Comparison of presentation and impact on quality of life of gastroesophageal reflux disease between young and old adults in a Chinese population - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Comparison of presentation and impact on quality of life of gastroesophageal reflux disease between young and old adults in a Chinese population
Shou-Wu Lee et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2011.
Abstract
Aim: To compare the presentation and impact on quality of life of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in old and young age groups.
Methods: Data from adult patients with GERD diagnosed by endoscopic and symptomic characteristics were collected between January and November 2009. Exclusion criteria included combined peptic ulcers, malignancy, prior surgery, antacid medication for more than 2 mo, and pregnancy. Enrolled patients were assigned to the elderly group if they were 65 years or older, or the younger group if they were under 65 years. They had completed the GERD impact scale, the Chinese GERD questionnaire, and the SF-36 questionnaire. Data from other cases without endoscopic findings or symptoms were collected and these subjects comprised the control group in our study.
Results: There were 111 patients with GERD and 44 normal cases: 78 (70.3%) and 33 patients (29.7%) were in the younger and elderly groups, respectively. There were more female patients (60.3%) in the younger group, and more males (72.7%) in the elderly group. The younger cases had more severe and frequent typical symptoms than the elderly patients. Significantly more impairment of daily activities was noted in the younger patients compared with the elderly group, except for physical functioning.
Conclusion: Elderly patients with GERD were predominantly male with rare presentation of typical symptoms, and had less impaired quality of life compared with younger patients in a Chinese population.
Keywords: Age factors; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Quality of life.
Figures
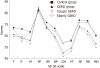
Figure 1
Scores of SF36 questionnaire among the control cases, and younger and elderly cases with gastroesophageal reflux disease. T: Total SF36 scores; P: Total physical health scores; M: Total metal health scores; RP: Role-physical; RF: Physical functioning; BP: Bodily pain; GH: General perception; VT: Vitality; MH: Mental health; SF: Social functioning; RE: Role-emotional; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Similar articles
- Quality of life, patient satisfaction, and disease burden in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease with or without laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms.
Gong EJ, Choi KD, Jung HK, Youn YH, Min BH, Song KH, Huh KC. Gong EJ, et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jul;32(7):1336-1340. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13716. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28052406 - The risk factors and quality of life in patients with overlapping functional dyspepsia or peptic ulcer disease with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Lee SW, Lee TY, Lien HC, Yeh HZ, Chang CS, Ko CW. Lee SW, et al. Gut Liver. 2014 Mar;8(2):160-4. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2014.8.2.160. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Gut Liver. 2014. PMID: 24672657 Free PMC article. - Prevalence, risk factors and impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: a population-based study in South China.
Chen M, Xiong L, Chen H, Xu A, He L, Hu P. Chen M, et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jul;40(7):759-67. doi: 10.1080/00365520510015610. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16118911 - Heartburn and regurgitation have different impacts on life quality of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Lee SW, Lien HC, Lee TY, Yang SS, Yeh HJ, Chang CS. Lee SW, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 14;20(34):12277-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12277. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25232262 Free PMC article. - Canadian Consensus Conference on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease in adults - update 2004.
Armstrong D, Marshall JK, Chiba N, Enns R, Fallone CA, Fass R, Hollingworth R, Hunt RH, Kahrilas PJ, Mayrand S, Moayyedi P, Paterson WG, Sadowski D, van Zanten SJ; Canadian Association of Gastroenterology GERD Consensus Group. Armstrong D, et al. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan;19(1):15-35. doi: 10.1155/2005/836030. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15685294 Review.
Cited by
- A Phase III Head-to-Head Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of Fexuprazan and Esomeprazole in Treating Patients with Erosive Esophagitis.
Jeong Y, Lee BJ, Han SH. Jeong Y, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 May 31;13(11):3262. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113262. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38892973 Free PMC article. Retracted. - The Role of a Plant-Only (Vegan) Diet in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Online Survey of the Italian General Population.
Rizzo G, Baroni L, Bonetto C, Visaggi P, Orazzini M, Solinas I, Guidi G, Pugliese J, Scaramuzza G, Ovidi F, Buselli I, Bellini M, Savarino EV, de Bortoli N. Rizzo G, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Nov 8;15(22):4725. doi: 10.3390/nu15224725. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38004119 Free PMC article. - Endoscopic Findings of Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease in Elderly and Younger Age Groups.
Adanir H, Baş B, Pakoz B, Günay S, Camyar H, Ustaoglu M. Adanir H, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 10;8:606205. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.606205. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34957130 Free PMC article. - Impact of Overlapping Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders on the Quality of Life in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.
Lee SW, Chang CS. Lee SW, et al. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Apr 30;27(2):176-184. doi: 10.5056/jnm19006. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33795540 Free PMC article. Review. - Gastroesophageal reflux disease and its related factors among women of reproductive age: Korea Nurses' Health Study.
Kim O, Jang HJ, Kim S, Lee HY, Cho E, Lee JE, Jung H, Kim J. Kim O, et al. BMC Public Health. 2018 Sep 21;18(1):1133. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6031-3. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30241473 Free PMC article.
References
- Wiklund I. Review of the quality of life and burden of illness in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis. 2004;22:108–114. - PubMed
- Mold JW, Reed LE, Davis AB, Allen ML, Decktor DL, Robinson M. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in elderly patients in a primary care setting. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991;86:965–970. - PubMed
- Furukawa N, Iwakiri R, Koyama T, Okamoto K, Yoshida T, Kashiwagi Y, Ohyama T, Noda T, Sakata H, Fujimoto K. Proportion of reflux esophagitis in 6010 Japanese adults: prospective evaluation by endoscopy. J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:441–444. - PubMed
- McDougall NI, Johnston BT, Collins JS, McFarland RJ, Love AH. Three to 4.5-year prospective study of prognostic indicators in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:1016–1022. - PubMed
- Zeitoun P, Salmon L, Bouché O, Jolly D, Thiéfin G. Outcome of erosive/ulcerative reflux oesophagitis in 181 consecutive patients 5 years after diagnosis. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;30:470–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical