Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression is regulated by microRNAs miR-26a and miR-26b allele-specific binding - PubMed (original) (raw)
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression is regulated by microRNAs miR-26a and miR-26b allele-specific binding
Viviana Caputo et al. PLoS One. 2011.
Abstract
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a neurotrophin that plays an essential role in neuronal development and plasticity. MicroRNA (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs of about 22-nucleotides in length regulating gene expression at post-transcriptional level. In this study we explore the role of miRNAs as post-transcriptional inhibitors of BDNF and the effect of 3'UTR sequence variations on miRNAs binding capacity. Using an in silico approach we identified a group of miRNAs putatively regulating BDNF expression and binding to BDNF 3'UTR polymorphic sequences. Luciferase assays demonstrated that these miRNAs (miR-26a1/2 and miR-26b) downregulates BDNF expression and that the presence of the variant alleles of two single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs11030100 and rs11030099) mapping in BDNF 3'UTR specifically abrogates miRNAs targeting. Furthermore we found a high linkage disequilibrium rate between rs11030100, rs11030099 and the non-synonymous coding variant rs6265 (Val66Met), which modulates BDNF mRNA localization and protein intracellular trafficking. Such observation led to hypothesize that miR-26s mediated regulation could extend to rs6265 leading to an allelic imbalance with potentially functional effects, such as peptide's localization and activity-dependent secretion. Since rs6265 has been previously implicated in various neuropsychiatric disorders, we evaluated the distribution of rs11030100, rs11030099 and rs6265 both in a control and schizophrenic group, but no significant difference in allele frequencies emerged. In conclusion, in the present study we identified two novel miRNAs regulating BDNF expression and the first BDNF 3'UTR functional variants altering miRNAs-BDNF binding.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Figure 1. Multiple genome alignment of BDNF 3′UTR in the region of polymorphic sites rs11030100 and rs11030099 (in bold letters).
Sequence analysis shows that sites are highly conserved among primate genomes.
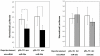
Figure 2. Luciferase assays for validation of miR-26a and -26b binding to BDNF 3′UTR.
HeLa cells were independently transfected with control plasmid (pRL-TK) or each of the two reporter plasmid (pluc-BDNF C–G, anc, and pluc-BDNF A–T, der) with either miR-26a or miR-26b. Data are presented as the normalized activity of different reporter genes. Introduction of exogenous miR-26a and miR-26b represses reporter activity of pluc-BDNF C–G but has no effect on pluc-BDNF A–T. Data represent the mean of five independent experiments +SD (p<0.05).
Figure 3. Schematic representation of base pairing between miR-26a sequence and BDNF 3′UTR ancestral (C–G) and derivative (A–T) alleles of rs11030100 and rs11030099 polymorphic sites.
MiR-26b has the same seed binding sequence.
Similar articles
- A set of differentially expressed miRNAs, including miR-30a-5p, act as post-transcriptional inhibitors of BDNF in prefrontal cortex.
Mellios N, Huang HS, Grigorenko A, Rogaev E, Akbarian S. Mellios N, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Oct 1;17(19):3030-42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn201. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Hum Mol Genet. 2008. PMID: 18632683 Free PMC article. - Multiple microRNA regulation of lipoprotein lipase gene abolished by 3'UTR polymorphisms in a triglyceride-lowering haplotype harboring p.Ser474Ter.
Caussy C, Charrière S, Meirhaeghe A, Dallongeville J, Lefai E, Rome S, Cuerq C, Euthine V, Delay M, Marmontel O, Di Filippo M, Lagarde M, Moulin P, Marçais C. Caussy C, et al. Atherosclerosis. 2016 Mar;246:280-6. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.01.010. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 26820803 - MicroRNA regulation of the synaptic plasticity-related gene Arc.
Wibrand K, Pai B, Siripornmongcolchai T, Bittins M, Berentsen B, Ofte ML, Weigel A, Skaftnesmo KO, Bramham CR. Wibrand K, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041688. Epub 2012 Jul 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22844515 Free PMC article. - Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and schizophrenia.
Di Carlo P, Punzi G, Ursini G. Di Carlo P, et al. Psychiatr Genet. 2019 Oct;29(5):200-210. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000237. Psychiatr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31465000 Free PMC article. Review. - New Frontiers in Neurodegeneration and Regeneration Associated with Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and the rs6265 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism.
Szarowicz CA, Steece-Collier K, Caulfield ME. Szarowicz CA, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 20;23(14):8011. doi: 10.3390/ijms23148011. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Targeting MicroRNAs Involved in the BDNF Signaling Impairment in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
You HJ, Park JH, Pareja-Galeano H, Lucia A, Shin JI. You HJ, et al. Neuromolecular Med. 2016 Dec;18(4):540-550. doi: 10.1007/s12017-016-8407-9. Epub 2016 May 21. Neuromolecular Med. 2016. PMID: 27209362 Review. - A Systematic Review of Psychobiotic Interventions in Children and Adolescents to Enhance Cognitive Functioning and Emotional Behavior.
Basso M, Johnstone N, Knytl P, Nauta A, Groeneveld A, Cohen Kadosh K. Basso M, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Jan 30;14(3):614. doi: 10.3390/nu14030614. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35276975 Free PMC article. Review. - Pathophysiological Aspects and Therapeutic Armamentarium of Alzheimer's Disease: Recent Trends and Future Development.
Dave BP, Shah YB, Maheshwari KG, Mansuri KA, Prajapati BS, Postwala HI, Chorawala MR. Dave BP, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):3847-3884. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01408-7. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37725199 Review. - Toward a unified biological hypothesis for the BDNF Val66Met-associated memory deficits in humans: a model of impaired dendritic mRNA trafficking.
Baj G, Carlino D, Gardossi L, Tongiorgi E. Baj G, et al. Front Neurosci. 2013 Oct 30;7:188. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00188. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198753 Free PMC article. Review. - miRNA profiles in plasma from patients with sleep disorders reveal dysregulation of miRNAs in narcolepsy and other central hypersomnias.
Holm A, Bang-Berthelsen CH, Knudsen S, Kornum BR, Modvig S, Jennum P, Gammeltoft S. Holm A, et al. Sleep. 2014 Sep 1;37(9):1525-33. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4004. Sleep. 2014. PMID: 25142559 Free PMC article.
References
- Yamada K, Mizuno M, Nabeshima T. Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci. 2002;70(7):735–744. - PubMed
- Egan MF, Kojima M, Callicott JH, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell. 2003;112(2):257–269. - PubMed
- Rybakowski JK, Borkowska A, Czerski PM, Skibińska M, Hauser J. Polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene and performance on a cognitive prefrontal test in bipolar patients. Bipolar Disord. 2003;5(6):468–472. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources