Vitamin D therapy in chronic kidney disease and end stage renal disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Vitamin D therapy in chronic kidney disease and end stage renal disease
Michal L Melamed et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Feb.
Abstract
Vitamin D has garnered much research and debate about supplementation in recent years, not only as it pertains to patients with kidney disease but also to those in the general population. This review discusses observational and available clinical trial evidence about the effects of both calcitriol and vitamin D analogs (active) and ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol (nutritional) vitamin D in patients with CKD and ESRD.
Figures
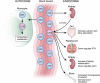
Figure 1.
Physiology of vitamin D in the body. It circulates as 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25D), which then gets converted in the kidney to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25D). The 1,25D has endocrine effects, shown at the right. 25D can also be taken up by monocytes and other cells where it is converted to 1,25D acting in an autocrine fashion to upregulate cathelicidin production.
Similar articles
- Clinical outcomes with active versus nutritional vitamin D compounds in chronic kidney disease.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP. Kalantar-Zadeh K, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Sep;4(9):1529-39. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02140309. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19661219 Review. - Optimal vitamin D, calcitriol, and vitamin D analog replacement in chronic kidney disease: to D or not to D: that is the question.
Moorthi RN, Kandula P, Moe SM. Moorthi RN, et al. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011 Jul;20(4):354-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283470450. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21654391 Review. - Cholecalciferol supplementation in hemodialysis patients: effects on mineral metabolism, inflammation, and cardiac dimension parameters.
Matias PJ, Jorge C, Ferreira C, Borges M, Aires I, Amaral T, Gil C, Cortez J, Ferreira A. Matias PJ, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 May;5(5):905-11. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06510909. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20203163 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D deficiency and toxicity in chronic kidney disease: in search of the therapeutic window.
Querfeld U, Mak RH. Querfeld U, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Dec;25(12):2413-30. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1574-2. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20567854 Review. - Nutritional vitamin D supplementation in dialysis: a randomized trial.
Bhan I, Dobens D, Tamez H, Deferio JJ, Li YC, Warren HS, Ankers E, Wenger J, Tucker JK, Trottier C, Pathan F, Kalim S, Nigwekar SU, Thadhani R. Bhan I, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):611-9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06910714. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25770176 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- Association of Vitamin D Deficiency and Insufficiency with Pathology in Hospitalized Patients.
Bucurica S, Prodan I, Pavalean M, Taubner C, Bucurica A, Socol C, Calin R, Ionita-Radu F, Jinga M. Bucurica S, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;13(5):998. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050998. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900141 Free PMC article. - 25-OH vitamin D threshold for optimal bone mineral density in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease.
Roy D, Ng CY, Kog ZX, Yeon W, Poh CB, Koduri S, Chionh CY, Sultana R, Hai Kiat Puar T. Roy D, et al. Front Aging. 2022 Oct 21;3:1026663. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.1026663. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 36338833 Free PMC article. - Severe 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Deficiency May Predict Poor Renal Outcomes in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Diabetic Nephropathy.
Zhou T, Shen L, Li Z, Jia J, Xing H, Wang N, Jiao Q, Fan Y. Zhou T, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 4;13:871571. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.871571. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35600603 Free PMC article. - Associations Between 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, Kidney Function, and Insulin Resistance Among Adults in the United States of America.
Geng J, Qiu Y, Li Y, Li J, Liao R, Du H, Jiang L, Wang L, Qin Z, Yang Q, Yu Q, Zhang Z, Su B. Geng J, et al. Front Nutr. 2022 Feb 15;8:716878. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.716878. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35242790 Free PMC article. - Effect of Early and Delayed Commencement of Paricalcitol in Combination with Enalapril on the Progression of Experimental Polycystic Kidney Disease.
Sagar PS, Saravanabavan S, Munt A, Wong ATY, Rangan GK. Sagar PS, et al. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021 Oct 29;8(11):144. doi: 10.3390/jcdd8110144. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021. PMID: 34821697 Free PMC article.
References
- Dusso A, Lopez-Hilker S, Rapp N, Slatopolsky E: Extra-renal production of calcitriol in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 34: 368–375, 1988 - PubMed
- Weisman Y, Vargas A, Duckett G, Reiter E, Root AW: Synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in the nephrectomized pregnant rat. Endocrinology 103: 1992–1996, 1978 - PubMed
- Raisz LG, Trummel CL, Holick MF, DeLuca HF: 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol: A potent stimulator of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science 175: 768–769, 1972 - PubMed
- Brumbaugh PF, Haussler MR: 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in intestine. I. Association of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol with intestinal mucosa chromatin. J Biol Chem 249: 1251–1257, 1974 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK080123/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21HL102882/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK087783/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK078774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK087783/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK084974/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL102882/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical