Dynamics of amyloid β fibrils revealed by solid-state NMR - PubMed (original) (raw)
Dynamics of amyloid β fibrils revealed by solid-state NMR
Holger A Scheidt et al. J Biol Chem. 2012.
Abstract
We have investigated the site-specific backbone dynamics of mature amyloid β (Aβ) fibrils using solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Overall, the known β-sheet segments and the turn linking these two β-strands exhibit high order parameters between 0.8 and 0.95, suggesting low conformational flexibility. The first approximately eight N-terminal and the last C-terminal residues exhibit lower order parameters between ∼0.4 and 0.8. Interestingly, the order parameters increase again for the first two residues, Asp(1) and Ala(2), suggesting that the N terminus could carry some structural importance.
Figures
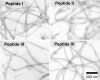
FIGURE 1.
Transmission electron micrographs of fibrils of Aβ(1–40). Shown are four different peptide preparations, made of Aβ peptides with varying isotopic labeling patterns (see “Experimental Procedures”).
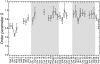
FIGURE 2.
Plot of 13Cα-1H order parameters for mature Aβ(1–40) fibrils at hydration level of 50 weight % as determined from quantitative measurements of 13Cα-1H dipolar couplings by DIPSHIFT experiment. Regions with a known β-sheet structure are highlighted. The error bars represent the uncertainty of the fitting procedure of the MAS time domain signals.
FIGURE 3.
Secondary 13C MAS NMR isotropic chemical shift values for Cα (□) and Cβ (●) for mature Aβ(1–40) fibrils at hydration level of 50 weight %. Data are given as the difference between a measured chemical shift for a specific amino acid and random coil chemical shifts taken from literature. Regions that are in agreement with β-sheet secondary structure are highlighted.
FIGURE 4.
Plot of 13C MAS NMR line widths (full-widths at half-maximum) for Cα (□) and Cβ (●) for mature Aβ(1–40) fibrils at hydration level of 50 weight %. Regions that are in agreement with β-sheet secondary structure are highlighted.
FIGURE 5.
Schematic representation of backbone 13Cα-1H order parameters along structure of mature Aβ(1–40) fibrils. The thick straight lines represent the two β-sheets that have been identified in solid-state NMR studies (1, 3, 5). The thin freehand lines represent the unstructured N terminus and the loop region connecting the two sheets.
Similar articles
- Conformational flexibility of Y145Stop human prion protein amyloid fibrils probed by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP. Helmus JJ, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Feb 24;132(7):2393-403. doi: 10.1021/ja909827v. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20121096 Free PMC article. - Supramolecular structural constraints on Alzheimer's beta-amyloid fibrils from electron microscopy and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance.
Antzutkin ON, Leapman RD, Balbach JJ, Tycko R. Antzutkin ON, et al. Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 24;41(51):15436-50. doi: 10.1021/bi0204185. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12484785 - Molecular structures of amyloid and prion fibrils: consensus versus controversy.
Tycko R, Wickner RB. Tycko R, et al. Acc Chem Res. 2013 Jul 16;46(7):1487-96. doi: 10.1021/ar300282r. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Acc Chem Res. 2013. PMID: 23294335 Free PMC article. Review. - Intermolecular alignment in Y145Stop human prion protein amyloid fibrils probed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Apostol MI, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP. Helmus JJ, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Sep 7;133(35):13934-7. doi: 10.1021/ja206469q. Epub 2011 Aug 15. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21827207 Free PMC article. - Solid-State Structure of Abeta (Aβ) in Alzheimer's Disease.
Lu JX, Dong XQ, Zhang JJ. Lu JX, et al. Protein Pept Lett. 2017;24(4):322-330. doi: 10.2174/0929866524666170208155108. Protein Pept Lett. 2017. PMID: 28183246 Review.
Cited by
- Transient dynamics of Aβ contribute to toxicity in Alzheimer's disease.
Hubin E, van Nuland NA, Broersen K, Pauwels K. Hubin E, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3507-21. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1634-z. Epub 2014 May 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24803005 Free PMC article. Review. - Amyloid-β peptides in interaction with raft-mime model membranes: a neutron reflectivity insight.
Rondelli V, Brocca P, Motta S, Messa M, Colombo L, Salmona M, Fragneto G, Cantù L, Del Favero E. Rondelli V, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 16;6:20997. doi: 10.1038/srep20997. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26880066 Free PMC article. - Rigidifying of the internal dynamics of amyloid-beta fibrils generated in the presence of synaptic plasma vesicles.
Vugmeyster L, Au DF, Frazier B, Qiang W, Ostrovsky D. Vugmeyster L, et al. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2024 Feb 7;26(6):5466-5478. doi: 10.1039/d3cp04824a. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2024. PMID: 38277177 - Fiber diffraction data indicate a hollow core for the Alzheimer's aβ 3-fold symmetric fibril.
McDonald M, Box H, Bian W, Kendall A, Tycko R, Stubbs G. McDonald M, et al. J Mol Biol. 2012 Oct 26;423(3):454-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Aug 16. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22903058 Free PMC article. - Dynamics of Serine-8 Side-Chain in Amyloid-β Fibrils and Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl Serine Amino Acid, Investigated by Solid-State Deuteron NMR.
Vugmeyster L, Au DF, Ostrovsky D, Rickertsen DRL, Reed SM. Vugmeyster L, et al. J Phys Chem B. 2020 Jun 11;124(23):4723-4731. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c02490. Epub 2020 May 27. J Phys Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32396356 Free PMC article.
References
- Petkova A. T., Leapman R. D., Guo Z., Yau W. M., Mattson M. P., Tycko R. (2005) Self-propagating, molecular level polymorphism in Alzheimer β-amyloid fibrils. Science 307, 262–265 - PubMed
- Bertini I., Gonnelli L., Luchinat C., Mao J., Nesi A. (2011) A new structural model of Aβ40 fibrils. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 16013–16022 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources