Type 1 interferons and antiviral CD8 T-cell responses - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Type 1 interferons and antiviral CD8 T-cell responses
Raymond M Welsh et al. PLoS Pathog. 2012 Jan.
No abstract available
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
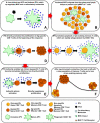
Figure 1. Effect of type 1 IFN on T-cell activation, proliferation, and apoptosis.
This schematic shows the effects of type 1 IFN on antiviral CD8 T-cell responses. (A) A virus infects an APC and induces IFN, which upregulates MHC and costimulatory molecules. (B) Activated APCs migrate into the spleen and lymph nodes to present viral pMHC to T cells. (C) IFN promotes apoptosis of preexisting memory T cells, which are rapidly phagocytosed by CD8α+ DCs. (D) IFN directly promotes the proliferation of antigen (Ag)-specific CD8 T cells at the beginning of the response. (E) IFN indirectly enables late comer Ag-specific T cells to become immediate effectors, but directly inhibits proliferation. (F) After synchronized contraction, the host is left with a new population of memory T cells and a loss of preexisting memory cells.
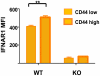
Figure 2. Higher type 1 IFN R (IFNAR1) expression on CD44 high memory phenotype CD8 T cells.
Isolated spleen leukocytes from wild-type (WT) or IFNR knockout (KO) mice were stained with fluorescently labeled monoclonal antibodies (mAb) specific for CD8 (53-6.7; BD Pharmingen), CD44 (IM7; BD Pharmingen), and IFNAR-1 (MAR1-5A3; BioLegend). Stained samples were acquired using a BD Biosciences LSR II flow cytometer with FACS Diva software and analyzed with FlowJo software. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for IFNAR1 is shown for CD44 low and CD44 high CD8 T cells, n = 3/group. **, p<0.005.
Similar articles
- Viral immunity: interferons jog old T-cell memories.
Gray D. Gray D. Curr Biol. 1996 Oct 1;6(10):1254-5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70710-0. Curr Biol. 1996. PMID: 8939561 Review. - [Type 1 interferons: induction and mechanisms of antiviral action].
Vasil'ev AN, Malinovskaia VV, Parfenov VV, Dmitrieva EV. Vasil'ev AN, et al. Antibiot Khimioter. 2009;54(7-8):50-5. Antibiot Khimioter. 2009. PMID: 20201404 Review. Russian. No abstract available. - Type I interferons: diversity of sources, production pathways and effects on immune responses.
Swiecki M, Colonna M. Swiecki M, et al. Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Dec;1(6):463-75. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.026. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22440910 Free PMC article. - Confronting complexity: real-world immunodominance in antiviral CD8+ T cell responses.
Yewdell JW. Yewdell JW. Immunity. 2006 Oct;25(4):533-43. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.09.005. Immunity. 2006. PMID: 17046682 Review. - Tickling memory T cells.
Ahmed R. Ahmed R. Science. 1996 Jun 28;272(5270):1904. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5270.1904. Science. 1996. PMID: 8658161 No abstract available.
Cited by
- HIF-1α is a negative regulator of interferon regulatory factors: Implications for interferon production by hypoxic monocytes.
Peng T, Du SY, Son M, Diamond B. Peng T, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 29;118(26):e2106017118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106017118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34108245 Free PMC article. - Challenges posed by COVID-19 in cancer patients: A narrative review.
Mohseni Afshar Z, Hosseinzadeh R, Barary M, Ebrahimpour S, Alijanpour A, Sayad B, Hosseinzadeh D, Miri SR, Sio TT, Sullman MJM, Carson-Chahhoud K, Babazadeh A. Mohseni Afshar Z, et al. Cancer Med. 2022 Feb;11(4):1119-1135. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4519. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 34951152 Free PMC article. Review. - Innate antiviral immune signaling, viral evasion and modulation by HIV-1.
Rustagi A, Gale M Jr. Rustagi A, et al. J Mol Biol. 2014 Mar 20;426(6):1161-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 8. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24326250 Free PMC article. Review. - Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus activates the transcription of interferon alpha/beta (IFN-α/β) in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (Mo-DC).
Zhang H, Guo X, Nelson E, Christopher-Hennings J, Wang X. Zhang H, et al. Vet Microbiol. 2012 Oct 12;159(3-4):494-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.04.025. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Vet Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22592217 Free PMC article. - The Dual Nature of Type I and Type II Interferons.
Lee AJ, Ashkar AA. Lee AJ, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 11;9:2061. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02061. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30254639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Muller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LFL, Hemmi S, Pavlovic J, et al. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994;264:1918–1921. - PubMed
- Gidlund M, Orn A, Wigzell H, Senik A, Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978;273:759–761. - PubMed
- Trinchieri G, Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978;147:1314–1333. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI081675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI-017672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI017672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI-081675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials