Mitigation of late renal and pulmonary injury after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Mitigation of late renal and pulmonary injury after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Eric P Cohen et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012.
Abstract
Purpose: To update the results of a clinical trial that assessed whether the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor captopril was effective in mitigating chronic renal failure and pulmonary-related mortality in subjects undergoing total body irradiation (TBI) in preparation for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
Methods and materials: Updated records of the 55 subjects who were enrolled in this randomized controlled trial were analyzed. Twenty-eight patients received captopril, and 27 patients received placebo. Definitions of TBI-HSCT-related chronic renal failure (and relapse) were the same as those in the 2007 analysis. Pulmonary-related mortality was based on clinical or autopsy findings of pulmonary failure or infection as the primary cause of death. Follow-up data for overall and pulmonary-related mortality were supplemented by use of the National Death Index.
Results: The risk of TBI-HSCT-related chronic renal failure was lower in the captopril group (11% at 4 years) than in the placebo group (17% at 4 years), but this was not statistically significant (p > 0.2). Analysis of mortality was greatly extended by use of the National Death Index, and no patients were lost to follow-up for reasons other than death prior to 67 months. Patient survival was higher in the captopril group than in the placebo group, but this was not statistically significant (p > 0.2). The improvement in survival was influenced more by a decrease in pulmonary mortality (11% risk at 4 years in the captopril group vs. 26% in the placebo group, p = 0.15) than by a decrease in chronic renal failure. There was no adverse effect on relapse risk (p = 0.4).
Conclusions: Captopril therapy produces no detectable adverse effects when given after TBI. Captopril therapy reduces overall and pulmonary-related mortality after radiation-based HSCT, and there is a trend toward mitigation of chronic renal failure.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Notification: conflicts of interest do not exist
Figures
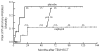
Fig. 1
Actuarial patient survival according to use of captopril or placebo. There was better patient survival in the subjects of the captopril group. This survival difference did not, however, attain statistical significance (p = 0.26). Cases censored for survival are shown as vertical bars and the number at risk at 24 month intervals is shown in parentheses.
Fig. 2
The cumulative incidence of pulmonary-related mortality according to use of captopril or placebo. The occurrence of pulmonary-related mortality was within the two years after the total body irradiation. The placebo group had a higher incidence than the captopril group, but this did not attain statistical significance (p = 0.18). Cases censored are shown as vertical bars and the number at risk at 24 month intervals is shown in parentheses; not shown are placebo cases censored for pulmonary-related mortality at 1.8, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.5 months.
Fig. 3
The cumulative incidence of bone marrow transplant (BMT) nephropathy and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) according to use of captopril or placebo. The occurrence of BMT nephropathy and HUS was within the first year after the total body irradiation. The placebo group had a higher incidence than the captopril group (p = 0.22). Cases censored are shown as vertical bars and the number at risk at 24 month intervals is shown in parentheses; not shown are placebo cases censored for nephropathy at 1.8, 1.9, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.7 months.
Similar articles
- Captopril to mitigate chronic renal failure after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a randomized controlled trial.
Cohen EP, Irving AA, Drobyski WR, Klein JP, Passweg J, Talano JA, Juckett MB, Moulder JE. Cohen EP, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 Apr 1;70(5):1546-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.08.041. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 18029109 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Long-term results of selective renal shielding in patients undergoing total body irradiation in preparation for bone marrow transplantation.
Lawton CA, Cohen EP, Murray KJ, Derus SW, Casper JT, Drobyski WR, Horowitz MM, Moulder JE. Lawton CA, et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997 Dec;20(12):1069-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1701022. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997. PMID: 9466280 - Factors Influencing Pulmonary Toxicity in Children Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in the Setting of Total Body Irradiation-Based Myeloablative Conditioning.
Abugideiri M, Nanda RH, Butker C, Zhang C, Kim S, Chiang KY, Butker E, Khan MK, Haight AE, Chen Z, Esiashvili N. Abugideiri M, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Feb 1;94(2):349-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.10.054. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26853343 - Male Gonadal Function After Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review.
Mathiesen S, Andrés-Jensen L, Nielsen MM, Sørensen K, Ifversen M, Jahnukainen K, Juul A, Müller K. Mathiesen S, et al. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Aug;28(8):503.e1-503.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.05.036. Epub 2022 May 26. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 35644480 - Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors for proteinuria and microalbuminuria in people with sickle cell disease.
Sasongko TH, Nagalla S, Ballas SK. Sasongko TH, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 4;2015(6):CD009191. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009191.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26041152 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
- Dose-modifying factor for captopril for mitigation of radiation injury to normal lung.
Medhora M, Gao F, Fish BL, Jacobs ER, Moulder JE, Szabo A. Medhora M, et al. J Radiat Res. 2012 Jul;53(4):633-40. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrs004. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22843631 Free PMC article. - Acute Toxicity of Total Body Irradiation Using Volumetric Arc Therapy With a Focus on the Effect of Lung Dose Rate.
Melton MK, Stanley DN, Iqbal Z, Keene KS, Simiele E, McDonald A. Melton MK, et al. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jan 1;9(4):101430. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101430. eCollection 2024 Apr. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38406392 Free PMC article. - Enalapril mitigates radiation-induced pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis if started 35 days after whole-thorax irradiation.
Gao F, Fish BL, Moulder JE, Jacobs ER, Medhora M. Gao F, et al. Radiat Res. 2013 Nov;180(5):546-52. doi: 10.1667/RR13350.1. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 24131041 Free PMC article. - Pulmonary toxicity generated from radiotherapeutic treatment of thoracic malignancies.
Deng G, Liang N, Xie J, Luo H, Qiao L, Zhang J, Wang D, Zhang J. Deng G, et al. Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):501-511. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6268. Epub 2017 May 26. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693198 Free PMC article. - Radiation Pneumonitis: Old Problem, New Tricks.
Jain V, Berman AT. Jain V, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2018 Jul 3;10(7):222. doi: 10.3390/cancers10070222. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29970850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Shank B. Toxicity due to total body irradiation. In: Shrieve D, Loeffler J, editors. Human Radiation Injury. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. pp. 133–139.
- Cohen EP. Radiation nephropathy after bone marrow transplantation. Kidney Int. 2000 Aug;58(2):903–918. - PubMed
- Sampath S, Schultheiss TE, Wong J. Dose response and factors related to interstitial pneumonitis after bone marrow transplant. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005 Nov 1;63(3):876–884. - PubMed
- Moulder JE, Fish BL, Cohen EP. Noncontinuous use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in the treatment of experimental bone marrow transplant nephropathy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997 Apr;19(7):729–735. - PubMed
- Moulder JE, Robbins ME, Cohen EP, Hopewell JW, Ward WF. Pharmacologic modification of radiation-induced late normal tissue injury. Cancer Treat Res. 1998;93:129–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical