Muscarinic receptors: their roles in disorders of the central nervous system and potential as therapeutic targets - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Muscarinic receptors: their roles in disorders of the central nervous system and potential as therapeutic targets
Elizabeth Scarr. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 May.
Abstract
Phylogenetically, acetylcholine is an ancient neurochemical. Therefore, it is not surprising that cholinergic neurons project extensively throughout the central nervous system, innervating a wide range of structures within the brain. In fact, acetylcholine is involved in processes that underpin some of our most basic central functions. Both muscarinic and nicotinic receptor families, which mediate cholinergic transmission, have been implicated in the pathophysiology of psychiatric and neurological disorders. The question that remains to be definitively answered is whether or not these receptors are viable targets for the development of future therapeutic agents.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
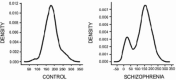
Figure 1
Distribution analyses of [3H]pirenzepine binding (_x_‐axis) to M1 receptors from control subjects (left) and subjects with schizophrenia (right) [37].
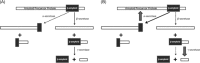
Figure 2
Schematic showing (A) amyloid precursor protein cleavage and (B) the effect of M1 agonists on this pathway.
Similar articles
- Regulators of cholinergic signaling in disorders of the central nervous system.
Winek K, Soreq H, Meisel A. Winek K, et al. J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(6):1425-1438. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15332. Epub 2021 Mar 19. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33638173 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Muscarinic Receptors in the Pathophysiology of Mood Disorders: A Potential Novel Treatment?
Jeon WJ, Dean B, Scarr E, Gibbons A. Jeon WJ, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13(6):739-49. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13666150612230045. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26630954 Free PMC article. Review. - Acetylcholine in Carcinogenesis and Targeting Cholinergic Receptors in Oncology.
Aronowitz AL, Ali SR, Glaun MDE, Amit M. Aronowitz AL, et al. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2022 Sep;6(9):e2200053. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200053. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35858206 Review. - Muscarinic receptor subtypes in neuronal and non-neuronal cholinergic function.
Eglen RM. Eglen RM. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2006 Jul;26(3):219-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2006.00368.x. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16879488 Review. - Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors and M-Currents Underlie Efferent-Mediated Slow Excitation in Calyx-Bearing Vestibular Afferents.
Holt JC, Jordan PM, Lysakowski A, Shah A, Barsz K, Contini D. Holt JC, et al. J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 15;37(7):1873-1887. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2322-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28093476 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Effect of Clemastine on Neurophysiological Outcomes in an Ovine Model of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy.
Mike JK, White Y, Hutchings RS, Vento C, Ha J, Iranmahboub A, Manzoor H, Gunewardena A, Cheah C, Wang A, Goudy BD, Lakshminrusimha S, Long-Boyle J, Fineman JR, Ferriero DM, Maltepe E. Mike JK, et al. Children (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;10(11):1728. doi: 10.3390/children10111728. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002819 Free PMC article. - Potential Role for Combined Subtype-Selective Targeting of M1 and M3 Muscarinic Receptors in Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases.
Tolaymat M, Sundel MH, Alizadeh M, Xie G, Raufman JP. Tolaymat M, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 4;12:786105. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.786105. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803723 Free PMC article. Review. - Cholinergic Dysfunction Involvement in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion-Induced Impairment of Medial Septum-dCA1 Neurocircuit in Rats.
Xu Y, Zhang S, Sun Q, Wang XQ, Chai YN, Mishra C, Chandra SR, Ai J. Xu Y, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Sep 29;14:586591. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.586591. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33132852 Free PMC article. - Allosteric Modulation of Muscarinic Receptors by Cholesterol, Neurosteroids and Neuroactive Steroids.
Szczurowska E, Szánti-Pintér E, Randáková A, Jakubík J, Kudova E. Szczurowska E, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 28;23(21):13075. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113075. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361865 Free PMC article. Review. - Anticholinergic medication: Related dry mouth and effects on the salivary glands.
Arany S, Kopycka-Kedzierawski DT, Caprio TV, Watson GE. Arany S, et al. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021 Dec;132(6):662-670. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2021.08.015. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34593340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Sarter M, Bruno JP. Cognitive functions of cortical acetylcholine: Toward a unifying hypothesis. Brain Res Rev 1997;23:28–46. - PubMed
- Perry E, Walker M, Grace J, Perry R. Acetylcholine in mind: A neurotransmitter correlate of consciousness Trends Neurosci 1999;22:273–280. - PubMed
- Dale HH. The action of certain esters and ethers of choline and their relation to muscarine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1914;6:147–190.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources