Detecting vital signs with wearable wireless sensors - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Detecting vital signs with wearable wireless sensors
Tuba Yilmaz et al. Sensors (Basel). 2010.
Abstract
The emergence of wireless technologies and advancements in on-body sensor design can enable change in the conventional health-care system, replacing it with wearable health-care systems, centred on the individual. Wearable monitoring systems can provide continuous physiological data, as well as better information regarding the general health of individuals. Thus, such vital-sign monitoring systems will reduce health-care costs by disease prevention and enhance the quality of life with disease management. In this paper, recent progress in non-invasive monitoring technologies for chronic disease management is reviewed. In particular, devices and techniques for monitoring blood pressure, blood glucose levels, cardiac activity and respiratory activity are discussed; in addition, on-body propagation issues for multiple sensors are presented.
Keywords: BAN networks; RF sensing; on-body sensors; wearable sensors; wireless telemetry.
Figures
Figure 1.
Blood pressure sensor by MIT [15].
Figure 2.
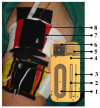
Arm module proposed in [23] (1) deep, (2) mid and (3) shallow electrodes. (4) Temperature sensor. (5) Sweat sensor. (6) Siliconwafer based optical reflection sensor. (7) Humidity sensor. (8) 3-axes acceleration sensor.
Figure 3.
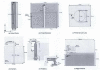
(a) Initial design of microwave sensor (b) Modified microwave sensor with silicon positioning aid [27].
Figure 4.
Capacitive electrodes proposed in [38].
Figure 5.
AMON wrist module [46].
Figure 6.
Antenna types used in [66].
Figure 7.
Inter-body propagation case in [71].
Similar articles
- Wireless pilot monitoring system for extreme race conditions.
Pino EJ, Arias DE, Aqueveque P, Melin P, Curtis DW. Pino EJ, et al. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:5014-7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347119. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23367054 - A comparative study of wireless sensor networks and their routing protocols.
Bhattacharyya D, Kim TH, Pal S. Bhattacharyya D, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(12):10506-23. doi: 10.3390/s101210506. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Sensors (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22163483 Free PMC article. Review. - Wireless integrated biosensors for point-of-care diagnostic applications.
Ghafar-Zadeh E. Ghafar-Zadeh E. Sensors (Basel). 2015 Feb 2;15(2):3236-61. doi: 10.3390/s150203236. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25648709 Free PMC article. Review. - Biosensors to monitor MS activity.
Graves JS, Montalban X. Graves JS, et al. Mult Scler. 2020 Apr;26(5):605-608. doi: 10.1177/1352458519888178. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Mult Scler. 2020. PMID: 31965896 Review. - Wearable sensor systems for infants.
Zhu Z, Liu T, Li G, Li T, Inoue Y. Zhu Z, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2015 Feb 5;15(2):3721-49. doi: 10.3390/s150203721. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25664432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Evaluation of Physical Stillness with Wearable Chest and Arm Accelerometer during Chan Ding Practice.
Chang KM, Chun YT, Chen SH, Lu L, Su HT, Liang HM, Santhosh J, Ching CT, Liu SH. Chang KM, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2016 Jul 20;16(7):1126. doi: 10.3390/s16071126. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27447641 Free PMC article. - Respiratory Monitoring by Ultrafast Humidity Sensors with Nanomaterials: A Review.
Kano S, Jarulertwathana N, Mohd-Noor S, Hyun JK, Asahara R, Mekaru H. Kano S, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 7;22(3):1251. doi: 10.3390/s22031251. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161997 Free PMC article. Review. - Remote Surveillance Technologies: Realizing the Aim of Right Patient, Right Data, Right Time.
Safavi KC, Driscoll W, Wiener-Kronish JP. Safavi KC, et al. Anesth Analg. 2019 Sep;129(3):726-734. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003948. Anesth Analg. 2019. PMID: 31425213 Free PMC article. Review. - Low-power wearable respiratory sound sensing.
Oletic D, Arsenali B, Bilas V. Oletic D, et al. Sensors (Basel). 2014 Apr 9;14(4):6535-66. doi: 10.3390/s140406535. Sensors (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24721769 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of 1-Year in-Home Monitoring Technology by Home-Dwelling Older Adults, Family Caregivers, and Nurses.
Pais B, Buluschek P, DuPasquier G, Nef T, Schütz N, Saner H, Gatica-Perez D, Santschi V. Pais B, et al. Front Public Health. 2020 Oct 2;8:518957. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.518957. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33134236 Free PMC article.
References
- Hall PS, Hao Y. Antennas and Propagation for Body-Centric Wireless Networks. 1st ed. Artech House; Boston, MA, USA: 2006.
- Hao Y, Foster R. Wireless body sensor networks for health-monitoring applications. Phys Meas. 2008;29:R27–R56. - PubMed
- Newman JD, Turner APF. Home blood glucose biosensors: A commercial perspective. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;20:2435–2453. - PubMed
- Pickering TG, Shimbo D, Hass D. Ambulatory blood-pressure monitoring. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2368–2374. - PubMed
- Moranes JCTB, Cerulli M, Ng PS. A Strategy for Determination of Systolic, Mean and Diastolic Blood Pressures from Oscillometric Pulse Profiles. Proceedings of Computers in Cardiology 2000; Cambridge, MA, USA. September 24–27, 2000; pp. 211–214.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical