The effect of combination treatment with aliskiren and blockers of the renin-angiotensin system on hyperkalaemia and acute kidney injury: systematic review and meta-analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The effect of combination treatment with aliskiren and blockers of the renin-angiotensin system on hyperkalaemia and acute kidney injury: systematic review and meta-analysis
Ziv Harel et al. BMJ. 2012.
Abstract
Objective: To examine the safety of using aliskiren combined with agents used to block the renin-angiotensin system.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources: Medline, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and two trial registries, published up to 7 May 2011.
Study selection: Published and unpublished randomised controlled trials that compared combined treatment using aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers with monotherapy using these agents for at least four weeks and that provided numerical data on the adverse event outcomes of hyperkalaemia and acute kidney injury. A random effects model was used to calculate pooled risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for these outcomes.
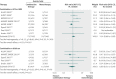
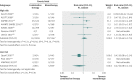
Results: 10 randomised controlled studies (4814 participants) were included in the analysis. Combination therapy with aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers significantly increased the risk of hyperkalaemia compared with monotherapy using angiotensin converting enzymes or angiotensin receptor blockers (relative risk 1.58, 95% confidence interval 1.24 to 2.02) or aliskiren alone (1.67, 1.01 to 2.79). The risk of acute kidney injury did not differ significantly between the combined therapy and monotherapy groups (1.14, 0.68 to 1.89).
Conclusion: Use of aliskerin in combination with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers is associated with an increased risk for hyperkalaemia. The combined use of these agents warrants careful monitoring of serum potassium levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi\_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; and no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Fig 1 Flow of studies through review
Fig 2 Risk of hyperkalaemia among participants given combined aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) versus monotherapy (ACE inhibitor, ARB, or aliskiren). Values less than 1.0 indicate a decreased risk of outcome with combination therapy
Fig 3 Risk of acute kidney injury among participants given combined aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) versus monotherapy (ACE inhibitor, ARB, or aliskiren). Values less than 1.0 indicate a decreased risk of outcome with combination therapy
Fig 4 Risk of hyperkalaemia stratified by severity among participants given combination therapy with aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) versus monotherapy with ACE inhibitor or ARB. Values less than 1.0 indicate a decreased risk of outcome with combination therapy
Fig 5 Risk of severe hyperkalaemia stratified by high and low risk participants given combination therapy with aliskiren and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) versus monotherapy with ACE inhibitor or ARB. Values less than 1.0 indicate a decreased risk of outcome with combination therapy
Comment in
- Dual renin-angiotensin system blockade.
de Leeuw PW. de Leeuw PW. BMJ. 2012 Feb 1;344:e656. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e656. BMJ. 2012. PMID: 22297794 No abstract available. - ACP Journal Club. Review: Aliskiren plus ACEIs or ARBs increases hyperkalemia more than aliskiren, ACEIs, or ARBs alone.
Moist L. Moist L. Ann Intern Med. 2012 Jun 19;156(12):JC6-9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-12-201206190-02009. Ann Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22711110 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- RAS blockade, hyperkalemia and AKI--look and you will find.
Toto RD. Toto RD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 May;8(5):257-8. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.62. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22473512 - No increase in adverse events during aliskiren use among ontario patients receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers.
Gilbert CJ, Gomes T, Mamdani MM, Hellings C, Yao Z, Garg AX, Wald R, Harel Z, Juurlink DN. Gilbert CJ, et al. Can J Cardiol. 2013 May;29(5):586-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Can J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23541666 - Combination antihypertensive treatment with aliskiren and blockers of the Renin-Angiotensin system-reassurance but with a note of caution.
Touyz RM. Touyz RM. Can J Cardiol. 2013 May;29(5):521-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2013.02.020. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Can J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23541659 No abstract available. - Direct inhibition of renin as a cardiovascular pharmacotherapy: focus on aliskiren.
Sepehrdad R, Frishman WH, Stier CT Jr, Sica DA. Sepehrdad R, et al. Cardiol Rev. 2007 Sep-Oct;15(5):242-56. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0b013e318093e43a. Cardiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17700383 Review. - Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension.
Musini VM, Fortin PM, Bassett K, Wright JM. Musini VM, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18843743 Updated. Review.
Cited by
- A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIa, clinical study on investigating the efficacy and safety of SPH3127 tablet in patients with essential hypertension.
Wang F, Liu L, Ruan H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Yu Z, Li Y, Guan Y, Wang J, Huang K, Yu S, Cao Y, Ding C, Chang L, Huang Y, Chen X, Lv Q, Ma C. Wang F, et al. Hypertens Res. 2024 Jul;47(7):1925-1933. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01657-z. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38632457 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - RNA Interference as a Therapeutic Approach for Managing Hypertension.
Tan JW, Bhalla V. Tan JW, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Feb 13;19(6):810-2. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000443. Online ahead of print. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38349665 No abstract available. - Quantitative Proteomics Combined with Network Pharmacology Analysis Unveils the Biological Basis of Schisandrin B in Treating Diabetic Nephropathy.
Song J, Zhang B, Zhang H, Cheng W, Liu P, Kang J. Song J, et al. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(2):284-297. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230505111903. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37151069 - Blood Levels of Angiotensinogen and Hypertension in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
Trainor PJ, Brambatti M, Carlisle SM, Mullick AE, Shah SJ, Kahlon T, Mostacero DO, Mousavi H, Morgan ES, Tami Y, Michos ED, Ouyang P, Tsimikas S, DeFilippis AP. Trainor PJ, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023 Apr 4;81(13):1248-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.01.033. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36990544 Free PMC article. - Efficacy of Direct Renin Inhibitors in Slowing Down the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis.
Akbariromani H, Haseeb R, Nazly S, Pandey S, Anirudh Chunchu V, Dhakal S, Claudine Avena MA, Ali N. Akbariromani H, et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 30;14(8):e28608. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28608. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36204481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Alfie J, Aparicio LS, Waisman GD. Current strategies to achieve further cardiac and renal protection through enhanced renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2011;6:134-46. - PubMed
- MacKinnon M, Shurraw S, Akbari A, Knoll GA, Jaffey J, Clark HD. Combination therapy with an angiotensin receptor blocker and an ACE inhibitor in proteinuric renal disease: a systematic review of the efficacy and safety data. Am J Kidney Dis 2006;48:8-20. - PubMed
- Phillips CO, Kashani A, Ko DK, Francis G, Krumholz HM. Adverse effects of combination angiotensin II receptor blockers plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors for left ventricular dysfunction: a quantitative review of data from randomized clinical trials. Arch Intern Med 2007;167:1930-6. - PubMed
- Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372:547-53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical