Prognostic and predictive significance of plasma HGF and IL-8 in a phase III trial of chemoradiation with or without tirapazamine in locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2012 Mar 15;18(6):1798-807.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2094. Epub 2012 Mar 1.
Richard Fisher, Kelly S Oliner, Richard J Young, Hongbin Cao, Christina Kong, Edward Graves, Rodney J Hicks, Grant A McArthur, Lester Peters, Brian O'Sullivan, Amato Giaccia, Danny Rischin
Affiliations
- PMID: 22383739
- PMCID: PMC3306471
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2094
Clinical Trial
Prognostic and predictive significance of plasma HGF and IL-8 in a phase III trial of chemoradiation with or without tirapazamine in locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer
Quynh-Thu Le et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2012.
Abstract
Purpose: Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a hypoxia-induced secreted protein that binds to cMet and regulates interleukin (IL)-8 expression. We evaluated the role of circulating HGF and IL-8 as prognostic and predictive factors for efficacy of tirapazamine (TPZ), a hypoxic cell cytotoxin.
Experimental design: Patients with stages III to IV head and neck cancer were randomized to receive radiotherapy with cisplatin (CIS) or CIS plus TPZ (TPZ/CIS). Eligibility for the substudy included plasma sample availability for HGF and IL-8 assay by ELISA and no major radiation deviations (N = 498). Analyses included adjustment for major prognostic factors. p16(INK4A) staining (human papillomavirus surrogate) was carried out on available tumors. Thirty-nine patients had hypoxia imaging with (18)F-fluoroazomycin arabinoside ((18)FAZA)-positron emission tomography.
Results: Elevated IL-8 level was associated with worse overall survival (OS) irrespective of treatment. There was an interaction between HGF and treatment arm (P = 0.053); elevated HGF was associated with worse OS in the control but not in the TPZ/CIS arm. Similar trends were observed in analyses restricted to p16(INK4A)-negative patients. Four subgroups defined by high and low HGF/IL-8 levels were examined for TPZ effect; the test for interaction with arm was P = 0.099. TPZ/CIS seemed to be beneficial for patients with high HGF and IL-8 but adverse for low HGF and high IL-8. Only HGF correlated with (18)FAZA tumor standard uptake value.
Conclusions: IL-8 is an independent prognostic factor irrespective of treatment. There is an interaction between HGF and treatment arm. Certain subgroups based on IL-8/HGF levels seemed to do better with TPZ/CIS while others did worse, highlighting the complexity of hypoxia targeting in unselected patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures
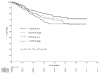
Figure 1
Overall survival for 498 patients by pre-treatment HGF levels and treatment arm
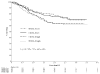
Figure 2
Overall survival for 498 patients by pre-treatment IL8 levels and treatment arm
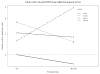
Figure 3
A. Interaction plot of relative risk for death (relative hazard rates, RHR, log scale) by treatment arm and IL8/HGF groups, adjusting for prognostic factors. The graph shows the RHRs rates for each of the eight combinations of treatment arm and IL8 and HGF levels, where a line joins the RHRs of CIS and TPZ/CIS arms for each IL8/HGF combination. No interaction would be indicated by all lines being parallel. The slope of each line is the log of the hazard ratio for arm (TPZ/CIS: CIS) for the given IL8/HGF subgroup. The figure suggests that OS is worse with TPZ/CIS for high IL8/low HGF patients and better for high IL8/high HGF patients, compared with CIS. B. Overall survival by treatment arm and HGF levels within the high IL8 group
Figure 3
A. Interaction plot of relative risk for death (relative hazard rates, RHR, log scale) by treatment arm and IL8/HGF groups, adjusting for prognostic factors. The graph shows the RHRs rates for each of the eight combinations of treatment arm and IL8 and HGF levels, where a line joins the RHRs of CIS and TPZ/CIS arms for each IL8/HGF combination. No interaction would be indicated by all lines being parallel. The slope of each line is the log of the hazard ratio for arm (TPZ/CIS: CIS) for the given IL8/HGF subgroup. The figure suggests that OS is worse with TPZ/CIS for high IL8/low HGF patients and better for high IL8/high HGF patients, compared with CIS. B. Overall survival by treatment arm and HGF levels within the high IL8 group
Similar articles
- Prognostic significance of plasma osteopontin in patients with locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated on TROG 02.02 phase III trial.
Lim AM, Rischin D, Fisher R, Cao H, Kwok K, Truong D, McArthur GA, Young RJ, Giaccia A, Peters L, Le QT. Lim AM, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;18(1):301-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2295. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22096023 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Tirapazamine, cisplatin, and radiation versus cisplatin and radiation for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (TROG 02.02, HeadSTART): a phase III trial of the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group.
Rischin D, Peters LJ, O'Sullivan B, Giralt J, Fisher R, Yuen K, Trotti A, Bernier J, Bourhis J, Ringash J, Henke M, Kenny L. Rischin D, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun 20;28(18):2989-95. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4449. Epub 2010 May 17. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20479425 Clinical Trial. - Phase III randomized trial of weekly cisplatin and irradiation versus cisplatin and tirapazamine and irradiation in stages IB2, IIA, IIB, IIIB, and IVA cervical carcinoma limited to the pelvis: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study.
DiSilvestro PA, Ali S, Craighead PS, Lucci JA, Lee YC, Cohn DE, Spirtos NM, Tewari KS, Muller C, Gajewski WH, Steinhoff MM, Monk BJ. DiSilvestro PA, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2014 Feb 10;32(5):458-64. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.4265. Epub 2014 Jan 6. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24395863 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Hypoxic sensitizer and cytotoxin for head and neck cancer.
Lee DJ, Moini M, Giuliano J, Westra WH. Lee DJ, et al. Ann Acad Med Singap. 1996 May;25(3):397-404. Ann Acad Med Singap. 1996. PMID: 8876907 Review. - Weekly Low-Dose Versus Three-Weekly High-Dose Cisplatin for Concurrent Chemoradiation in Locoregionally Advanced Non-Nasopharyngeal Head and Neck Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Aggregate Data.
Szturz P, Wouters K, Kiyota N, Tahara M, Prabhash K, Noronha V, Castro A, Licitra L, Adelstein D, Vermorken JB. Szturz P, et al. Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1056-1066. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0015. Epub 2017 May 22. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28533474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- AZU1 (HBP/CAP37) and PRKCG (PKC-gamma) may be candidate genes affecting the severity of acute mountain sickness.
Xu Z, Li Q, Shen X. Xu Z, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Feb 20;16(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01457-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36803152 Free PMC article. - Plasma proteins as prognostic biomarkers in radiotherapy treated head and neck cancer patients.
Brøndum L, Eriksen JG, Singers Sørensen B, Mortensen LS, Toustrup K, Overgaard J, Alsner J. Brøndum L, et al. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2017 Feb 7;2:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2017.01.001. eCollection 2017 Feb. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29658000 Free PMC article. - Causal association of serum biomarkers with oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancer: a mendelian randomization study.
Liu W, Liu Y, Li P, Wang Z, Chen J, Liu H, Ye J. Liu W, et al. BMC Oral Health. 2023 Dec 9;23(1):987. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03729-x. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38071306 Free PMC article. - Plasma macrophage-stimulating protein and hepatocyte growth factor levels are associated with prostate cancer progression.
Sugie S, Mukai S, Yamasaki K, Kamibeppu T, Tsukino H, Kamoto T. Sugie S, et al. Hum Cell. 2016 Jan;29(1):22-9. doi: 10.1007/s13577-015-0123-5. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Hum Cell. 2016. PMID: 26250899 - Targeting the tumour vasculature: exploitation of low oxygenation and sensitivity to NOS inhibition by treatment with a hypoxic cytotoxin.
Baker JH, Kyle AH, Bartels KL, Methot SP, Flanagan EJ, Balbirnie A, Cran JD, Minchinton AI. Baker JH, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 28;8(10):e76832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076832. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204680 Free PMC article.
References
- Le QT, Denko NC, Giaccia AJ. Hypoxic gene expression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:293–310. - PubMed
- Le QT, Giaccia AJ. Therapeutic exploitation of the physiological and molecular genetic alterations in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:4287–95. - PubMed
- Overgaard J. Hypoxic radiosensitization: adored and ignored. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4066–74. - PubMed
- Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005;307:58–62. - PubMed
- Hill RP. Targeted treatment: insights from studies of osteopontin and hypoxia. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:733–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01- CA67166/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01 CA118582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118582-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA067166-15/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA067166/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical