Transcriptional regulation by Pol II(G) involving mediator and competitive interactions of Gdown1 and TFIIF with Pol II - PubMed (original) (raw)
Transcriptional regulation by Pol II(G) involving mediator and competitive interactions of Gdown1 and TFIIF with Pol II
Miki Jishage et al. Mol Cell. 2012.
Erratum in
- Mol Cell. 2012 Aug 10;47(3):491-2
Abstract
Pol II(G) is a distinct form of RNA polymerase II that contains the tightly associated Gdown1 polypeptide (encoded by POLR2M). Unlike Pol II, Pol II(G) is highly dependent upon Mediator for robust activator-dependent transcription in a biochemically defined in vitro system. Here, in vitro studies show that Gdown1 competes with TFIIF for binding to the RPB1 and RPB5 subunits of Pol II, thereby inhibiting an essential function of TFIIF in preinitiation complex assembly, but also that Mediator can actually facilitate Pol II(G) binding to the promoter prior to subsequent Mediator functions. Complementary ChIP and RNAi analyses reveal that Pol II(G) is recruited to promoter regions of subsets of actively transcribed genes, where it appears to restrict transcription. These and other results suggest that Pol II(G) may act to modulate some genes while simultaneously, as a poised (noninitiated) polymerase, setting the stage for Mediator-dependent enhancement of their activity.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
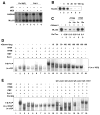
Figure 1. Gdown1 competes with TFIIF for binding to Pol II in vitro
(A) p53-dependent and basal transcription with Pol II and Pol II(G). Transcription was assayed in a completely defined system containing GTFs, PC4 and plasmids containing the adenovirus major late (AdML) core promoter and either p53-binding sites (GADD45) (An et al., 2004) or no activator binding sites (MLΔ53). p53 and Mediator were added as indicated. (B) Inhibitory effect of recombinant Gdown1 on basal transcription. In vitro transcription reactions were reconstituted with 10 ng of TBP, 10 ng of TFIIB, 25 ng of TFIIF and 50 ng of Pol II. The indicated amounts of rGdown1 were added to reaction mixtures. Reaction mixtures also contained 50 ng of pMLΔ53. (C) Partial recovery of basal transcription by addition of excess TFIIF. In vitro transcription reaction mixtures were as described in (B). Reaction mixtures contained 5- or 10-fold excesses of rTFIIB or rTFIIF and 20 ng of rGdown1 as indicated. (D) Inhibition of PIC assembly by Gdown1. An end-labeled Ad ML oligonucleotide (−40 to +20) probe was incubated with the indicated combinations of factors: TFIIB (10 ng, lane 2–5), TFIIF (50 ng, lanes 2–5), and bovine Pol II (50 ng). All reactions contained PC4 (65 ng) and TBP (10 ng). Reactions were incubated at 30°C for 40 min and purified RNA products resolved by native PAGE. (E) Pol II(G)-promoter complex formation in the absence of TFIIF. EMSA was performed as described in D. Indicated combinations of factors were incubated with the probe. All the reactions contained TFIIB (10 ng), PC4 (65 ng), and TBP (10 ng). One μg of a purified IgG (lane 6) or Gdown1 antibody (lane 7) was added to the reactions. A single asterisk denotes the upper band and two asterisks denote the middle band. See also Figure S1.
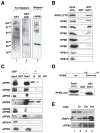
Figure 2. Analysis of Pol II complexes
(A) Purification of Gdown1 complex. Nuclear extracts from HeLa cells (lane 1) or from cell lines that stably express FLAG-tagged Gdown1 (lane 2) or FLAG-tagged RPB9 (lane 3) were directly purified on M2 agarose in Buffer C containing 0.18 M KCl and 0.1% NP40 and bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by SDS-PAGE with silver staining. (B) Mass spectrometric analysis of the Gdown1 complex. Proteins identified by MALDI mass spectrometry are indicated. (C and D) Gel filtration (Superose 6) analyses of FLAG-Gdown1 (C) and FLAG-RPB9 (D) complexes. Fractions were analyzed by immunoblot. (E) Pol II(G) does not interact with TFIIF. Fractions 24 and 25 in (C) were immunoprecipitated with rabbit IgG or anti-Gdown1 antibodies. The antibody-bound or unbound fractions were analyzed by immunoblot with indicated antibodies.
Figure 3. Gdown1 interacts with RPB5 and RPB1
(A) Far Western blot assay. Purified Pol II was resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted to a membrane that then was incubated with GST (lane 1) or GST-Gdown1 (lane 2) protein as a probe. Membrane bound proteins were detected with HRP-labeled anti-GST antibody. The membrane that was probed with GST-Gdown1 was stripped and immunoblotted with an anti- RPB5 antibody (lane 3). (B) GST pulldown assay. Selected subunits of Pol II were expressed as 35S-labeled proteins in a rabbit reticulocyte coupled transcription and translation system and incubated with immobilized GST or GST-Gdown1. Bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (C) Cross-linking assay. Immobilized GST or GST-Gdown1 was incubated with purified Pol II. Proteins bound to the beads were incubated with/without DSP for the indicated times. After washing with 8 M urea buffer, the crosslinks were reversed and bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblot. (D) GST pulldown assay. Immobilized GST or GST-Gdown1 was incubated with 35S-labeled RPB5-jaw domain and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (E) Dissociation of Gdown1 from Pol II by excess TFIIF. Pol II(G) was purified as described in Experimental Procedures. A 5-, 10-, or 25-fold excess of rTFIIF was added to the Pol II(G) immobilized beads in Buffer C containing 0.3 M KCl and 0.1% NP40. After washing the beads with Buffer C containing 0.1 M KCl and 0.1% NP40, the proteins that remained on the beads were analyzed by immunoblot.
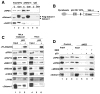
Figure 4. Pol II(G) is recruited to the promoter in an activator- and Mediator-dependent fashion
(A) Comparison of the levels of Pol II(G) in HeLa or HeLa f:Gdown1 nuclear extracts. Pol II in HeLa (C) or HeLa f:Gdown1 (Gdn) nuclear extracts was immunoprecipitated with mouse IgG (lane 5 and 6) or 8WG16 (lane 3 and 4) antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblot. (B) Schematic of the immobilized template used. (C) Pol II(G) is recruited to the promoter in an activator- and Mediator-dependent fashion. M280-streptavidin Dynabeads carrying a biotinylated DNA fragment were incubated with HeLa f:Gdown1 or HeLa nuclear extract with p53 (lane 2) or without p53 (lane 1). After 1.5 h incubation, the beads were washed and bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblot. (D) Mediator-dependent Pol II(G) recruitment to DNA template. Mediator was immuno-depleted from HeLa f:Gdown1 nuclear extract as described in Experimental Procedures. Factor recruitment was monitored as described in (C). See also Figure S2.
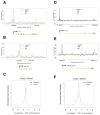
Figure 5. Pol II(G) is enriched at promoter regions of a subset of genes
ChIP-seq data for Gdown1, Pol II and IgG using antibodies that recognize Gdown1 (black), the RPB1 subunit (blue) and IgG (orange) are shown for four genes, plotted as relative read density versus base pair units. The start site and direction of transcription are shown by arrows, with boxes depicting exons and lines representing introns. (A) FUS (B) RPL19 (D) PRKCI (E) ANKRD13a. (C, F) Averaged read densities of Pol II (blue) and Pol II(G) (black) with Class II (C) or Class I (F) genes identified by ChIP-seq are shown. See also Table S1.
Figure 6. Effects of Gdown1 knockdown on gene expression
(A) Gene expression of Pol II(G) target genes in Gdown1 knockdown cells. Error bars correspond to standard deviation from five independent experiments. (B) Gdown1 knockdown in IMR90 cells. Inset, whole cell lysates were prepared from control or knockdown cells and analyzed by immunoblot. (B)–(F) Doxorubicin effects on expression of the Pol II(G) target genes (B to D) or apoptotic genes (E, F). Error bars correspond to standard deviation from three independent experiments. (G and H) ChIP-seq data for PIK3R3 (G) and GADD45A (H). (I) ChIP analysis on the promoter regions of PIK3R3 and GADD45A genes. ChIP analysis was performed with indicated antibodies. Error bars correspond to standard deviation from three independent experiments. See also Figures S3 and S4.
Comment in
- Get back TFIIF, don't let me Gdown1.
Espinosa JM. Espinosa JM. Mol Cell. 2012 Jan 13;45(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.12.016. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22244325 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Gdown1 Associates Efficiently with RNA Polymerase II after Promoter Clearance and Displaces TFIIF during Transcript Elongation.
DeLaney E, Luse DS. DeLaney E, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Oct 7;11(10):e0163649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163649. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27716820 Free PMC article. - Functional interactions of the RNA polymerase II-interacting proteins Gdown1 and TFIIF.
Mullen Davis MA, Guo J, Price DH, Luse DS. Mullen Davis MA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 18;289(16):11143-11152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.544395. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24596085 Free PMC article. - Functional association of Gdown1 with RNA polymerase II poised on human genes.
Cheng B, Li T, Rahl PB, Adamson TE, Loudas NB, Guo J, Varzavand K, Cooper JJ, Hu X, Gnatt A, Young RA, Price DH. Cheng B, et al. Mol Cell. 2012 Jan 13;45(1):38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.10.022. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22244331 Free PMC article. - The Mediator complex and transcription elongation.
Conaway RC, Conaway JW. Conaway RC, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.017. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22983086 Free PMC article. Review. - The Mediator complex and transcription regulation.
Poss ZC, Ebmeier CC, Taatjes DJ. Poss ZC, et al. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Nov-Dec;48(6):575-608. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.840259. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24088064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Gdown1 Associates Efficiently with RNA Polymerase II after Promoter Clearance and Displaces TFIIF during Transcript Elongation.
DeLaney E, Luse DS. DeLaney E, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Oct 7;11(10):e0163649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163649. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27716820 Free PMC article. - Functional interactions of the RNA polymerase II-interacting proteins Gdown1 and TFIIF.
Mullen Davis MA, Guo J, Price DH, Luse DS. Mullen Davis MA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 18;289(16):11143-11152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.544395. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24596085 Free PMC article. - Transcriptional down-regulation of metabolic genes by Gdown1 ablation induces quiescent cell re-entry into the cell cycle.
Jishage M, Ito K, Chu CS, Wang X, Yamaji M, Roeder RG. Jishage M, et al. Genes Dev. 2020 Jun 1;34(11-12):767-784. doi: 10.1101/gad.337683.120. Epub 2020 May 7. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32381628 Free PMC article. - RNA polymerase II transcription elongation control.
Guo J, Price DH. Guo J, et al. Chem Rev. 2013 Nov 13;113(11):8583-603. doi: 10.1021/cr400105n. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 23919563 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - An Integrated Genomic Strategy Delineates Candidate Mediator Genes Regulating Grain Size and Weight in Rice.
Malik N, Dwivedi N, Singh AK, Parida SK, Agarwal P, Thakur JK, Tyagi AK. Malik N, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 22;6:23253. doi: 10.1038/srep23253. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27000976 Free PMC article.
References
- Baek HJ, Kang YK, Roeder RG. Human Mediator enhances basal transcription by facilitating recruitment of transcription factor IIB during preinitiation complex assembly. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15172–15181. - PubMed
- Chung WH, Craighead JL, Chang WH, Ezeokonkwo C, Bareket-Samish A, Kornberg RD, Asturias FJ. RNA polymerase II/TFIIF structure and conserved organization of the initiation complex. Molecular Cell. 2003;12:1003–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK071900/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM64474/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA129325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071900/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 GM090929/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064474/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases