The miR-29 family: genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The miR-29 family: genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury
Alison J Kriegel et al. Physiol Genomics. 2012.
Abstract
The human miR-29 family of microRNAs has three mature members, miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c. miR-29s are encoded by two gene clusters. Binding sites for several transcriptional factors have been identified in the promoter regions of miR-29 genes. The miR-29 family members share a common seed region sequence and are predicted to target largely overlapping sets of genes. However, the miR-29 family members exhibit differential regulation in several cases and different subcellular distribution, suggesting their functional relevance may not be identical. miR-29s directly target at least 16 extracellular matrix genes, providing a dramatic example of a single microRNA targeting a large group of functionally related genes. Strong antifibrotic effects of miR-29s have been demonstrated in heart, kidney, and other organs. miR-29s have also been shown to be proapoptotic and involved in the regulation of cell differentiation. It remains to be explored how various cellular effects of miR-29s determine functional relevance of miR-29s to specific diseases and how the miR-29 family members may function cooperatively or separately.
Figures
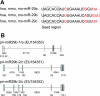
Fig. 1.
Mature sequences and primary transcripts of the miR-29 family. A: mature sequences of the miR-29 family members are conserved in human (hsa-), mouse (mmu-), and rat (rno-), and share identical seed regions. Nucleotides that differ among the miR-29 family members are shown in red. B: primary transcripts of the miR-29 gene clusters in human. Exons and introns are shown as vertical boxes and horizontal lines, respectively. The hairpins indicate the locations of the sequences encoding precursors of miR-29s. Numbers indicate the nucleotide length of each exon or intron.
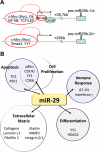
Fig. 2.
Transcriptional regulators and target genes of miR-29s. A: transcriptional factors with experimentally supported binding sites in miR-29 promoter regions. B: several cellular processes and genes that have been reported to be targeted by miR-29s.
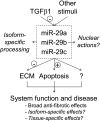
Fig. 3.
An overview of the biology and disease relevance of the miR-29 family.
Similar articles
- Tumour-suppressive microRNA-29s directly regulate LOXL2 expression and inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion in renal cell carcinoma.
Nishikawa R, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Inoguchi S, Ishihara T, Matsushita R, Goto Y, Fukumoto I, Nakagawa M, Seki N. Nishikawa R, et al. FEBS Lett. 2015 Jul 22;589(16):2136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 19. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26096783 - A regulatory circuitry comprising TP53, miR-29 family, and SETDB1 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Chen B, Wang J, Wang J, Wang H, Gu X, Tang L, Feng X. Chen B, et al. Biosci Rep. 2018 Sep 13;38(5):BSR20180678. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180678. Print 2018 Oct 31. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30054425 Free PMC article. - miR-29c regulates NAV3 protein expression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Zong Y, Yu P, Cheng H, Wang H, Wang X, Liang C, Zhu H, Qin Y, Qin C. Zong Y, et al. Brain Res. 2015 Oct 22;1624:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26212654 - The role of miR-29 family in disease.
Horita M, Farquharson C, Stephen LA. Horita M, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2021 Jul;122(7):696-715. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29896. Epub 2021 Feb 2. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33529442 Free PMC article. Review. - MiR-146a/b: a family with shared seeds and different roots.
Paterson MR, Kriegel AJ. Paterson MR, et al. Physiol Genomics. 2017 Apr 1;49(4):243-252. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00133.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Physiol Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28213571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Loss of miR-29b following acute ischemic stroke contributes to neural cell death and infarct size.
Khanna S, Rink C, Ghoorkhanian R, Gnyawali S, Heigel M, Wijesinghe DS, Chalfant CE, Chan YC, Banerjee J, Huang Y, Roy S, Sen CK. Khanna S, et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013 Aug;33(8):1197-206. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.68. Epub 2013 May 1. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013. PMID: 23632968 Free PMC article. - Families of microRNAs Expressed in Clusters Regulate Cell Signaling in Cervical Cancer.
Servín-González LS, Granados-López AJ, López JA. Servín-González LS, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 5;16(6):12773-90. doi: 10.3390/ijms160612773. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26057746 Free PMC article. Review. - miR-29c is downregulated in renal interstitial fibrosis in humans and rats and restored by HIF-α activation.
Fang Y, Yu X, Liu Y, Kriegel AJ, Heng Y, Xu X, Liang M, Ding X. Fang Y, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 May 15;304(10):F1274-82. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00287.2012. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23467423 Free PMC article. - HIF-2α-dependent induction of miR-29a restrains TH1 activity during T cell dependent colitis.
Czopik AK, McNamee EN, Vaughn V, Huang X, Bang IH, Clark T, Wang Y, Ruan W, Nguyen T, Masterson JC, Tak E, Frank S, Collins CB, Li H, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Gerich ME, Furuta GT, Yuan X, Sood AK, de Zoeten EF, Eltzschig HK. Czopik AK, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 14;15(1):8042. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52113-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39271652 Free PMC article. - Regulation of cellular senescence by extracellular matrix during chronic fibrotic diseases.
Blokland KEC, Pouwels SD, Schuliga M, Knight DA, Burgess JK. Blokland KEC, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Oct 30;134(20):2681-2706. doi: 10.1042/CS20190893. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33084883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Arturo S. B-MYB, a transcription factor implicated in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis and cancer. Eur J Cancer 41: 2479– 2484, 2005. - PubMed
- Boon RA, Seeger T, Heydt S, Fischer A, Hergenreider E, Horrevoets AJ, Vinciguerra M, Rosenthal N, Sciacca S, Pilato M, van Heijningen P, Essers J, Brandes RP, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. MicroRNA-29 in aortic dilation: implications for aneurysm formation. Circ Res 109: 1115– 1119, 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL082798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-082798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-085267/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-029587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-084405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources