Model of Atg7CTD (adenylation domain)-Atg8-ATP based on superposition with MoeB-MoaD-ATP (Lake et al., 2001) compared with other E1-UBL structures +/- ATP. PDB codes are shown below each structure.
Figure 3. Roles of Atg7NTD and Atg3FR in Atg7-Atg3 interactions
A) Schematic of Atg3, highlighting location of flexible-region (FR). B) ITC data for binding between indicated Atg7 and Atg3 constructs. Upper panels - raw power data from titrations. Lower panels - fits of standard binding equations using MicroCal software. C) Summary of thermodynamic parameters determined by ITC. N value is based on total concentration, not of homodimers. Error ranges refer to standard deviation.
Figure 4. Structural basis for Atg7NTD-Atg3FRpep interaction
A) Structure of Atg7NTD (pink)-Atg3FRpep (cyan). B) Residues involved in Atg7NTD (pink, semi-transparent surface)-Atg3FRpep (cyan) interaction are shown in sticks. Oxygens are colored red, nitrogens blue, and sulfurs yellow. C) Pull-downs from E. coli co-expressing wild-type (WT) and mutant versions of Atg7NTD and Atg3FR. LM→A = Atg3(L135A, M139A); LI→A = Atg3(L135A, I141A); and MI→A = Atg3(M139A, I141A). D) Pulse-chase assays showing time courses of [32P]Atg8 transfer from indicated versions of Atg7 to Atg3. E) Atg8 lipidation in presence of wild-type (WT), P283D, or catalytic cysteine (C507A) mutant versions of Atg7. * = E. coli nickel-binding Crp and SlyD (Bolanos-Garcia and Davies, 2006) copurifying with Atg12∼Atg5.
Figure 5. Conservation of the Atg7NTD-Atg3FR interaction across species
A) Conservation among Atg7s displayed on the surface of Atg7NTD in complex with Atg3FRpep (cyan) White - 0 conservation; magenta - 100% conservation across species. Leu135, Met139 and Ile141 on Atg3FRpep shown in sticks. B) Pull-downs from E. coli co-expressing indicated versions of mouse Atg7NTD based on conservation with yeast Atg3FR-binding site, and Atg3 or Atg3FR. C) Anti-LC3, Atg12, Atg7, and GADPH (loading control) westerns of lysates of Atg7 null MEFs expressing the indicated versions of GFP-Atg7 treated with chloroquine.
Figure 6. Transthiolation in trans: a working model for transfer of Atg8 from Atg7 to Atg3
A) Analysis of the interference-free SAXS curve for Atg7CTD (gray) and Atg7 (black), with theoretical scattering calculated with FoXS (Schneidman-Duhovny et al., 2010) from crystal structure and atomistic model, respectively, in red (χ2 = 2.1, Atg7CTD; χ2 = 1.5, Atg7). For reference, a poorly fitting theoretical SAXS curve if Atg7CTD were a monomer is shown in green. Inset – Guinier plots indicating aggregation-free data (magenta). B) SEC-MALS data plotted as a molar mass distribution (red) superimposed on chromatogram of differential refractive index as a function of elution volume. Shown is molecular weight (MW) determined by SEC-MALS, with theoretical value in parenthesis. C) Model of homodimeric Atg7 (dark and light pink) bound to two Atg3s (cyan and light blue), with Atg7 and Atg3 catalytic cysteines (green spheres) in close proximity for catalysis. The Cys of the cyan Atg3 bound via its FR to the NTD of the dark pink Atg7 is close to the Cys in the CTD of the light pink Atg7, enabling transthiolation in trans. For clarity, Atg8, which would be transferred from the catalytic Cys of Atg7 to the catalytic Cys of Atg3, is not shown. D) Schematics of wild-type Atg7, and Atg7trans and Atg7cis dimers. Pro283 that binds Atg3FR is cyan and Atg7's catalytic Cys507 is green. Black Xs indicate mutation of Pro283 to Asp or Cys507 to Ala to impair binding of Atg3 or prevent thiolester formation with Atg8, respectively. E) Autoradiogram for time course of transfer of [32P]Atg8 from Atg7 to Atg3. WT - wild-type Atg7 homodimer; trans - Atg7 heterodimer composed of Atg7(P283D) and Atg7(C507A); cis - Atg7 heterodimer composed of wild-type Atg7 and Atg7(P283D, C507A). F) BMOE-crosslinking between Atg3C234only and the indicated variants of Atg7 at concentrations of either 60 or 120 nM, detected by anti-Atg7 western. G) Autoradiogram showing time course of [32P]Atg8 transfer to Atg3 from the indicated versions of Atg7.
Similar articles
- Structural basis of Atg8 activation by a homodimeric E1, Atg7.
Noda NN, Satoo K, Fujioka Y, Kumeta H, Ogura K, Nakatogawa H, Ohsumi Y, Inagaki F. Noda NN, et al. Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 4;44(3):462-75. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.035. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22055191 - Insights into noncanonical E1 enzyme activation from the structure of autophagic E1 Atg7 with Atg8.
Hong SB, Kim BW, Lee KE, Kim SW, Jeon H, Kim J, Song HK. Hong SB, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 6;18(12):1323-30. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2165. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22056771 - Noncanonical E2 recruitment by the autophagy E1 revealed by Atg7-Atg3 and Atg7-Atg10 structures.
Kaiser SE, Mao K, Taherbhoy AM, Yu S, Olszewski JL, Duda DM, Kurinov I, Deng A, Fenn TD, Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA. Kaiser SE, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1242-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2415. Epub 2012 Nov 11. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23142976 Free PMC article. - Allosteric regulation through a switch element in the autophagy E2, Atg3.
Qiu Y, Zheng Y, Grace CRR, Liu X, Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA. Qiu Y, et al. Autophagy. 2020 Jan;16(1):183-184. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1688550. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31690182 Free PMC article. Review. - In vitro assays of lipidation of Mammalian Atg8 homologs.
Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E. Tanida I, et al. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2014 Sep 2;64:11.20.1-13. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb1120s64. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25181299 Review.
Cited by
- Stat3-mediated Atg7 expression regulates anti-tumor immunity in mouse melanoma.
Zimmerman SM, Suh E, Smith SR, Souroullas GP. Zimmerman SM, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Sep 5;73(11):218. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03804-4. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39235510 Free PMC article. - Decrypting UFMylation: How Proteins Are Modified with UFM1.
Banerjee S, Kumar M, Wiener R. Banerjee S, et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 14;10(10):1442. doi: 10.3390/biom10101442. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33066455 Free PMC article. Review. - Complete set of the Atg8-E1-E2-E3 conjugation machinery forms an interaction web that mediates membrane shaping.
Alam JM, Maruyama T, Noshiro D, Kakuta C, Kotani T, Nakatogawa H, Noda NN. Alam JM, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;31(1):170-178. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01132-2. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38057553 - Current Outlook on Autophagy in Human Leukemia: Foe in Cancer Stem Cells and Drug Resistance, Friend in New Therapeutic Interventions.
Rothe K, Porter V, Jiang X. Rothe K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 22;20(3):461. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030461. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30678185 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy Mediates Astrogenesis in Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells.
Ha S, Jeong SH, Yi K, Chu JJ, Kim S, Kim EK, Yu SW. Ha S, et al. Exp Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;28(2):229-246. doi: 10.5607/en.2019.28.2.229. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Exp Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31138991 Free PMC article.
References
- Bolanos-Garcia VM, Davies OR. Structural analysis and classification of native proteins from E. coli commonly co-purified by immobilised metal affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:1304–1313. - PubMed
- Duda DM, Walden H, Sfondouris J, Schulman BA. Structural analysis of Escherichia coli ThiF. J Mol Biol. 2005;349:774–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 RR015301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM034496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077053/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR-15301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI40646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM077053/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM034496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM034496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH5P30CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI040646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases